Search results
1638 results found.
Curated Education Information
1638 results found.
Felzkowski and Stroebel say the bill would make it easier for retired teachers to fill workforce shortages in local school districts in order to meet the needs of students. Since 2009-10, the number of Wisconsin teachers has declined by 1,338, or 2.2%, while the number of public school students over the same time frame decreased by 2,269 , or 0.5%, according to the Wisconsin Association of School Boards.
“While I think the teacher shortage has pushed our districts toward really creative solutions, we are reaching a tipping point where even these innovations will not be able to shield a district from feeling the effects of these shortages down the road,” Felzkowski said. “One of the best resources to address this issue is at our fingertips — retired educators.”
But the bill comes with a catch that its authors argue would account for the change and ensure the continued integrity of the Wisconsin Retirement System: Raising the minimum retirement age at which a participant may begin collecting benefits from 55 to 59½. The change would only affect employees under the age of 40 at the time the bill becomes law, and would also exclude protective service occupations, such as police officers and firefighters.
An emphasis on adult employment:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee.
WILL:
Waukesha Circuit Court Judge Bohren issued a summary judgement order Tuesday in favor of School Choice Wisconsin Action (SCWA), a WILL client, that sued the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction (DPI), the state education agency, for their unfair, illegal treatment of private schools in Wisconsin’s choice programs. WILL filed the lawsuit on behalf of SCWA in March after DPI denied private choice schools the opportunity to fully utilize online, virtual learning as part of classroom instruction.
Judge Bohren wrote in his decision, “There is not a legitimate government interest in denying Choice Schools the opportunity to use “virtual learning” as Public schools do. The denial is harmful to the Choice Schools and its students.”
The Quotes: Libby Sobic, Director of Education Policy at the Wisconsin Institute for Law & Liberty said, “Today, the Waukesha Circuit Court ruled that the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction broke the law when it denied private schools in the choice program the opportunity to fully utilize online learning as part of classroom instruction. For too long, DPI has been unfair in their treatment of private schools in Wisconsin’s choice programs and today’s decision affirms that when they break the law, they will be held accountable.”
Terry Brown, Chair of School Choice Wisconsin Action said, “State statutes are created and changed by elected officials accountable directly to the public. State agencies run by unelected bureaucrats are not allowed to modify or interpret those laws without legislative oversight.”
Nygren and Thiesfeldt Call for Audit of the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction
Long overdue. An “emphasis on adult employment.”
The Wisconsin DPI, long lead by our new Governor, Tony Evers, has granted thousands of mulligans to elementary reading teachers unable to pass a content knowledge examination. This exam, the Foundations of Reading is identical to the highly successful Massachusetts’ MTEL teacher requirement.
Despite spending far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts, Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
Keri Rodrigues and Alma Marquez said they were so appalled by the low standards of America’s public school teachers unions, they formed the National Parents Union (NPU), so families could have a greater say in their children’s education.
Rodrigues, a mother of three from Boston, and Marquez, a mother of one from Los Angeles, are no strangers to public-sector unions. Rodrigues worked for the Service Employees International Union (SEIU), while Marquez grew up in a union household and worked for Green Dot Public Schools — a public charter organization
“I worked in labor, working for the SEIU, and I spent a big chunk of my career in politics,” Rodrigues told Fox News. “But at the same time, I’m a single mom with three little boys. My oldest son has Asperger’s and ADHD. So we knew from a very young age that he was going to need help.”
Her son had been suspended from kindergarten 36 times and was supposed to be aided by an individualized education program (IEP). Instead, Rodrigues said she was met with indifference and ineptitude from instructors who were supposed to be helping her boy.
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
“The tyranny of low expectations.
–State Representative John Nygren (R-Marinette), Co-Chair of the Joint Committee on Finance and State Representative Jeremy (R-Fond du Lac), Chair of the Assembly Education Committee released the following statement calling for an audit of the Department of Public Instruction:
“Representing nearly one-fifth of the entire state budget, the Department of Public Instruction budget has increased by nearly $3 billion since 2012,” said Rep. Nygren. “Despite providing more resources than ever for public schools, student achievement in reading, unfortunately, continues to decline.”
“Wisconsin’s overall test scores are headed in the wrong direction. Especially concerning is the downward trend in reading scores, the core of education attainment,” said Rep. Thiesfeldt. “Recent Forward Exam results show that 60% of Wisconsin students cannot read or write at grade level. Taxpayers and students deserve better.”
The proposed audit would examine approaches to reading instruction and resulting student achievement. Specifically, LAB would examine methods of reading instruction utilized in Wisconsin’s schools, the impact of the Foundations of Reading Test on teacher licensure, and whether DPI consistently measures student achievement. A similar audit was conducted in 1998.
“Given the significant level of taxpayer resources dedicated to education, the need for oversight and accountability could not be clearer,” said Reps. Nygren and Thiesfeldt. “It is our hope that this audit will provide long overdue oversight of funding provided to DPI and help inform legislative action to improve student outcomes.”
Long overdue. An “emphasis on adult employment.”
The Wisconsin DPI, long lead by our new Governor, Tony Evers, has granted thousands of mulligans to elementary reading teachers unable to pass a content knowledge examination. This exam, the Foundations of Reading is identical to the highly successful Massachusetts’ MTEL teacher requirement.
Despite spending far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts, Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
The largest organization representing Minnesota educators announced Wednesday that it opposes a plan to change the state Constitution in an effort to narrow the state’s persistent academic achievement gap.
Education Minnesota, the union representing 80,000 members who work in pre-K and K-12 schools and higher-education institutions, announced its opposition as the authors of the proposal launched a public effort to woo support for their “out-of-the-box” idea.
Alan Page, a former Minnesota Supreme Court justice, and Neel Kashkari, president of the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, want to make quality public education a civil right for all children. To do that, they propose amending the Constitution’s current language on education, which has remained largely the same since it was written in 1857.
But the teachers union argues that the change would pave the way for taxpayer-funded vouchers for private schools, which they’ve long opposed.
“The public schools paid for by the taxpayers should be available to every Minnesota family no matter where they are from, how they pray, whether their children have special needs, or who they love,” Education Minnesota President Denise Specht said in a written statement.
The proposal would remove the mandate for a uniform system of public education, creating even wider inequities between wealthy and poor districts, Specht wrote in a series of tweets.
Related: “An emphasis on adult employment“.
Five of the six other board members, all representing other local school districts, agreed. Only the state superintendent of public instruction’s designee to the board, David Carlson, voted against keeping the district open.
District employees, students and community members packing the district’s middle school gymnasium where the board was meeting erupted in applause when the fourth vote in favor of keeping the district open was announced, and then again when the final vote was tallied.
“I am just happy to give this to our students. … and to know that our juniors are going to graduate next year as Panthers means the world to me and their families,” said Tara LeRoy, a mother of two students in the district and a main force behind a citizens group working to preserve the district, named the Panther Community Network after the district’s mascot.
Palmyra-Eagle has seen its enrollment drop over the last 14 years from 1,154 students to 769 in 2018-19. It’s lacked commercial and industrial development to drive property tax revenues and seen an increase in the number of students in the district — up to 40% — opting to go to school in other surrounding districts under the state’s open enrollment program.
Related: An emphasis on adult employment.
The Madison Metropolitan School District’s practice of barring an outside therapy organization from providing classroom support for students with special needs is being questioned after a parent’s request to do so was at first allowed, and later prohibited.
The parent, who asked not to be named to protect the identity of her son, has a 4K student with autism. She has fought district officials since the end of October over the decision to forbid a third-party service provider, which her son had worked with throughout his early childhood and whom she was paying, to assist her son in his classroom twice a week.
According to the student’s initial Individualized Education Program — finalized at the end of September after being developed by special education staff and the student’s parents — the provider was to “come to school twice a week for an hour to support (the student) within the school setting.” An IEP outlines the needs of, and goals for, a student in special education, and can include things like prompts to help the student remain on task or ways to respond to misbehavior.
I recall the rejection of parents attempting to offer math tutoring some years ago, due to a union complaint.
“An emphasis on adult employment.”
Michael Clark & Jeremy Kelley:
Public school buildings, which previously have been rated high enough by the Ohio Department of Education’s annual building report cards that families did not have access to the school-choice exit option, will instead be designated as “underperforming” if only a subset of students or academic subjects now fall into that category.
Some local school officials say the changes are jeopardizing millions of dollars of their operating budgets and creating chaos in planning staffing for public school enrollments starting in the 2020-21 school year.
Next school year, according to the ODE, 36 school buildings in eight of Butler County’s 10 public school districts will be designated as underperforming, so parents will be eligible for EdChoice funding to send their children to private schools.
“An emphasis on adult employment“.
Meanwhile, a top priority for labor has been sitting quietly on Pelosi’s desk and, unlike USMCA, already commands enough support to get it over the House finish line. The Protecting the Right to Organize Act would be the most comprehensive rewrite of U.S. labor law in decades. It would eliminate right-to-work laws, impose new penalties on employers who retaliate against union organizing, crack down on worker misclassification, and establish new rules so that employers cannot delay negotiating collective bargaining contracts. Introduced by Rep. Bobby Scott, D-Va., in May, it already has 215 co-sponsors in the House and 40 in the Senate.
2010: Influence and money: WEAC $1.57M for four (state) senators
2009:
To make matters more dire, the long-term legislative proposal specifically exempts school district arbitrations from the requirement that arbitrators consider and give the greatest weight to revenue limits and local economic conditions. While arbitrators would continue to give these two factors paramount consideration when deciding cases for all other local governments, the importance of fiscal limits and local economic conditions would be specifically diminished for school district arbitration.
An emphasis on adult employment.
Have you heard? Teachers unions are no longer interested in negotiating only the salaries, benefits and working conditions of their members, but affordable housing, restorative justice, climate change and a host of other social issues as well.
Unions call this “bargaining for the common good” and have parlayed the concept into positive — to the point of fawning — media coverage. As a public relations exercise, it has to be considered a resounding success, but our press outlets repeatedly overlook the flaws in the argument that public employee contracts are the proper place to address public policy issues.
The phrase arose from a 2014 conference organized by Georgetown University’s Kalmanovitz Initiative for Labor and the Working Poor. The conference included 130 public-sector union activists, community organizers, academics and researchers, there by invitation only, “to address the threats posed by financialization, privatization, growing income inequality and retirement insecurity to the lives of public-sector workers and the well-being of the communities they serve.”
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
The Chicago Teachers Union did not budge during its 11-day strike.
“We should return to work in the schools pending one thing – and that one thing is a return-to-work agreement,” CTU President Jesse Sharkey said on the 11th and last day of the strike on Oct. 31.
The union and Mayor Lori Lightfoot agreed to make up five instructional days. But now, not three weeks later, Pritzker Elementary School’s assistant principal sent a letter to parents about the Nov. 27, Jan. 2, and Jan. 3 makeup days, stating, “We anticipate a need or substitutes to cover the classes of teachers who have made advance plans for those days and will not be in attendance in school.”
The letter called on parents themselves to step in as substitute teachers. And principals say it is happening district-wide.
Kozlov asked Sharkey about all this.
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
Wisconsin’s new Governor, Democrat Tony Evers, recently acknowledged his support for thousands of elementary reading teacher content knowledge exam mulligans.
Now comes Politifact:
As proof, Thiesfeldt’s staff pointed to the most recent Wisconsin Student Assessment System results. The annual tests include the Forward Exam for grades three to eight and ACT-related tests for grades nine to 11.
In the 2018-19 tests, 39.3% of students were rated as proficient or advanced in English Language Arts, and 40.1% reached those levels for math, according to the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction.
For starters, calling 60% the “vast majority” is overstating things quite a bit.
But let’s focus on the “grade level” part of Thiesfeldt’s claim. Is it reasonable to say anyone below proficient is also below grade level?
Politifact is correct to say that proficiency on state txams don not necessarily align with grade level performance, a nebulous term which means different things at different times in different contexts. This means Representative Jeremy Thiesfeldt was technically incorrect when he equated the two during a radio interview.
Technically.
But Thiesfeldt was not being technical. He was not having a conversation about psychometrics and cut-scores, how to set them and how to anchor them from one year to the next so scores can be compared over time. He was making the point that we’re not doing very well. He was pointing to the bar and making sure we know how few students get over it. We can forgive him If that complex story is hard to tell in the kind of one sentence sound bites the media both requires and then dissects.
It might help to know that before 2013, before we were required to set our categorical cut-scores for proficient. advanced, etc., at new, more rigorous levels aligned with national standards.
Wisconsin set them at laughably low levels. The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel missed this part of the story when it reviewed
The Wisconsin Department of Public instruction, long lead by our new Governor, Tony Evers, has waived thousands of elementary teacher reading content knowledge requirements (Foundations of Reading, based on Massachusetts’ best in the States MTEL requirement)
“the majority of ALL 11th-grade students in Madison read and write below basic proficiency. Translated: they are functionally illiterate.
“The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”.
More on our long term, disastrous reading results, here.
“an emphasis on adult employment”.
Betsy DeVos is coming to Wisconsin. So I’m heading to Milwaukee early tomorrow morning to join @MTEAunion and Milwaukee families in sending a crystal clear message: the Trump/DeVos team might not believe in public schools, but we do. https://t.co/XHUzMPbuVn
— Ben Wikler (@benwikler) September 16, 2019
Biggs and Richwine are especially effective in dissecting the annual reports on the “teacher pay gap” published by the union-backed Economic Policy Institute. They demonstrate that when EPI’s methodology is applied to other professions, it shows “pay gaps” for about 40 percent of all occupations. EPI’s methods suggest telemarketers are woefully underpaid.
Biggs and Richwine don’t stop there. It’s amazing what an examination of the data tells us:
Teachers leaving the profession in droves? Nope.
Former teachers earning more when they switch to new professions? Nope.
Widespread teacher shortages? Nope.
Teachers work more hours than private-sector professionals? Nope.
Teaching is more stressful than most other occupations? Nope.
An emphasis on Adult Employment .
Wiseye @ 24 September WisPolitics Lunch:
Jim Zellmer:
Thank you for your service Governor Evers.
Under your leadership, the Wisconsin d.p.i. granted Mulligan’s to thousands of elementary teachers who couldn’t pass a reading exam (that’s the “Foundations of Reading” elementary teacher reading content knowledge exam), yet our students lag Alabama, a state that spends less and has fewer teachers per students.
What message are we sending to parents, citizens, taxpayers and those students (who lack proficiency).
Governor Evers: I’m not sure how many mulligans we issued but they are all mulligans that the local school districts are asking for because there are people that generally speaking were people that worked in those schools while they are trying to pass that test they are very close to getting there hitting the mark there.
So I believe that the mulligans that we did issue were were the right thing to do.
The other thing that concerned me and I supported putting that piece in place around passing that test and I still do but the data that concerned me was that the test may have been biased and that it was probably.
34:09
Yes disproportionate number of people of color were not passing that test and this I know the state of Massachusetts had that problem and the state of Wisconsin had that problem. so given that there were we were and I can honestly say I don’t know what came out of the study but we are working with Massachusetts to take a look at that issue and see how how we can correct it.
2005: When all third graders read at grade level or beyond by the end of the year, the achievement gap will be closed…and not before.
2009: “An emphasis on adult employment”.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
2010: WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
2011: A Capitol Conversation on our disastrous reading results.
The followup legislation lead to the MTEL based Foundations of Reading: an elementary reading teacher content knowledge examination.
Subsequently undermined:
The Wisconsin Department of Public instruction, long lead by our new Governor, Tony Evers, has waived thousands of elementary teacher reading content knowledge requirements (Foundations of Reading, based on Massachusetts’ best in the States MTEL requirement)
Alan Borsuk on MTEL and our disastrous reading results.
“the majority of ALL 11th-grade students in Madison read and write below basic proficiency. Translated: they are functionally illiterate.
“The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”.
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
2021: Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
More on our long term, disastrous reading results, here.
Interestingly, a number of local and state media folks attended this event, but I’ve seen no coverage of this vital question.
“an emphasis on adult employment”.
Betsy DeVos is coming to Wisconsin. So I’m heading to Milwaukee early tomorrow morning to join @MTEAunion and Milwaukee families in sending a crystal clear message: the Trump/DeVos team might not believe in public schools, but we do. https://t.co/XHUzMPbuVn
— Ben Wikler (@benwikler) September 16, 2019
Evers signs record number of executive orders in first year
Last school year, the district began using a 35-page guidance document on student gender identity, which is based on federal and state laws and School Board policies regarding anti-bullying and non-discrimination, Hohs said.
While the document was not voted on by the Madison School Board, members received updates on it when it was in development, she said.
The document covers topics like when a student’s name can be changed in the district’s student information system, the policy for restroom and changing area use, and how to communicate with the family of transgender and non-binary students about their identity.
The document states: “School staff shall not disclose any information that may reveal a student’s gender identity to others, including parents or guardians and other school staff, unless legally required to do so or unless the student has authorized such disclosure.”
The things Madison public schools won’t tell you.
They’re teaching your children that they may not be boy or girl. Five and six years old. Gender confusion, et cetera. But don’t tell mom or dad. Because the policy enacted one year ago was secret. Until now.
The Wisconsin Institute for Law and Liberty uncovered this policy, never before revealed to Madison voters or parents:
Related: The notion that parents inherently know what school is best for their kids is an example of conservative magical thinking.”
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
Yet, we have long tolerated disastrous reading results.
Democrats, in leadership in Hartford since 1971, are responsible for the city’s educational failures, Lewis said.
“[The party] doesn’t serve black people, it doesn’t serve middle-class or poor white people, it doesn’t serve Hispanics,” Lewis said. “It serves people at the top tier of the party.“No matter how many times people from the party have said education is better than ever, the research doesn’t lie. It’s very clear, especially in the city of Hartford, the system is not doing well.”
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
Yet, we have long tolerated disastrous reading results.
Years ago, a senior Madison teacher mentioned to me that the local union leadership traded benefit growth for reduced salary increases, which affected younger teachers.
The Madison school district has benefited greatly from a growing property tax base – supported by a massive federal taxpayer electronic medical record subsidy (nearly $40B since 2011!). Will that continue? What happens if things change?
Mr Bernanke’s unorthodox “cash for trash” scheme, otherwise known as quantitative easing, drove up asset prices and bailed out baby boomers at the profound political cost of pricing out millennials from that most divisive of asset markets, property. This has left the former comfortable, but the latter with a fragile stake in the society they are supposed to build.
As we look towards the 2020 US presidential election, could Ms Ocasio-Cortez’s leftwing politics become the anthem of choice for America’s millennials?
But before we look forward, it is worth going back a bit. The 2008 crash itself didn’t destroy wealth, but rather revealed how much wealth had already been destroyed by poor decisions taken in the boom. This underscored the truism that the worst of investments are often taken in the best of times.
Mr Bernanke, a keen student of the 1930s, understood that a “balance sheet recession” must be combated by reflating assets. By exchanging old bad loans on the banks’ balance sheets with good new money, underpinned by negative interest rates, the Fed drove asset prices skywards. Higher valuations fixed balance sheets and ultimately coaxed more spending and investment. However, such “hyper-trickle-down” economics also meant that wealth inequality was not the unintended consequence, but the objective, of policy.
In addition to a higher base wage, the district has said that, on the average, employees will receive another 2% salary increase this year based on a salary schedule that awards experience and education.
But MTI has said about 1,000 employees, including some of the lowest paid, won’t receive more money through the salary schedule, arguing a full base-wage bump is necessary to keep up with the cost of living.
The agreement won’t take effect until approved by both the union members and the School Board, according to the Facebook post.
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
Yet, we have long tolerated disastrous reading results.
Years ago, a senior Madison teacher mentioned to me that the local union leadership traded benefit growth for reduced salary increases, which affected younger teachers.
The Madison school district has benefited greatly from a growing property tax base – supported by a massive federal taxpayer electronic medical record subsidy (nearly $40B since 2011!). Will that continue? What happens if things change?
Mr Bernanke’s unorthodox “cash for trash” scheme, otherwise known as quantitative easing, drove up asset prices and bailed out baby boomers at the profound political cost of pricing out millennials from that most divisive of asset markets, property. This has left the former comfortable, but the latter with a fragile stake in the society they are supposed to build.
As we look towards the 2020 US presidential election, could Ms Ocasio-Cortez’s leftwing politics become the anthem of choice for America’s millennials?
But before we look forward, it is worth going back a bit. The 2008 crash itself didn’t destroy wealth, but rather revealed how much wealth had already been destroyed by poor decisions taken in the boom. This underscored the truism that the worst of investments are often taken in the best of times.
Mr Bernanke, a keen student of the 1930s, understood that a “balance sheet recession” must be combated by reflating assets. By exchanging old bad loans on the banks’ balance sheets with good new money, underpinned by negative interest rates, the Fed drove asset prices skywards. Higher valuations fixed balance sheets and ultimately coaxed more spending and investment. However, such “hyper-trickle-down” economics also meant that wealth inequality was not the unintended consequence, but the objective, of policy.
The results of money printing can be seen in Venezuela.
Do kids who attend private schools w publicly funded tuition vouchers do better than public schools? Research is mixed. Here’s a comprehensive look at the highs and lows in Milwaukee, which I wrote right as @BetsyDeVosED was rising to office. https://t.co/esSBjs5T7C
— Erin Richards (@emrichards) September 16, 2019
.@betsydevosed was involved early in Wisconsin’s voucher school expansion and has donated hundreds of thousands to Republican lawmakers since 2003. Here’s my story from 2017: https://t.co/E13KGVGg5h https://t.co/Sz2I4PtaUR
— Molly Beck (@MollyBeck) September 16, 2019
Despite the fact that media & security & @BetsyDeVosED are in their class, these 8th grade girls are absorbed in trying to “diagnose” the source of a patient’s symptoms. They already dissected a sheep brain. ? Kids are pretty focused at @StMarcusSchool. pic.twitter.com/z0oJrEwQuN
— Erin Richards (@emrichards) September 16, 2019
Why a Milwaukee voucher school to start a fall tour for @BetsyDeVosED? “This is where education freedom started,” says her press sec. (The Milwaukee voucher program started in 1990. Now 30K+ kids here attend private, mostly religious schools w public $$.) pic.twitter.com/eTk06S2yrV
— Erin Richards (@emrichards) September 16, 2019
Related: Mission vs Organization. Then Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 speech to the Madison Rotary Club:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.”
Betsy DeVos is coming to Wisconsin. So I’m heading to Milwaukee early tomorrow morning to join @MTEAunion and Milwaukee families in sending a crystal clear message: the Trump/DeVos team might not believe in public schools, but we do. https://t.co/XHUzMPbuVn
— Ben Wikler (@benwikler) September 16, 2019
An interview with St. Marcus Superintendent Henry Tyson.
Taxpayer supported K-12 school districts substantially outspend voucher schools. Madison’s $18-20K per student is more than double typical voucher school taxpayer support.
Providence teachers describe a climate of negativity, an air of uncertainty and a culture of blame hovering over their district since the release of a report by the Johns Hopkins Institute for Education Policy this summer on the state of the schools.
But for them, the anxiety caused by the scathing report, the impending state takeover and what they see as a barrage of criticism aimed at them in the media, fades away when they greet their students.
“The moment we step on the front step of that school, that’s it, you leave it there,” said Cynthia Robles, a special education collaborative teacher at Roger Williams Middle School. “You have to leave that negativity at the door, because the kids are depending on you.”
Six educators from around the district shared this week what it’s like to be a teacher in the thick of a national controversy over their schools.
“It doesn’t affect me one bit, one bit,” said Allison Campbell, a kindergarten dual-language English teacher at Carl G. Lauro Elementary School, who said she always gets swept up in her students and the pace of the school day.
But about 100 teachers have resigned this year, some because they were recruited by other districts and others because of the mounting pressure on Providence teachers in the wake of the report, said Ed German, dean of students at Hope High School.
“People don’t want to be associated with education in Providence,” he said. “We’ve lost good administrators. We’ve lost good teachers
Richard Zimman (2009 – then Ripon, WI Superintendent):
Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.”
waow:
If we get this property and we will get it we will start the groundwork for a Christian school,” said Wade Reimer of Shepherd’s Watch.
However, there is confusion over who owns the building.
The confusion over the ownership led to a lawsuit between the Village of Mattoon, Town of Hutchins and The Antigo School District.
“The Antigo School District says they own the building and refuses to sell it unless there is a promise made to not use it for a school,” said Anthony LoCoco a deputy counsel on the case.
“They don’t want the competition of a private school because some children from Mattoon would go to a local elementary school and they would lose funds,” said LoCoco.
LoCoco said the vacant building is costing taxpayers up to $40,000 a year.
The small town is just hopeful the rust on the unused swings disappear and the school playgrounds fill back up with the sound of laughter.
There is a hearing for the lawsuit on July 26th in Shawano County.
News 9 reached out to Antigo School District and they refused to comment pending the litigation.
Related: An emphasis on adult employment.
Mark Seidenberg, a UW-Madison professor and cognitive neuroscientist, has spent decades researching the way humans acquire language. He is blunt about Wisconsin’s schools’ ability to teach children to read: “If you want your kid to learn to read you can’t assume that the school’s going to take care of it. You have to take care of it outside of the school, if there’s someone in the home who can do it or if you have enough money to pay for a tutor or learning center.”
Theresa Morateck, literacy coordinator for the district, says the word “balanced” is one that’s been wrestled with for many years in the reading world.
“I think my perspective and the perspective of Madison currently is that balanced means that you’re providing time to explicitly teach those foundational skills, but also that’s not the end-all be-all of your program,” Morateck says.
According to the district, students in elementary school get 120 minutes of daily literacy instruction.
Lisa Kvistad, the district’s assistant superintendent for teaching and learning, lays out what those two hours look like for kindergarten, first and second grade. For 30 minutes, students focus on foundational skills including print awareness (the difference between letters, words and punctuation), phonemic awareness (the ability to hear, identify and make individual sounds), and phonics (correlating sounds with letters or groups of letters).
Then teachers move into a 15-minute group lesson on a topic the class is focusing on. That’s followed by a workshop in which students are broken up into different groups for 20 to 40 minutes.
In these workshops, says Kvistad, “students are in varying groups and approaching literacy acquisition through opportunities to work with the teacher, read independently, and engage in word study.”
That independent learning allows students to choose books at their assessed skill level, Kvistad says. The district also offers a supplemental online program called Lexia for students who want to work on phonics.
At the end of the workshop, teachers bring students together again to connect their independent or small group study with the mini-lesson they started with.
After reading, 30 to 50 minutes are dedicated to writing, which is also done in a workshop model. The 120 minutes are rounded out by about 20 minutes of “speaking, listening and handwriting.”
For third, fourth and fifth graders, the 120-minute block looks similar, except no time is spent on foundational skills — except for the continued ability to use Lexia.
Kvistad explains that getting the right balance of foundational skills and exposure to grade-level curriculum is an art.
“There’s always a temptation to do more phonics,” Kvistad says. But she says there are drawbacks to that: “Those little ones never get a chance to access grade level curriculum, to engage in rich dialogue with the students in class, to have experience with grade-level vocabulary.”
But for those who advocate for a purely science-based approach to teaching reading, children need to master foundational reading skills before they have any hope of progressing to the more advanced skills that are emphasized with balanced literacy.
Steven Dykstra of the Wisconsin Reading Coalition, an organization that advocates for science-based reading instruction, pulls no punches, calling balanced literacy the “current name for the bad way to teach reading.” He says it evolved from “whole language,” a now-discredited type of instruction.
“In whole language you would have taught no phonics, and when you read books with kids you would have taught them to guess and use pictures,” Dykstra says. “In balanced literacy you teach some phonics, but when you sit and read a book you still give priority to guessing and pictures as a way to identify words. And you resort to phonics as a last resort.”
The UW’s Seidenberg explores the complex science of reading in his book Language at the Speed of Sight.
“What happens when you become a skilled reader is that your knowledge of print and your knowledge of spoken language become deeply integrated in behavior and in the brain,” he tells Isthmus. “So that when you are successful at becoming a reader you have this close, intimate relationship between print and sound.”
Related:
2018: “The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”.
“Plenty of resources”. Madison has long spent far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts, between $18 to 20K per student, depending on the district documents one reviews.
2005: When all third graders read at grade level or beyond by the end of the year, the achievement gap will be closed…and not before
THE PRICE OF TEACHER MULLIGANS: “I DIDN’T STOP TO ASK MYSELF THEN WHAT WOULD HAPPEN TO ALL THE KIDS WHO’D BEEN LEFT IN THE BASEMENT WITH THE TEACHER WHO COULDN’T TEACH”
– MICHELLE OBAMA.
The Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction has granted thousands of elementary teacher reading content knowledge waivers.
Wisconsin elementary teachers are, by law, required to pass the Foundations of Reading exam. This requirement – our only teacher content knowledge imperative – is based on Massachusetts’ highly successful MTEL initiative.
An emphasis on adult employment.
At that time Matt filed an ethics complaint with the State Ethics Commission. The Commission issued an Advisory Opinion on April 3d. (See the bottom of this post for the full opinion.) Regarding Lorenzo Richardson, the Commission opined that
Mr. Richardson may have opted to support the JCEA over the Board and its individual members when he joined the JCEA in filing a lawsuit. Whether Mr. Richardson’s decision was predicated on the support he received from the JCEA during his election, or stemmed from his belief that the actions of certain Board members were inappropriate, his action has the appearance of paying allegiance to the JCEA. By aligning himself with the JCEA to the detriment of the Board and its individual members, it would be reasonable for a member of the public to believe that his involvement violated N.J.S.A. 18A:12-24(b) and/or N.J.S.A. 18A:12-24(c). Therefore, the Commission advises that Mr. Richardson should refrain from being involved in future negotiation discussions and meetings, as well as votes related to the JCEA, for the remainder of his current term
Related: “An emphasis on adult employment”.
Without telling me, she went over to the school and began a weeks-long process of behind-the-scenes lobbying, which led to me and a couple of other high-performing kids getting quietly pulled out of class, given a battery of tests, and about a week later reinstalled permanently into a bright and orderly third-grade class upstairs, governed by a smiling, no-nonsense teacher who knew her stuff.
It was a small but life-changing move. I didn’t stop to ask myself then what would happen to all the kids who’d been left in the basement with the teacher who couldn’t teach. Now that I’m an adult, I realize that kids know at a very young age when they’re being devalued, when adults aren’t invested enough to help them learn. Their anger over it can manifest itself as unruliness. It’s hardly their fault. They aren’t “bad kids.” They’re just trying to survive bad circumstances.
The Constitutionally independent Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction, long lead by our new Governor, Tony Evers, has granted thousands of elementary reading teacher content knowledge waivers .
Wisconsin elementary teachers are, by law, required to pass the Foundations of Reading exam. This requirement – our only teacher content knowledge imperative – is based on Massachusetts’ highly successful MTEL initiative.
An emphasis on adult employment.
Parents, you do have a choice, thanks to Tommy Thompson, Scott Walker and the Republican legislature.
Low income choice
If you are low-income, you can participate in the WI Parental Choice Program. Your annual household income for a family of three must not exceed $45,716. Application period ends April 20.
Unfortunately, state law mandates that no more than 4% of the pupil membership of a public school district may participate in the WPCP. The DPI conducts random drawings.
Much more on open
Enrollment, charter~/a< and voucher student options.
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
“The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
The Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction “DPI”, lead for many years by new Governor Tony Evers, has waived thousands of elementary reading teacher content knowledge requirements. This, despite our long term, disastrous reading results.
Chan Stroman tracks the frequent Foundations of Reading (FoRT) mulligans:
Yet the statutory FoRT requirement is now deemed satisfied by “attempts” to pass pic.twitter.com/xSS0lxgo8g
— Chan Stroman (@eduphilia) March 28, 2019
Contrary to what was represented to @usedgov in the approved state ESSA plan pic.twitter.com/fuNKxlc0Q7
— Chan Stroman (@eduphilia) March 28, 2019
DPI Rhetoric: “We set a high bar for achievement”.
Wisconsin DPI efforts to weaken the Foundations of Reading Test for elementary teachers
Foundations of Reading Elementary Reading Teacher Exam Results.
December, 2018: “The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
2013: Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
2011: A Capitol Conversation on Wisconsin’s Reading Challenges.
K-12 attempts to address learning include the implementation – and abandonment – of “one size fits all” courses, such as English 10 and “small learning communities“.
2009: An emphasis on adult employment.
2006: “They’re all Rich White Kids, and they’ll do just fine” – NOT!.
2005: Lowering the bar – When all third graders read at grade level or beyond by the end of the year, the achievement gap will be closed…and not before:
Yet, spending continues to grow, substantially. Governor Evers has proposed a double digit increase in K-12 tax and spending for the next two years. Once in a great while, a courageous soul dives in and evaluates spending effectiveness: a proposed (not heard from again) Madison maintenance referendum audit.
“Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” – Former Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman.
2011: A majority of the Madison School Board aborted the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School. Curiously, former school board member Ed Hughes, who voted against Madison Prep, is supporting Kaleem Caire for school board, 8 years hence. Yet, how many students have we failed as time marches on?
Of the 65 students plus or minus it kind of changes this year 24 of them are regular ed students.
Another way to say they don’t have an IEP so there is no excuse for that reading intervention in (that group).
12 of those 24 have been enrolled in Madison School since Pre-K kindergarten or kindergarden. 12 students have been in Madison Schools.
They have High attendance. They have been in the same (you know) feeder school they have not had high mobility. There is no excuse for 12 of my students to be reading at the first second or third grade level and that’s where they’re at and I’m angry and I’m not the only one that’s angry.
The teachers are angry because we are being held accountable for things that we didn’t do at the high school level. Of those 24 students, 21 of them have been enrolled in Madison for four or more years.
Tap for a larger version.
Raw data [Excel Numbers] via Sara Hynek.
Note that taxpayer supported K-12 school districts receive funds from a variety of sources, including federal taxpayer funds along with local fees.
Madison plans to spend $518,955,288 during the 2018-2019 school year. That’s about $20,000 per student (26,917, which includes 4k), which is far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 schools, nearly 3X voucher organizations, for example. Much more on spending comparisons, here.
An “emphasis on adult employment“.
Former Madison School Board Member Ed Hughes:
It turns out that this isn’t true. Explaining why gets a bit complicated, but here goes.
Mr. Hughes voted against the proposed Madison Preparatory IB Charter School.
Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results, despite spending far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts.
Madison Wisconsin High School Graduation Rates, College Readiness, and Student Learning.
Mr. Hughes curiously intervened in the recent Arbor Community School proposal.
”an emphasis on adult employment”.
This points up one of the frustrating aspects of trying to follow school issues in Madison: the recurring feeling that a quoted speaker – and it can be someone from the administration, or MTI, or the occasional school board member – believes that the audience for an assertion is composed entirely of idiots.
Under a proposal being developed confidentially, Beutner would divide the system into 32 “networks,” moving authority and resources out of the central office and into neighborhoods. He is expected to make his plan public next month.
In L.A. Unified’s downtown headquarters, managers and other employees recently have been asked to explain their duties — and to justify why their jobs should continue to exist in a leaner, more localized school system.
The network strategy is not a plan to break up or end L.A. Unified, but it could transform how the school system functions.
“The superintendent is trying to move toward a decentralized system that puts the student first,” said one person close to the process who was not authorized to comment publicly. “He’s trying to generate better educational outcomes. That’s the No. 1 goal.
“Savings from the central bureaucracy could be plowed back into education at the school level,” he said, “as well as [used] to deal with the fiscal crisis the district faces.”
Beutner declined to comment on the plan, saying it would be premature to talk about a work in progress.
Related: Madison spends far more than most, yet we’ve long tolerated disastrous reading results.
2006: They’re all Rich White Kids, and they’ll do just fine, NOT!”
2013: “Plenty of Resources“.
“What’s different, this time?”
2017: Adult employment.
2018: Seeing the Forest: Unpacking the Relationship Between Madison School District (WI) Graduation Rates and Student Achievement

Madison has long spent far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts, now around $20k per student.
Yet, we have long tolerated disastrous reading results.
On November 7, Superintendent Art Rainwater made his annual report to the Board of Education on progress toward meeting the district’s student achievement goal in reading. As he did last fall, the superintendent made some interesting claims about the district’s success in closing the academic achievement gap “based on race”.
According to Mr. Rainwater, the place to look for evidence of a closing achievement gap is the comparison of the percentage of African American third graders who score at the lowest level of performance on statewide tests and the percentage of other racial groups scoring at that level. He says that, after accounting for income differences, there is no gap associated with race at the lowest level of achievement in reading. He made the same claim last year, telling the Wisconsin State Journal on September 24, 2004, “for those kids for whom an ability to read would prevent them from being successful, we’ve reduced that percentage very substantially, and basically, for all practical purposes, closed the gap”. Last Monday, he stated that the gap between percentages scoring at the lowest level “is the original gap” that the board set out to close.
Unfortunately, that is not the achievement gap that the board aimed to close.More.
2006: They’re all Rich White Kids, and they’ll do just fine, NOT!”
2013: “Plenty of Resources“.
“What’s different, this time?”
2017: Adult employment.
2018: Seeing the Forest: Unpacking the Relationship Between Madison School District (WI) Graduation Rates and Student Achievement
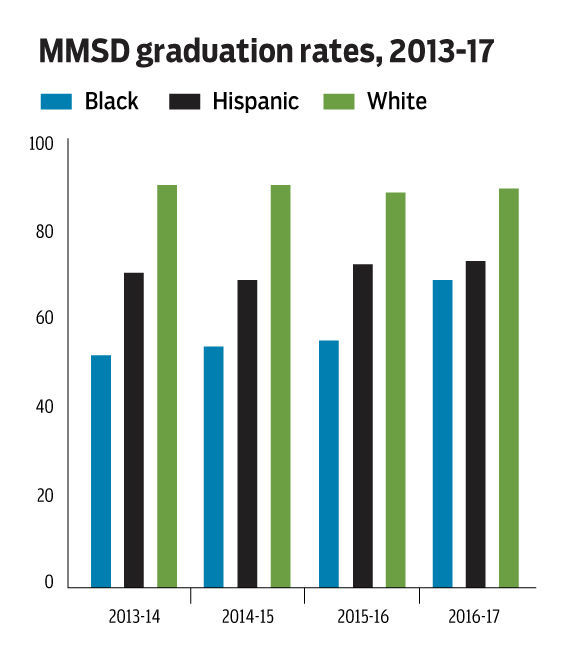
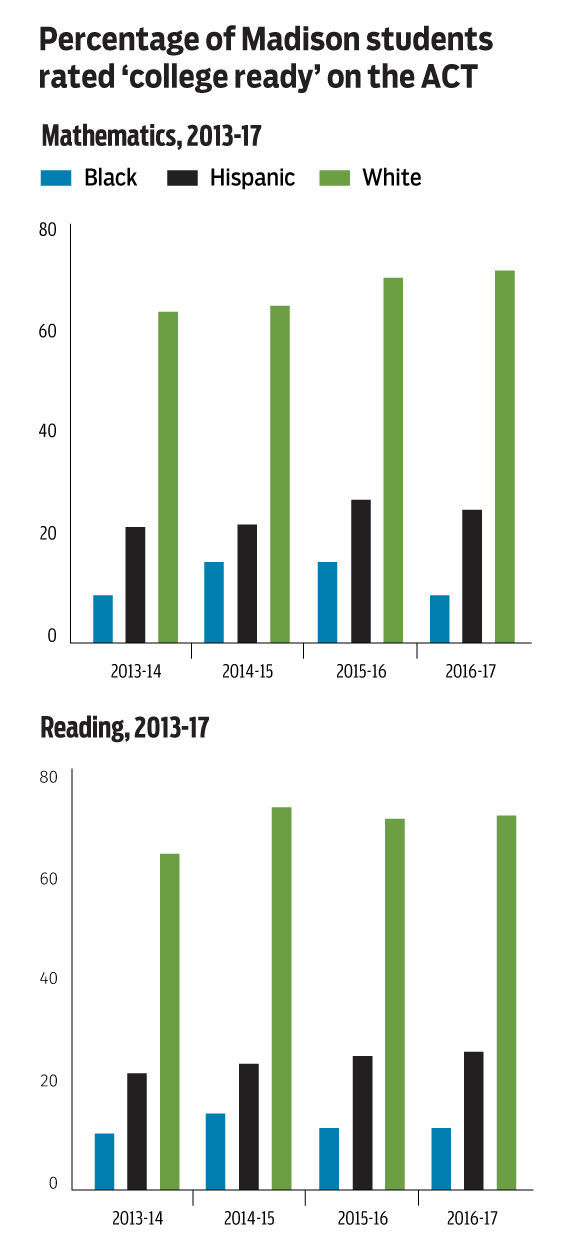
To make their point, the couple traced reading and math proficiency rates for the class of 2017 through the years, finding that the black and Hispanic cohorts saw little if any improvements between grades three to 11 and trailed white students by as many as 50 percentage points.
“Both of these things suggest to us that the district’s efforts to educate our minority students have failed (for whatever reason or reasons),” they wrote. “Nevertheless, we are finding ways to give these students high school diplomas. But what good is a high school diploma to a young person if they cannot read or do math?”
They’re calling for more resources, especially in younger grades, like reading specialists to oversee literacy programming, and reading specialists to run intervention programs in the middle and high schools.
“Further, we need to hold those people and other school staff accountable for improving literacy in their student body — i.e., for increasing the percentage of students (in every demographic group) in their school who are reading at grade level,” they wrote.
In the Isthmus article, Henriques and Frost also accused the district of whitewashing data.
“We have long been frustrated by the way the district selectively compiles, analyzes, and shares student data with the community,” they wrote, adding, “For too many district administrators and school board members over the 20+ years we have been paying attention, making the district look good has been more important than thoroughgoing honesty about how our students are doing.”
Cheatham bristled at the criticism, maintaining that the district publicly posts all data, both favorable and unfavorable, and that there’s nothing wrong with publicizing good results.
“We’ll never hide our progress,” she said, “and it’s important to recognize the progress we have made, which is substantial.”
Madison has long spent far more than most taxpayer supported K-12 school districts, now around $20k per student.
Yet, we have long tolerated disastrous reading results.
On November 7, Superintendent Art Rainwater made his annual report to the Board of Education on progress toward meeting the district’s student achievement goal in reading. As he did last fall, the superintendent made some interesting claims about the district’s success in closing the academic achievement gap “based on race”.
According to Mr. Rainwater, the place to look for evidence of a closing achievement gap is the comparison of the percentage of African American third graders who score at the lowest level of performance on statewide tests and the percentage of other racial groups scoring at that level. He says that, after accounting for income differences, there is no gap associated with race at the lowest level of achievement in reading. He made the same claim last year, telling the Wisconsin State Journal on September 24, 2004, “for those kids for whom an ability to read would prevent them from being successful, we’ve reduced that percentage very substantially, and basically, for all practical purposes, closed the gap”. Last Monday, he stated that the gap between percentages scoring at the lowest level “is the original gap” that the board set out to close.
Unfortunately, that is not the achievement gap that the board aimed to close.More.

2006: They’re all Rich White Kids, and they’ll do just fine, NOT!”
2013: “Plenty of Resources“.
“What’s different, this time?”
2017: Adult employment.
2018: Seeing the Forest: Unpacking the Relationship Between Madison School District (WI) Graduation Rates and Student Achievement
<a href=”https://madison.com/ct/news/local/education/democratic-legislators-look-to-make-big-changes-to-state-education/article_882a0ddd-3671-5769-b969-dd9d2bc795db.html”>Negassi Tesfamichael</a>:
<blockquote> Many local Democratic state legislators say much of the future of K-12 education in Wisconsin depends on the outcome of the Nov. 6 election, particularly the gubernatorial race between state superintendent Tony Evers, a Democrat, and Republican Gov. Scott Walker.
Legislators spoke at a forum at Christ Presbyterian Church Wednesday night, stressing mainly to an older crowd that their signature education initiatives, including restoring collective bargaining rights for public schoolteachers and making significant changes to the state Legislature’s school funding formula, rest on the election outcome.
“As far as Republicans we can work with, we try to talk to Republicans every time we’re there and we’re not successful yet,” said state Rep. Dianne Hesselbein, D-Middleton. “November is coming.”
Wednesday’s event was sponsored by the group <a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/?s=Grandparents+for+Madison+Public+Schools”>Grandparents for Madison Public Schools</a>, <a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/?s=Madison+teachers+inc”>Madison Teachers Inc</a>. and the <a href=”https://duckduckgo.com/?q=wisconsin+public+education+network&t=brave&ia=web”>Wisconsin Public Education Network</a>
</blockquote>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; caret-color: rgb(43, 43, 43); color: rgb(43, 43, 43); font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”>Madison, despite<span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span><a href=”https://mmsdbudget.wordpress.com/” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>spending far more than most,</a><a href=”https://mmsdbudget.wordpress.com/” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”><span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span></a>has tolerated<span class=”Apple-converted-space” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”> </span><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/2013/03/31/reading_recover_3/” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>long term, disastrous reading results.</a></p>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; caret-color: rgb(43, 43, 43); color: rgb(43, 43, 43); font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”>Tony Evers,<span class=”Apple-converted-space” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”> </span><a href=”https://www.tonyevers.com/” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>currently runnng for Governor</a>, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction<span class=”Apple-converted-space” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”> </span><a href=”https://dpi.wi.gov/statesupt/about” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>since 2009</a>. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?</p>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; caret-color: rgb(43, 43, 43); color: rgb(43, 43, 43); font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”>The<span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/?s=Foundations+of+reading” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>Wisconsin DPI has aborted our one attempt at teacher content knowledge requirements: “Foundations of Reading”</a><span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span>for elementary teachers.<span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/?s=Mtel” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>Massachusetts’ MTEL</a><span class=”Apple-converted-space”> </span>substantially raised the teacher content knowledge bar, leading to their top public school rank.</p>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; caret-color: rgb(43, 43, 43); color: rgb(43, 43, 43); font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”>An<span class=”Apple-converted-space” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”> </span><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/?s=An+emphasis+on+adult+employment” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>emphasis on adult employment</a>, also<span class=”Apple-converted-space” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”> </span><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/archives/2009/08/the_madison_sch_4.php” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>Zimman</a>.</p>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; caret-color: rgb(43, 43, 43); color: rgb(43, 43, 43); font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”><a href=”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/2018/06/01/i-didnt-have-one-phone-call-i-dont-have-one-email-about-this-naep-data/” style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 16px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(31, 60, 117); text-decoration: underline”>Alan Borsuk</a>:</p>
<blockquote style=”border: 0px; font-family: Lato, sans-serif; font-size: 19px; font-style: italic; font-weight: 300; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline; -webkit-hyphens: none; quotes: none; color: rgb(118, 118, 118); line-height: 1.2631578947; font-variant-caps: normal; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: auto; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; white-space: normal; widows: auto; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(26, 26, 26, 0.301961); -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration: none”>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 19px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”>“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …</p>
<p style=”border: 0px; font-family: inherit; font-size: 19px; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; margin: 0px 0px 24px; outline: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: baseline”>“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?</p>
</blockquote>
Less discussed in Wisconsin is the tremendous impact that economic status has on student achievement. A school with a population of 100% students who are economically disadvantaged would be expected to have proficiency rates more than 40% lower than a school with wealthier students. Indeed, this economics achievement gap is far larger in terms of proficiency effects than the racial achievement gap, and has important implications for the rural areas of the state, where the percentage of low-income families is higher than most suburban and some rural areas.
While the initial data release by DPI did not include sufficient data for apples-to-apples comparisons among private schools in the choice program, the data was comprehensive enough for charter schools. Particularly in Milwaukee, these schools continue to outperform their peer schools. For this preliminary analysis, we pulled out independent and non-instrumentality charters from MPS, while leaving instrumentality charters—or charters in name-only—as part of the district’s performance. In both mathematics and English/language arts, charter schools continue to outperform their other public school peers.
In English/Language Arts, “free” charters had approximately 9% higher proficiency than traditional public schools. In mathematics, these schools had 6.9% higher proficiency. This is consistent with our past analyses which have found that independence from MPS is a key component of better student outcomes, whether through the chartering or the school choice program.
“We set a high bar for achievement,” DPI spokesman Tom McCarthy said.
Madison, despite spending far more than most, has tolerated long term, disastrous reading results.
Tony Evers, currently runnng for Governor, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction since 2009. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?
The Wisconsin DPI has aborted our one attempt at teacher content knowledge requirements: “Foundations of Reading” for elementary teachers. Massachusetts’ MTEL substantially raised the teacher content knowledge bar, leading to their top public school rank.
An emphasis on adult employment, also Zimman.
“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …
“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?
“We set a high bar for achievement,” DPI spokesman Tom McCarthy said. “To reach more than half (proficiency), we would need to raise the achievement of our lowest district and subgroup performers through policies like those recommended in our budget, targeted at the large, urban districts.”
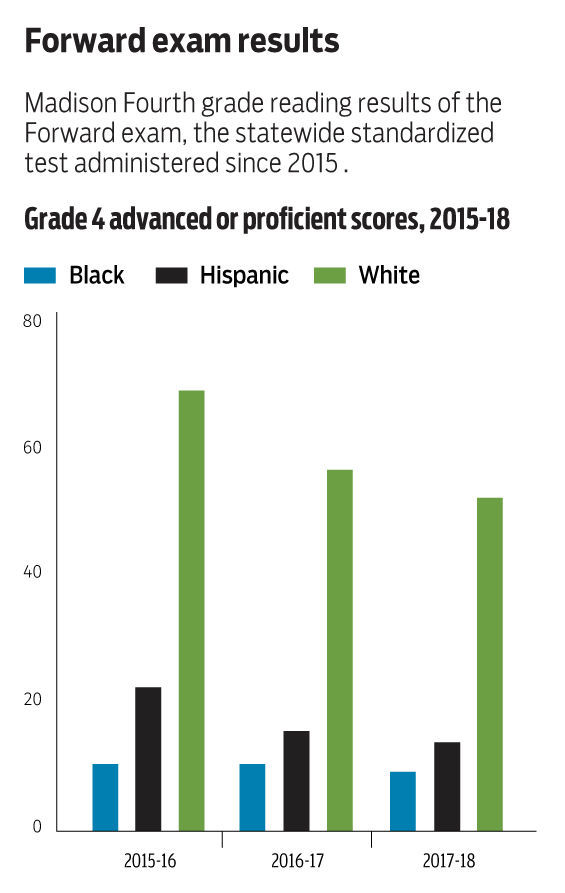
The new scores reveal the state’s persistent gap in academic achievement between its black and white students remains large.
Twelve percent of black third-graders are considered proficient or advanced in English, compared to 48 percent of white students, for example.
In math, about 17 percent of black students in third grade scored proficient or advanced in the 2017-’18 school year, while 60 percent of white students scored at the same level.
Less discussed in Wisconsin is the tremendous impact that economic status has on student achievement. A school with a population of 100% students who are economically disadvantaged would be expected to have proficiency rates more than 40% lower than a school with wealthier students. Indeed, this economics achievement gap is far larger in terms of proficiency effects than the racial achievement gap, and has important implications for the rural areas of the state, where the percentage of low-income families is higher than most suburban and some rural areas.
While the initial data release by DPI did not include sufficient data for apples-to-apples comparisons among private schools in the choice program, the data was comprehensive enough for charter schools. Particularly in Milwaukee, these schools continue to outperform their peer schools. For this preliminary analysis, we pulled out independent and non-instrumentality charters from MPS, while leaving instrumentality charters—or charters in name-only—as part of the district’s performance. In both mathematics and English/language arts, charter schools continue to outperform their other public school peers.
In English/Language Arts, “free” charters had approximately 9% higher proficiency than traditional public schools. In mathematics, these schools had 6.9% higher proficiency. This is consistent with our past analyses which have found that independence from MPS is a key component of better student outcomes, whether through the chartering or the school choice program.
Madison, despite spending far more than most, has tolerated long term, disastrous reading results.
Tony Evers, currently runnng for Governor, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction since 2009. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?
The Wisconsin DPI has aborted our one attempt at teacher content knowledge requirements: “Foundations of Reading” for elementary teachers. Massachusetts’ MTEL substantially raised the teacher content knowledge bar, leading to their top public school rank.
An emphasis on adult employment, also Zimman.
“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …
“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?
Evers, a Democrat, is asking for $1.4 billion in additional funds for the state’s K-12 schools in the 2019-21 budget. The $15.4 billion request, submitted by Evers on Monday, comes less than two months before Walker and Evers will meet on the ballot — and Evers’ budget letter includes a swipe at the governor.
“Wisconsin has a proud history and tradition of strong public schools. Our state’s education system — from early childhood through higher education — has served as the pathway to prosperity for generations of Wisconsinites and the key to a skilled workforce and strong economy,” Evers wrote. “In recent years, however, historic cuts to education have impeded our progress.”
Evers’ budget request includes $606 million in new funding for special education programs, bringing funding for the programs up to $900 million by 2021. It also dedicates an additional $58 million to mental health programs, and an additional $41 million for bilingual-bicultural programs.
The DPI budget would also expand and fund new programs in the state’s five largest school districts — Milwaukee, Kenosha, Green Bay, Madison and Racine — which have disproportionate shares of students with significant achievement gaps. The proposals targeted toward those districts include expanding summer school grants, offering new funding for 3K programs and offering extra funding to National Board certified teachers who teach in high-poverty schools in those five districts.
The amounts noted above exclude substantial local taxpayer property taxes, redistributed federal taxpayer dollars and various grants. (The proposed taxpayer expenditure increase was 12.3% a few days ago).
Madison has benefited substantially from a $38B+ federal taxpayer electronic medical record subsidy.
Madison spends far more than most, nearly $20k per student.
Unfortunately, the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction (DPI), lead for years by Mr. Evers, has killed our one (!) attempt to follow Massachusetts’ successful teacher content knowledge requirement(s) – MTEL.
The DPI has granted thousands of annual waivers for the elementary teacher reading content knowledge exam: Foundations of Reading.
An emphasis on adult employment (2009).
You can read the study here. Allegretto and Mishel argue that teacher demonstrations and shortages around the country are driven by the fact that educators in K-12 public schools are making less money compared to other college graduates and “professionals” over the past several decades. “The teacher wage penalty was 1.8 percent in 1994, grew to 4.3 percent in 1996, and reached a record 18.7 percent in 2017,” they write. According to their analysis, the “penalty” shrinks to 11.1 percent when you add in total compensation.
Their agenda is straightforward: They think teachers should be paid more, both in absolute terms and relative to other workers with college degrees or professional status. They have amassed a number of statistics from credible sources which show that inflation-adjusted teacher wages have in fact been flat for about the past 20 years.
I don’t agree with Allegretto and Mishel that average teacher pay should be increased and I don’t buy into their framework of a teacher “pay penalty.” But that’s besides the point that the Time story constitutes something akin to journalistic malpractice by suggesting that teachers such as Brown, who are pulling down salaries in the mid-50s, are being forced to sell bodily fluids to make ends meet. Indeed, according to Time’s sister publication, Money, the median household income in Kentucky is $45,215, meaning that Brown is making about $10,000 more than half of all other households in the Bluegrass State.
And in fact, teachers are doing well compared to households on the national level, too. The median household income in the United States is $61,372. According to the largest teachers union, the National Education Association (NEA),
“An emphasis on adult employment (2009)”.
That’s an injustice and there’s no way to spin that. There shouldn’t have been a strike. I found the last two weeks mind-numbingly frustrating because it was preventable. If the McCleary Settlement was done with transparency, rather than dead-of-night-last-second deal making, we wouldn’t be here. If a fair contract had been offered from the beginning of negotiations, we wouldn’t be here. If young teachers in our city felt valued and knew they wouldn’t have to pick-up side-hustles to stay in their apartments, we wouldn’t be here.
Lastly for the school board, we elect school board members not spokespeople. Canceling school board meetings, ghosting from social media, and responding to community members with auto-form replies is not the way for school board members to lead. The community didn’t vote for the district public information office, we elected you. If you don’t want to face an angry public when things are bad, perhaps elected office isn’t your calling.
This will be my thirteenth year of teaching. I have worked in Tacoma my entire teaching career. But, my mentor in the profession departed during this strike. I am still not over that. Despite reaching a contract agreement, I have lingering concerns about our ability to retain many of the great teachers we have. I want for Tacoma Schools to be the world-class system our students deserve, but nothing that happened over the last two weeks brought us closer to that.
“An emphasis on adult employment”.
Walker proposed $13.7 billion in total state support for public schools for the 2017-19 biennium. That includes about $2.2 billion in property tax credits that are counted as K-12 funding, but don’t go directly into the classroom.
Walker’s campaign spokesman Brian Reisinger touched on the record amount in a Saturday statement:
“Scott Walker made record actual-dollar investments in our schools, the most in state history in what Tony Evers himself called a pro-kid budget,” Reisinger said. “He will continue to make historic investments in schools without raising taxes on hard-working families and seniors to do it.”
Evers’ spokesman Sam Lau referred questions to DPI’s McCarthy.
McCarthy said in an interview Saturday that the last time school finance was overhauled in Wisconsin this way was for the 1995-97 budget cycle when the state added $1.37 billion.
Evers’ request for $15.4 billion in state support for K-12 schools in 2019-21, up 12.3 percent from the $13.7 billion distributed to school districts in the 2017-19 cycle, is similar to what the Legislature agreed to more than two decades ago, McCarthy said.
Britt Cudaback, spokeswoman for the Evers campaign, did not say how Evers would pay for the increase if elected governor, but indicated he would make education funding a priority.
“Budgets are about priorities. If we can find $4.5 billion for a foreign corporation, we can make the investments needed in our students,” Cudaback said, referring to incentives passed for Foxconn to build $10 billion worth of facilities in Wisconsin. “Tony’s priority is to fully fund our schools which can be done without increasing property taxes or forcing over a million taxpayers to go to referenda to pick up the tab. Tony is prepared to make tough decisions as governor and will do whatever is necessary to ensure we’re doing what’s best for our kids.”
Walker, a Republican, and Evers, the only Democrat leading a major state agency, have been at odds for years over how much funding to provide schools and where to spend it.
In the current state budget, Walker adopted much of Evers’ budget request, which included $649 million in new funding — a plan similar to requests that had been rejected by Walker previously.
Walker spokesman Brian Reisinger didn’t release details of the governor’s plans for school spending in the 2019-’21 state budget, but signaled that he also would continue to make K-12 education spending a priority.
“Scott Walker made record actual-dollar investments in our schools, the most in state history, in what Tony Evers himself called a ‘pro-kid budget,’ ” Reisinger said, referring to Evers’ remarks when the current budget was passed. “He will continue to make historic investments in schools without raising taxes on hard-working families and seniors to do it.”
The amounts noted above exclude substantial local taxpayer property taxes, redistributed federal taxpayer dollars and various grants.
Madison has benefited substantially from a $38B+ federal taxpayer electronic medical record subsidy.
Madison spends far more than most, nearly $20k per student.
Unfortunately, the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction (DPI), lead for years by Mr. Evers, has killed our one (!) attempt to follow Massachusetts’ successful teacher content knowledge requirement(s) – MTEL.
The DPI has granted thousands of annual waivers for the elementary teacher reading content knowledge exam: Foundations of Reading.
An emphasis on adult employment (2009).
The lesson for journalists (or anyone) working amidst intractable conflict: complicate the narrative. First, complexity leads to a fuller, more accurate story. Secondly, it boosts the odds that your work will matter — particularly if it is about a polarizing issue. When people encounter complexity, they become more curious and less closed off to new information. They listen, in other words.
There are many ways to complicate the narrative, as described in detail under the six strategies below. But the main idea is to feature nuance, contradiction and ambiguity wherever you can find it. This does not mean calling advocates for both sides and quoting both; that is simplicity, and it usually backfires in the midst of conflict. “Just providing the other side will only move people further away,” Coleman says. Nor does it mean creating a moral equivalence between neo-Nazis and their opponents. That is just simplicity in a cheap suit. Complicating the narrative means finding and including the details that don’t fit the narrative — on purpose.
The idea is to revive complexity in a time of false simplicity. “The problem with stereotypes is not that they are untrue but that they are incomplete,” novelist Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie says in her mesmerizing TED Talk “A Single Story.” “[I]t’s impossible to engage properly with a place or a person without engaging with all of the stories of that place and that person.”
Usually, reporters do the opposite. We cut the quotes that don’t fit our narrative. Or our editor cuts them for us. We look for coherence, which is tidy — and natural. The problem is that, in a time of high conflict, coherence is bad journalism, bordering on malpractice.
In the midst of conflict, our audiences are profoundly uncomfortable, and they want to feel better. “The natural human tendency is to reduce that tension,” Coleman writes, “by seeking coherence through simplification.” Tidy narratives succumb to this urge to simplify, gently warping reality until one side looks good and the other looks evil. We soothe ourselves with the knowledge that all Republicans are racist rednecks — or all Democrats are precious snowflakes who hate America.
Complexity counters this craving, restoring the cracks and inconsistencies that had been air-brushed out of the picture. It’s less comforting, yes. But it’s also more interesting — and true.
Reporting depth is critical, but rarely found.
A few SIS examples:
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
An emphasis on adult employment.
Expanding Madison’s least diverse schools.
They’re all rich white kids and they’ll do just fine, NOT!
Police calls, Madison area schools 1996-2006.
Wisconsin Reading Coalition E-Alert:
We have sent the following message and attachment to the members of the Joint Committee for Review of Administrative Rules, urging modifications to the proposed PI-34 educator licensing rule that will maintain the integrity of the statutory requirement that all new elementary, special education, and reading teachers, along with reading specialists, pass the Foundations of Reading Test. To see where these modifications fit in, use the most recent version of PI-34, which can be found at https://docs.legis.wisconsin.gov/code/chr/all/cr_17_093
Please contact the committee to express your support of these modifications. Your message will have extra impact if you are a constituent of any of the following committee members. Thank you for your assistance! Your voice is important.
Representative Ballweg (Co-Chair)
Memo to the Joint Committee for Review of Administrative Rules
Thank you for putting the PI-34 licensing rule on hold to consider whether modifications should be made. As you know, Wisconsin Reading Coalition is interested in upholding the intent and integrity of the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test (FORT) for elementary, special education, and reading teachers, as well as the administrative position of reading specialist. We suggest the attached PI-34 modifications, which we drafted as narrowly as possible to impact only the FORT requirement. You may want to hold final action on PI-34 until the recommendations of the legislative study committee on dyslexia have been received.
In cases where a school district cannot find a fully licensed teacher of reading, we do support a one-year exemption from the FORT via a tier I license. However, we must remember that granting 1400 tier I licenses to individuals who failed the FORT means that approximately 28,000 beginning and struggling readers will have an underqualified teacher for that year. The teachers have that year to get up to speed, but the students don’t get a do-over. Exemption from the FORT for district need is a major concession, as it undoes statutory protection for students. This exemption should be as restrictive as possible, with passage of the FORT required before any license renewal.
We see no reason for PI-34 to allow exemptions from the FORT beyond situations of school district need or where it is statutorily required (e.g., online preparation under 118.197 and certain out-of-state teachers under 118.193). Further exemptions undo statutory protection for students without a compelling, overriding public interest. In promulgating these additional exemptions, DPI is essentially usurping legislative authority.
Ironically, while providing numerous avenues to get around the FORT, PI-34 does nothing to ensure that more individuals will be able to clear the FORT hurdle in the future. Subchapter III of PI-34 provides an opportunity for DPI to exercise its responsibility to set standards for educator preparation program approval, and to implement improvement plans for programs where large numbers of potential teachers are failing the FORT. We hope that the 2018 legislative study committee on dyslexia will put forward draft legislation that addresses this problem, as DPI has not addressed it on its own.
Despite being called “stakeholder revisions,” PI-34 ignores the important stakeholder groups of students and their families. The current draft heavily represents the special interests of school district administrators. In fact, this is what the director of one administrators’ organization said about PI-34: “ . . . you should understand that the rules proposal is not a product of DPI. It resulted from nearly two years of work by critical stakeholders to address the significant workforce issues facing the learning environments for children in Wisconsin’s schools.” Our recent conversations with DPI indicate that they may be amendable to amending the draft document. Undoubtedly, they have been under considerable pressure from school district administrators, judging from the talking points below.
Sincerely,
Talking Points for School District Administrators with WRC comments:
1. Wisconsin school districts are facing growing school staffing issues including high turnover, fewer applicants for positions, and candidate shortages in a variety of disciplines. With fewer new teachers entering the profession, new approaches to educator recruitment and retention are critical to ensure all children have access to high-quality educators. We are not opposed to an exemption from the FORT in true emergency cases where a district shows it is unable to hire a fully-licensed teacher, but we should not call these individuals high-quality educators. We are opposed to allowing those licenses to be renewed year-after-year without the teacher passing the FORT. A one-year time limit for passing the FORT would be sufficient to help districts meet immediate candidate shortages while working toward having a highly-qualified educator in that classroom.
2. The licensure flexibility afforded under CR17-093 is universally supported by school leaders in their effort to address the growing workforce challenges faced by Wisconsin school districts. This is simply inaccurate. There are school leaders, both superintendents and school board members, who have spoken against exemptions from the FORT.
3. We must also point out that districts are currently operating under these proposed rule changes as part of the current Emergency Rule. These proposals are already making a positive difference in meeting these workforce challenges in districts throughout Wisconsin. This is also inaccurate. The current Emergency Rule is much narrower than the proposed PI-34. It allows 1-year, renewable licenses with a FORT exemption only if the district shows it cannot find a fully-licensed teacher. The PI-34 draft allows any in-state or out-of-state graduate of an educator preparation program to obtain a Tier I license and teach in districts that have not shown shortages.
4. School administrators support all aspects of the proposed rule but, of particular importance are the flexibilities and candidate expanding aspects in the Tier 1 license. This will allow for a much-needed district sponsored pathway to licensure, immediate licensure for out of state candidates, licensing for speech and language pathologists with a Department of Safety and Professional Services license and licensing for individuals coming into a district on an internship or residency status. These are effective, no-cost solutions to a significant workforce need in Wisconsin school districts. We are opposed to district-sponsored and out-of-state pathways to licensure where the candidates do not have to take and pass the same outcome exams required of other educators. There is no reason to hold these programs to a lower standard. District-sponsored pathways to licensure surely come at some cost to the district, which is obligated to provide “appropriate professional development and supervision to assist the applicant in becoming proficient in the license program content guidelines.” They can also come at great cost to beginning and struggling readers if they are taught by someone who has not passed the FORT.
5. Educator licensure is simply a minimum requirement. District leadership is responsible for hiring and developing successful educators, and ultimately determining educator quality based on actual teacher performance and student outcomes. Districts and families should be able to count on licensed applicants having the basic information about reading that they will need to successfully teach all students on day one. This is particularly important in districts that have fewer applicants from which to choose. Leaving educator quality standards to Wisconsin districts over the years produced stagnant reading scores and a declining national ranking. Section 118.19(14) of the statutes was enacted to protect students and provide better outcomes for our society, not to provide ultimate flexibility to local administrators.
6. Reducing the Tier 1 license flexibility in the rule has the potential to impact as many as 2,400 teaching licenses, many of which are FORT-related stipulations. Any portion of these licensees that lose their ability to teach will exacerbate an already troubling workforce challenge and reduce educational opportunities for children. This concern can be met by maintaining a one-year emergency Tier I exception for districts that can show a fully-licensed candidate is not available. Eliminating the continuous renewal option for these licenses and requiring the FORT for district-sponsored pathway and other licenses will help ensure quality educational opportunities for children. The quality of the teachers is just as important as the quantity. Meanwhile, DPI should set appropriate standards in reading for educator preparation programs, and institute improvement plans for institutions that have low passing rates on the FORT. What does it say about Wisconsin that DPI reports there are over 1400 teachers in the classroom under Emergency Rules specifically because they have not passed the FORT? At some point, we need to address the root of the problem if we are to have sufficient numbers of highly-qualified teachers for every beginning or struggling reader.
Suggested Modifications (PDF).
Foundations of Reading: Wisconsin’ only teacher content knowledge requirement…
Compare with MTEL
Mark Seidenberg on Reading:
“Too often, according to Mark Seidenberg’s important, alarming new book, “Language at the Speed of Sight,” Johnny can’t read because schools of education didn’t give Johnny’s teachers the proper tools to show him how”
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
Tony Evers, currently runnng for Governor, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction since 2009. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?
An emphasis on adult employment, also Zimman.
“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …
“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?
Cody Miller, via a kind reader:
I’ve been a member of the New Jersey Education Association (NJEA) — one of the nation’s most powerful state teachers unions — since I started working in education a year and a half ago. I’ve been an advocate for education my entire life, served on a board of trustees at a county college, and am proud to come from a family of teachers.
My grandmother was an elementary school teacher, my uncle is an assistant principal and my aunt is a principal. And even though I believe in the vital role that unions have to play in protecting workers’ rights, especially when it comes to educators, I’m confident that Janus vs. AFSCME is a victory for rank and file teachers.
Here’s why: big unions like the NJEA have become increasingly concerned with accumulating political power and rewarding their leadership, even while they have neglected their obligations to working class teachers and put our union in financial peril.
While this is a problem plaguing teachers unions nationwide, you would be hard-pressed to find a stronger example than here in New Jersey.
In 2016 — the most recent year for which this data is available — the NJEA gave their top leadership a 42 percent pay raise. On average, the fourteen officers identified as NJEA leaders earned more than $530,000 — up from $379,000 the year before.
Related:
An emphasis on adult employment
Wisconsin Reading Coalition, via a kind email:
Thanks to everyone who contacted the legislature’s Joint Committee for Review of Administrative Rules (JCRAR) with concerns about the new teacher licensing rules drafted by DPI. As you know, PI-34 provides broad exemptions from the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test (FORT) that go way beyond providing flexibility for districts to deal with emergency teacher shortage situations.
As a result of written and oral testimony on PI-34, the JCRAR put a hold on PI-34 and will meet again on July 13th. We hope at that time they will seek modifications to the rule to more closely align with the statutory requirement that new elementary teachers, special education teachers, reading teachers, and reading specialists pass the FORT. This statute was passed for the protection of our beginning and struggling readers, and to encourage educator preparation programs to do a better job of covering this basic content information about reading acquisition. It is particularly critical in a state like Wisconsin where student reading scores are low for all sub-groups and have not improved for over two decades.
Of course, there is pushback from the people who recommended these licensing changes to DPI. Various associations of school administrators have urged their members to lobby the JCRAR members in favor of allowing individuals to become teachers of record without passing the FORT. The talking points they have provided to their members are enumerated below, along with our comments.
Please contact the JCRAR once more in advance of July 13th, asking them to maintain the integrity of the statutory FORT requirement. Following are the members of the committee:
Talking Points for School District Administrators with WRC comments:
Wisconsin school districts are facing growing school staffing issues including high turnover, fewer applicants for positions, and candidate shortages in a variety of disciplines. With fewer new teachers entering the profession, new approaches to educator recruitment and retention are critical to ensure all children have access to high-quality educators. We are not opposed to an exemption from the FORT in true emergency cases where a district shows it is unable to hire a fully-licensed teacher, but we should not call these individuals high-qualified educators. We are opposed to allowing those licenses to be renewed year-after-year without the teacher passing the FORT. A one-year time limit for passing the FORT would be sufficient to help districts meet immediate candidate shortages while working toward having a highly-qualified educator in that classroom.
The licensure flexibility afforded under CR17-093 is universally supported by school leaders in their effort to address the growing workforce challenges faced by Wisconsin school districts. This is simply inaccurate. There are school leaders, both superintendents and school board members, who have spoken against exemptions from the FORT.
We must also point out that districts are currently operating under these proposed rule changes as part of the current Emergency Rule. These proposals are already making a positive difference in meeting these workforce challenges in districts throughout Wisconsin. This is also inaccurate. The current Emergency Rule is much narrower than the proposed PI-34. It allows 1-year, renewable licenses with a FORT exemption only if the district shows it cannot find a fully-licensed teacher. PI-34 allows any in-state or out-of-state college graduate to obtain a Tier I license and teach in districts that have not shown shortages.
School administrators support all aspects of the proposed rule but, of particular importance are the flexibilities and candidate expanding aspects in the Tier 1 license. This will allow for a much-needed district sponsored pathway to licensure, immediate licensure for out of state candidates, licensing for speech and language pathologists with a Department of Safety and Professional Services license and licensing for individuals coming into a district on an internship or residency status. These are effective, no-cost solutions to a significant workforce need in Wisconsin school districts. We are opposed to district-sponsored and out-of-state pathways to licensure where the candidates do not have to take and pass the same outcome exams required of other educators. There is no reason to hold these programs to a lower standard.
Educator licensure is simply a minimum requirement. District leadership is responsible for hiring and developing successful educators, and ultimately determining educator quality based on actual teacher performance and student outcomes. District administrators and families should be able to count on licensed applicants having the basic information about reading that they will need to successfully teach all students on day one. This is particularly important in districts that have fewer applicants from which to choose.
Reducing the Tier 1 license flexibility in the rule has the potential to impact as many as 2,400 teaching licenses, many of which are FORT-related stipulations. Any portion of these licensees that lose their ability to teach will exacerbate an already troubling workforce challenge and reduce educational opportunities for children. This concern can be met by maintaining an one-year emergency exception for districts that can show a fully-licensed candidate is not available. Eliminating the continuous renewal option for these licenses and requiring the FORT for district-sponsored and out-of-state pathway licenses will help ensure quality educational opportunities for children. The quality of the teachers is just as important as the quantity. Meanwhile, DPI should set appropriate standards in reading for educator preparation programs, and institute improvement plans for institutions that have low passing rates on the FORT. What does it say about Wisconsin that we have over 1400 teachers in the classroom under Emergency Rules specifically because they have not passed the FORT? At some point, we need to address the root of the problem if we are to have sufficient numbers of highly-qualified teachers for every beginning or struggling reader.
Foundations of Reading: Wisconsin’ only teacher content knowledge requirement…
Compare with MTEL
Mark Seidenberg on Reading:
“Too often, according to Mark Seidenberg’s important, alarming new book, “Language at the Speed of Sight,” Johnny can’t read because schools of education didn’t give Johnny’s teachers the proper tools to show him how”
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
Tony Evers, currently runnng for Governor, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction since 2009. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?
An emphasis on adult employment, also Zimman.
“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …
“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?
Wisconsin Reading Coalition, via a kind email:
Wisconsin Reading Coalition has alerted you over the past 6 months to DPI’s intentions to change PI-34, the administrative rule that governs teacher licensing in Wisconsin. We consider those changes to allow overly-broad exemptions from the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test for new teachers. The revised PI-34 has gone through DPI public hearings and was sent to the education committees of the Wisconsin Assembly and Senate, where no action was taken.
PI-34 is now sitting with the Wisconsin Legislature Joint Committee on Administrative Rules, which is the last stop before it becomes a permanent rule. Because of concerns it has heard from Wisconsin Reading Coalition and other groups and individuals, the committee will hold a public hearing on Thursday, June 7th, at 10:00 AM in the State Capitol. We urge you to attend this hearing and make a statement. If you cannot attend, please consider sending an e-mail comment to the committee members prior to the hearing. A list of committee members follows. As always, it is a good idea to copy your own legislators. If you copy Wisconsin Reading Coalition, we will make sure your comments are delivered in hard copy.
To refresh your memory of the issues involved, please see this WRC memo to the Committee on Administrative Rules.
Joint Committee on Administrative Rules (contact information provided in links):
*There are currently over 358,000 K-5 students in Wisconsin public schools alone.
51.7% of Wisconsin 4th graders were not proficient in reading on the 2016-17 state Forward exam. Non-proficient percentages varied among student sub-groups, as shown below in red and black, and ranged from approximately 70-80% in the lower-performing districts to 20-35% in higher-performing districts.While we appreciate DPI’s concerns with a possible shortage of teacher candidates in some subject and geographical areas, we feel it is important to maintain teacher quality standards while moving to expand pathways to teaching.
- Statute section 118.19(14) currently requires new K-5 teachers, reading teachers, reading specialists, and special education teachers to pass the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test (WI-FORT) before getting an initial license to teach. The intent of this statute, passed in 2012 on a bipartisan vote following a recommendation of the non-partisan Read to Lead task force, was to enhance teacher quality by encouraging robust reading courses in educator preparation programs, and to ensure that beginning and struggling readers had an effective teacher. The WI-FORT is the same test given in Massachusetts, which has the highest 4th grade reading performance in the country. It covers basic content knowledge and application skills in the five components of foundational reading that are necessary for successfully teaching all students.
- The annual state Forward exam and the newly-released results of the 2017 National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) highlight the importance of having high-quality teachers in Wisconsin classrooms. 65% of our 4th graders were not proficient in reading on the NAEP. Our national ranking has slipped to 34th, and all sub-groups of students perform below their national averages. Our black students rank 49th among black students in the country, and our white students rank 41st.
- The revised teacher licensure rules that DPI has presented to the legislature in the re-written administrative rule PI 34, create a new Tier I license that provides broad exemptions from the WI- FORT.
- We encourage the education committees to table the adoption of this permanent rule until it is amended to better support teacher quality standards and align with the intent of statute 118.19(14).
- We favor limiting the instances where the WI-FORT is waived to those in which a district proves it cannot find a fully-qualified teacher to hire, and limiting the duration of those licenses to one year, with reading taught under the supervision of an individual who has passed the WI-FORT. Renewals should not be permitted except in case of proven emergency.
- We favor having DPI set out standards for reading instruction in educator preparation programs that encompass both the Standards for Reading Professionals (International Literacy Association) and the Knowledge and Practice Standards for Teachers of Reading (International Dyslexia Association). This will enable aspiring teachers to pass the WI-FORT and enter the classroom prepared to teach reading.
- We favor having DPI implement a corrective action plan for educator preparation programs where fewer than 85% of students pass the WI-FORT on the first attempt in any year. Students putting in four years of tuition and effort should be able to expect to pass the WI-FORT.
Foundations of Reading: Wisconsin’ only teacher content knowledge requirement…
Compare with MTEL
Mark Seidenberg on Reading:
“Too often, according to Mark Seidenberg’s important, alarming new book, “Language at the Speed of Sight,” Johnny can’t read because schools of education didn’t give Johnny’s teachers the proper tools to show him how”
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
Tony Evers, currently runnng for Governor, has lead the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction since 2009. I wonder if anyone has addressed Wisconsin achievement challenges vis a vis his DPI record?
An emphasis on adult employment, also Zimman.
“I didn’t have one phone call, I don’t have one email about this NAEP data. But my phone can ring all day if there’s a fight at a school or can ring all day because a video has gone out about a board meeting. That’s got to change, that’s just got to change. …
“My best day will be when we have an auditorium full of people who are upset because of our student performance and our student achievement and because of the achievement gaps that we have. My question is, where is our community around these issues?
Wisconsin Reading Coalition (PDF), via a kind email:
As we reported recently, districts in Wisconsin, with the cooperation of DPI, have been making extensive use of emergency licenses to hire individuals who are not fully-licensed teachers. Click here to see how many emergency licenses were issued in your district in 2016-17 for elementary teachers, special education teachers, reading teachers, and reading specialists. You may be surprised at how high the numbers are. These are fields where state statute requires the individual to pass the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test to obtain a full initial license, and the emergency licenses provide an end-run around that requirement.
These individuals did not need to pass the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test, which would be required for full initial licensure *districts include individuals that are listed only once, but worked in multiple locations or positions
Information provided by the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction
New Online Certificate Program
Now there is an even more misguided opportunity for districts to hire unprepared teachers. The budget bill, set for an Assembly vote this Wednesday, followed by a vote in the Senate, requires DPI to issue an initial license to anyone who has completed the American Board online training program. That program, for career switchers with bachelor’s degrees, can be completed in less than one year and includes no student teaching (substitute or para-professional experience is accepted). We have no objection to alternate teacher preparation programs IF they actually prepare individuals to Wisconsin standards. In the area of reading, the way to determine that is for the American Board graduates to take the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test (FORT). If they cannot pass, they should not be granted anything more than an emergency license, which is what is available to individuals who complete Wisconsin-based traditional and alternate educator preparation programs but cannot pass the FORT. Wisconsin should not accept American Board’s own internal assessments as evidence that American Board certificate holders are prepared to teach reading to beginning and struggling students.Action Requested
Please contact your legislators and tell them you do not want to weaken Wisconsin’s control over teacher quality by issuing initial licenses to American Board certificate holders who have not, at a minimum, passed the Wisconsin Foundations of Reading Test. Ask them to remove this provision from the budget bill. Find your legislators and contact information here.
How Should Wisconsin Address Its Teacher Shortages?
As pointed out in a recent fact sheet from the National Council on Teacher Quality, teacher shortages are particular to certain fields and geographic areas, and solutions must focus on finding and addressing the reasons for those shortages. This requires gathering and carefully analyzing the relevant data, including the quality of teacher preparation at various institutions, the pay scale in the hiring districts, and the working conditions in the district.
Related: WISCONSIN ELEMENTARY TEACHER CONTENT KNOWLEDGE EXAM RESULTS (FIRST TIME TAKERS).
Am emphasis on adult employment.
In a 5-2 decision on Monday, the Madison School Board voted to postpone the charter approval of Isthmus Montessori Academy.
The board wanted more clarity around the school’s proposed attendance area, financial and academic accountability standards at their three-year mark, and language in the proposal that asks for waivers that apply to early release and lesson planning time promised to all Madison Metropolitan School District teachers via the employee handbook.
IMA has until Aug. 21 to finish negotiations with the district to iron out the details. The board is expected to take up the vote again at its next regular meeting on Aug. 28.
If the board approves the charter, IMA, which is currently a private school, would cease operation and reopen as Isthmus Montessori Academy Charter School in the fall of 2018 serving students in 4K through ninth grade.
IMACS would be a free public charter school, operating under the authority of the Madison School Board.
Some history on (aborted) independent charter schools in Madison, including:
the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School and
the Studio School.
2009: “An emphasis on adult employment“.
Unfortunately, Madison continues to support a non diverse K-12 Governance model, this despite spending far more per student than most districts and tolerating long term, disastrous reading results.
Related: an Independent (!) Charter School RFP for Madison or Milwaukee.
University of Wisconsin System Office of Educational Opportunity, via a kind email:
As home to the nation’s first public kindergarten, Wisconsin has a proud history of visionary educators incubating innovative educational opportunities for students, families, and their communities.
The Office of Educational Opportunity is proud to be a partner in the Badger State’s living legacy of educational innovations. Our role is to connect students, families, professional educators, and community leaders with an opportunity to create a school that meets their needs and interests.
If you have an idea for a school, then we invite you to review and respond to our Request for Proposal (RFP). Details about how we will score applications are provided in the linked rubrics, but for us to “green light” any proposal, it must provide access to new educational innovations, incubate existing educational practices in new ways, and/or increase educational equity.
The Office of Educational Opportunity will begin seeking proposals for public charter schools in Madison and Milwaukee on August 2, 2017.
Phase 1 submissions will be scored on a rolling basis using the reviewer guide shared below.
Applicants with approved Phase 1 applications will be invited to submit a Phase II application (Phase II applications that are submitted without an approved Phase 1 will be returned to the applicant without being reviewed).
The School Selection Committee will score Phase 2 submissions using the reviewer guide provided below. The Committee will make authorization recommendations to OEO’s Director.
Applicants who receive a recommendation for authorization from the School Selection Committee may commence contract negotiations with OEO’s Director – subject to the Director accepting the Committee’s recommendation for authorization.
If mutually agreeable contract terms are reached, then the University of Wisconsin System Board of Regents must approve of the contract for any school to be officially authorized by OEO.
Some history on (aborted) independent charter schools in Madison, including:
the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School and
the Studio School.
2009: “An emphasis on adult employment“.
Unfortunately, Madison continues to support a non diverse K-12 Governance model, this despite spending far more per student than most districts and tolerating long term, disastrous reading results.
Much more on Gary Bennett’s office of Educational Opportunity.
The RFP respondents need not conform to Madison or Milwaukee’s legacy organization structure – that is, they would be a “non instrumentality” school.
This is positive. I hope and pray that we see interesting proposals and schools.
The Teamsters are complaining that Oakland’s Mills College took jobs away from working men and women and gave them to goats.
The union’s top official in the East Bay has told college officials that Mills may have violated its work agreement with the Teamsters when, instead of dispatching union workers to clear and haul away brush, it assigned the task to a herd of 500 goats with the four-footed brush clearance crew Goats R Us.
The college has three choices, says Teamsters Local 70 Secretary-Treasurer Chuck Mack, if it wishes to avoid a formal grievance:
It could agree to not enter into any future goat contracts without first discussing the matter with the union.
An emphasis on adult employment.
New Jersey Star Ledger Editorial:
The Newark parents who sued, arguing that forcing school districts to prioritize seniority over teacher talent hurts their kids, just lost their case in court. That’s a real blow to students, who don’t have a special interest union.
But make no mistake: this fight is far from over. Their families can appeal, of course, and while it may be a long shot to argue that the state constitution should decide this, the issue is in no way settled – because changing the policy itself is essential.
The Legislature should have fixed this long ago; these parents never should have had to go to court. Absolute seniority rights are about Democratic fealty to the teacher’s union, not what’s best for children.
Much more on the New Jersey Last in, First Out (LIFO) teacher governance lawsuit, here.
Related: An emphasis on adult employment.
Attendance, graduation rates and college enrollment were generally on the upswing beginning five to seven years before Hancock started moving toward selective enrollment. More to the point for Madison and West High is that improvements began happening at Hancock before Boran took over or even worked there.
Regardless of who or what is responsible for Hancock’s performance, though, that performance is not universally good. Test scores and the growth in test scores at Hancock, for example, are below national averages. The average ACT score last year was 16.9, or below the Chicago district average of 18.4.
Despite spending around $18k/student annually – far more than most K-12 government school districts, Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
“Their priorities are distorted. We need to make a decision to put kids first. Especially when they’re savings is about $500,000 to $750,000, when they’re paying out a million dollars on, on public relations specialists and on lobbyists, a million dollars.”
Former Superintendent Art Rainwater frequently attempted to kill Madison’s strings program.
Like Albuquerque, Madison long had a lobbyist. Do they have one today?
Madison, with “plenty of resources” spends about $18,000 per student annually – well above the national average.
An emphasis on “adult employment“.
Matthew Frankel, via a kind email:
Friends –
As we only try to curate and update you on some of the most informative stories regarding this NJ LIFO Lawsuit – I did want to flag these three items for your files:
1.) Here is a moving testimonial interview today showcasing one of the Newark parents involved in the suit. It was published in Laura Waters’ great NJ education blog NJ Left Behind. This piece provides more personal narrative and background than some of the published news stories:
http://njleftbehind.blogspot.com/2017/04/newark-mom-on-lifo-lawsuit-im-just.html
2.) Earlier this week, PEJ Executive Director Ralia Polechronis did a live interview with Eric Dawson and Rashon Hasan, of Newark’s SPLASH RADIO 94.3FM Radio. There is some great in-depth background on the case You can listen to it here –
https://soundcloud.com/user-516806286/april-4-2018
3.) And if you go to the influential news site – Insider NJ – later this week you will see our aggressive video ad buy, which will drive readers to the animated video we produced explaining the LIFO lawsuit. Which in just a couple of weeks have already garnered over 35K views.
https://www.insidernj.com
I know many of you are deeply interested and supportive of these legal efforts and the communication work that is dovetailing this strategy, so I hope this email is helpful…Thanx.Matthew Frankel
MDF Strategies
41 Watchung Plaza, Suite 355
Montclair NJ 07042
917.617.7914
matthew@mdfstrategies.com
mdfstrategies.com
Much more on the New Jersey Last In First Out Teacher Governance lawsuit, here.
2009, Richard Zimman:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Because of its location near the nation’s capital, its charming historic Old Town, and its median family income of $109,228 (the highest of any city in Virginia), outsiders might think that Alexandria boasts a first-rate public-school system. It doesn’t. The quality of the public schools within the city varies greatly, and system as a whole lags behind those in neighboring Arlington and Fairfax Counties. Pick your measuring stick: U.S. News & World Report, Zillow, GreatSchools.org, Trulia, parental chat boards, the Washington Post ranking of local high schools. Alexandria performs poorly by any metric. SchoolDigger ranks the district 96th out of 130 districts in the state. This isn’t to say Alexandria schools are bad, exactly, but some of them are particularly subpar for an area with such relative wealth.
Jefferson-Houston, which teaches students from pre-K to eighth grade, lost its accreditation in 2012. The school, which is 67 percent black, narrowly avoided being taken over by the state in a subsequent court battle. A little more than 15,000 students attend 16 public schools in Alexandria, and the district spends $16,999 per student, according to the latest statistics. Class sizes are small, averaging 18 students in elementary school, 20 in middle school, and 22 in high school. Despite those advantages, students in Alexandria’s public schools underperform the statewide average in subject after subject. In the 2015–16 school year, 80 percent of Virginia students passed English proficiency exams; 73 percent of students in Alexandria did. In math, 80 percent statewide passed; 68 percent of Alexandria students did. Statewide, 77 percent of students passed a test of writing proficiency; 69 percent of Alexandria students did. In history, 86 percent of students passed statewide; 77 percent of Alexandria students did. In science, 83 percent of students statewide passed; 69 percent of Alexandria students did.
Madison spends more, about $18,000 per student. Despite this far above average spending, Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment“.
Paying for Plan A was accomplished in part by persuading members last year to raise their dues by about 50%, to around $1,000 a year.
Caputo-Pearl has added eight senior union positions, with a ninth paid for by a national parent union. In line with his organizing and political goals, these jobs include a campaign research director, a political director, four organizers and two staff members to represent teachers at charter schools.
For years, Caputo-Pearl said, “UTLA was operating in a way that lacked sufficient strategy, coherence, and direction. … We have addressed this, and UTLA is operating with unprecedented strength.”
An emphasis on “adult employment“.
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, via Gary Bennett:
The University interprets its responsibility to authorize charter schools as a part of a larger attempt to improve education for children and in this instance, the education of children in the City. Charter schools must have programs that provide quality education to urban students and address the critical issues of today’s urban education environment. The academic achievement of children who are viewed as at-risk should be the central focus of the charter school application. Substantive outcomes must be given priority over process experiences if academic achievement is to serve as the central focus.
Being granted a charter to operate a school requires thought and planning as well as a committed organization that can sustain the development and operational requirements of a charter school. Potential applicants must be able to commit eighteen to twenty-four months of planning time before a charter school can become a reality.
The University and SOE consider the following principles to be essential to the development of charter schools authorized by the University. These principles are as follows:
Draft Wisconsin Recovery School Bill (PDF):
This bill authorizes the director of the Office of Educational Opportunity in the University of Wisconsin System to contract with a person to operate, as a four-year pilot project, one recovery charter school for no more than 15 high school pupils in recovery from substance use disorder or dependency. Under the bill, the operator must provide an academic curriculum that satisfies the requirement for graduation from high school as well as therapeutic programming and support for pupils attending the charter school. The bill requires a pupil who wishes to attend the recovery charter school to apply and to agree to all of the following: 1) that the pupil has begun treatment in a substance use disorder or dependency program; 2) that the pupil has maintained sobriety for at 30 days prior to attending the charter school; and 3) that the pupil will submit to a drug screening assessment and, if appropriate, a drug test prior to being admitted. The operator of the charter school may not admit a pupil who tests positive for the presence of a drug in his or her system. In addition, a pupil who enrolls in the school must receive counseling from substance use disorder or dependency counselors while enrolled in the charter school.
The contract between the operator of the recovery charter school and OEO must contain a requirement that, as a condition of continuing enrollment, an applicant for enrollment in the recovery charter school submit claims for coverage of certain services provided by the recovery charter school to his or her health care plan for which the applicant is covered for mental health services. The bill also requires the director of OEO to, following the fourth year of the operation of the charter school, submit a written report to the Department of Health Services regarding the operation and effectiveness of the charter school.
A majority of the Madison School Board rejected the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School several years ago.
Related: An emphasis on adult employment.
A spokeswoman for Senate Majority Leader Scott Fitzgerald, R-Juneau, said Act 10 has been an “undisputed victory for Wisconsin taxpayers.”
“Wisconsin’s declining union membership since the passage of right-to-work legislation only reflects that workers now have the ability to make their own decision about the costs and benefits of union membership,” said spokeswoman Myranda Tanck. “Senator Fitzgerald maintains that the heart of this issue is a simple matter of individual freedom.”
Nationally, according to Thursday’s BLS report, about 14.6 million workers were members of unions in 2016 — down by 240,000 members, or 0.4 percent, from 2015. By comparison, the union membership rate was 20.1 percent, or 17.7 million workers, in 1983.
UW-Madison economist Steven Deller said the level of union membership nationally has been declining for years — a trend that is likely to continue with large-scale, labor-intensive manufacturing being replaced with smaller-scale technology that requires more capital but less manual labor. Large-scale manufacturing companies tend to be unionized and their replacements are more likely not to be.
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
An emphasis on adult employment.
WEAC: $1.57 million for four senators.
Madison schools 18k per student budget, up from about 15k in 2010.
Plenty, according to members of the “Save Camden High School” cadre, who have rebranded themselves under the New Jersey Communities United banner and are planning a confrontation tonight at the Camden Board of Education meeting. Instead of following Sheriff Wilson’s example of placing children’s academic needs on top, this group has decided a years-old, dead-end debate will be its issue du jour, even if it’s to the detriment of students. More broadly, the group’s members represent a microcosm of those who masquerade as social justice warriors while placing adult-centric politics over systemic school improvement.
Eight years ago the Star Ledger described the debilitated state of the “Castle on the Hill”: “emergency scaffolding protects students entering and leaving the school from pieces of plaster and masonry falling off the decaying high school. A new chain-link fence keeps pedestrians clear of other portions of the wall, and broken windows dot the three-story facade.” More recent problems–as shown in the school district’s own video– include cracked steps, crumbling infrastructure, leaking pipes, “indoor vegetation growth,” and an ancient boiler that has required over a million dollars in chewing gum and bailing wire.
Related: “an emphasis on adult employment“.
Compared with other large Colorado school districts, Denver Public Schools has a higher proportion of teachers set to lose tenure under a sweeping educator effectiveness law passed six years ago.
Forty-seven Denver teachers are poised to lose non-probationary status — or tenure — after two consecutive years of being rated ineffective at their jobs, according to district officials. Those teachers represent about 2 percent of the total number of non-probationary teachers in DPS, the state’s largest school district.
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
CPS’ budget crisis was not created overnight. For more than a decade, the district has struggled with a widening structural budget deficit. Since 2001, inflation-adjusted spending per pupil increased by nearly 40 percent. In 2001, CPS spent close to $12,000 per student; in 2015, $16,432. Yet revenue has not kept pace: CPS per-pupil revenue has not matched per-pupil spending, with revenue falling short, on average, by $1,000 per pupil since 2001. More recently, the revenue gap has widened to nearly $3,000 per year.
CPS has papered over its annual shortfalls by borrowing vast sums from bond markets. As a result, CPS bonds are now rated as “junk” and the district has to pay a huge premium to get anyone to buy them (three times the rate for benchmark government bonds).
What’s more, by failing to make the necessary pension contributions, CPS has borrowed even larger amounts from its current and former teachers through the pension fund—today the district owes the fund billions upon billions. CPS owes bondholders and the pension fund more than $38,000 for every student, up from less than $10,000 in 2001.
What’s more, by failing to make the necessary pension contributions, CPS has borrowed even larger amounts from its current and former teachers through the pension fund—today the district owes the fund billions upon billions. CPS owes bondholders and the pension fund more than $38,000 for every student, up from less than $10,000 in 2001.
It is useful for the 4th estate to review spending, debt and outcome data.
“An emphasis on adult employment“.
Comparing Madison’s daycare and early childhood education programs with Madison’s public schools would not be apples-to-apples. But the quality of care available to Madison’s young children appears to stand in stark contrast to the quality of education those children later receive in Madison’s public schools.
Everyone knows about the district’s racial achievement gaps, but quality overall is also solidly mediocre, according to the most recent state report card and other state-reported metrics, including test scores.
Despite this, Madison administrators and School Board members have long resisted spending tax dollars to educate Madison students at schools they don’t directly control
Related: Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results and a focus on adult employment.
A couple of weeks ago, Means outlined a plan in which an unknown number of schools (maybe three?) would be designated to be part of the new program — and the agency that would run them would be MPS itself, with oversight from an independent school operator.
The teachers would be MPS employees, the money to run the schools (at the charter school funding rate, which is about $2,000 less than what MPS itself gets) would go to MPS and the schools would go back to being regular MPS schools in five years if performance improved.
There are ideas for programs at the schools raised in Means’ proposal, which generally are in-line with the “community schools” initiative that MPS itself is trying to grow. This involves extending more services to students and their families, while making changes to academic programs.
I spoke to many of the key players last week. Just about everyone is edgy and uncertain what’s going to happen next.
Related: “an emphasis on adult employment“.
Julian Ring and Madeline Stocker:
Over the next three weeks, 177 faculty and staff must decide whether or not they want to take the College up on its offer to retire early in exchange for a relatively hefty severance package.The deal, which administrators are projecting will save the College between $1.5–3.5 million per year, is known as a voluntary severance incentive package and is the first step in the administration’s long-term plan to cut spending while slowing the rate of tuition increase.
The payout is relatively straightforward. If a qualifying faculty or staff member — one who is at least 52 years of age, has held their position for 10 years or more and for whom the combination of age and service is a minimum of 75 years — chooses to take the deal, the College will pay the retiree one year’s salary and waive health insurance premiums for the first year after retirement.
“The places I’m familiar with that have done it have found that it’s really been a win-win,” College President Marvin Krislov said. “It’s helped people retire in a way that preserves their dignity and gives them some extra money, and it helps the institution in that it allows for predictability.”
Related: “An emphasis on adult employment“.
She wrote in the book that she was convinced “that a large part of the answer to poor schooling in this country is to understand what strong preparation for teachers looks like and can do, and to undertake policy changes needed to ensure that all teachers can have access to such preparation.”
She told me that maybe a quarter of education schools in the U.S. had programs of that quality. Many are OK, but not at that level. And some should not be in the business. She said there should be minimum requirements for the quality of teacher education programs.
But, she added, “If there’s been a lot of teacher bashing, there’s been even more teacher education bashing.” Don’t count her in on that. Do count her in on standing up for teachers, for good teacher training and for supporting teachers so they have the most positive impact.
Related: National Council on Teacher Quality and a focus on adult employment.
The primary point on which we seem to disagree is how best to obtain such highly qualified middle school math teachers. It is my strong belief that the MMSD will never succeed in fully staffing all of our middle schools with excellent math teachers, especially in a timely manner, if the primary mechanism for doing so is to provide additional, voluntary math ed opportunities to the District’s K-8 generalists who are currently teaching mathematics in our middle schools. The District currently has a small number of math-certified middle school teachers. It undoubtedly has some additional K-8 generalists who already are or could readily become terrific middle school math teachers with a couple of hundred hours of additional math ed training. However, I sincerely doubt we could ever train dozens of additional K-8 generalists to the level of content knowledge necessary to be outstanding middle school math teachers so that ALL of our middle school students could be taught mathematics by such teachers.
Part of our disagreement centers around differing views regarding the math content knowledge one needs to be a highly-qualified middle school math teacher. As a scientist married to a mathematician, I don’t believe that taking a couple of math ed courses on how to teach the content of middle school mathematics provides sufficient knowledge of mathematics to be a truly effective teacher of the subject. Our middle school foreign language teachers didn’t simply take a couple of ed courses in how to teach their subject at the middle school level; rather, most of them also MAJORED or, at least, minored in the subject in college. Why aren’t we requiring the same breathe and depth of content knowledge for our middle school mathematics teachers? Do you really believe mastery of the middle school mathematics curriculum and how to teach it is sufficient content knowledge for teachers teaching math? What happens when students ask questions that aren’t answered in the teachers’ manual? What happens when students desire to know how the material they are studying relates to higher-level mathematics and other subjects such as science and engineering?
A Supreme Court decision coming by the end of June could be devastating for organized labor. The case, Friedrichs v. California Teachers Association (CTA), challenges a 1977 ruling allowing public-sector unions to charge nonmembers covered by union contracts mandatory fees to pay for the costs of collective bargaining. The lead plaintiff, Rebecca Friedrichs, is an elementary school teacher. She claims that being forced to pay money to California’s politically powerful and overwhelmingly Democratic teachers’ union as a condition of her employment violates her First Amendment rights.
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
In a city with the greatest economic inequity in the country and with a rapidly expanding charter school now serving nearly half of the city’s students, D.C. is one of the few traditional public school districts in the country with enrollment gains and is on track to exceed 50,000 students by 2017. Much of the credit goes to Henderson’s leadership.
STRONG LEADERSHIP
Henderson’s relentless energy and boundless public praise in support of her teachers and principals has created positive morale and considerable buy-in among classroom educators to what is one of the most ambitious reform agendas in the country.She has also maintained labor peace even while driving an aggressive teacher quality agenda that links evaluation and compensation in part to student growth, something few other urban superintendents can claim.
Madison rejected a proposed IB charter school several years ago.
“An emphasis on adult employment“.
Wisconsin’s stürm and drang over “Act 10” is somewhat manifested in Madison. Madison’s government schools are the only Wisconsin District, via extensive litigation, to still have a collective bargaining agreement with a teacher union, in this case, Madison Teachers, Inc.
The Madison School Board and Administration are working with the local teachers union on a new “Handbook”. The handbook will replace the collective bargaining agreement. Maneuvering over the terms of this very large document illuminates posturing and power structure(s) in our local government schools.
Madison Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham wrote recently (September 17, 2015 PDF):
The Oversight group was able to come to agreement on all of the handbook language with the exception of one item, job transfer in the support units. Pursuant to the handbook development process, this item was presented to me for review and recommendation to the Board. My preliminary recommendation is as follows:
Job Transfer for all support units
(See Pages 151, 181, 197, 240, 261)Superintendent Recommendation
That the language in the Handbook with regard to transfer state as follows: Vacancies shall first be filled by employees in surplus. The District has the right to determine and select the most qualified applicant for any position. The term applicant refers to both internal and external candidates for the position.The District retains the right to determine the job qualifications needed for any vacant position. Minimum qualifications shall be established by the District and equally applied to all persons.
Rationale/Employee Concern
Rationale:
It is essential that the District has the ability to hire the most qualified candidate for any vacant position—whether an internal candidate or an external candidate. This language is currently used for transfers in the teacher unit. Thus, it creates consistency across employee groups.
By providing the District with the flexibility of considering both internal and external candidates simultaneously the District can ensure that it is hiring the most qualified individual for any vacant position. It also gives the District opportunities to diversify the workforce by expanding the pool of applicants under consideration. This change would come with a commitment to provide stronger development opportunities for internal candidates who seek pathways to promotion.Employee Concern:
The existing promotional system already grants a high degree of latitude in selecting candidates, including hiring from the outside where there are not qualified or interested internal applicants. It also helps to develop a cadre of dedicated, career-focused employees.
September 24, 2015 Memo to the Madison government schools board of education from Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham:
To: Board of Education
From: Jennifer Cheatham, Superintendent of Schools
RE: Update to Handbook following Operations Work GroupThe Operations Work Group met on Monday September 21, 2015. Members of the Oversight Group for development of the Employee Handbook presented the draft Employee Handbook to the Board. There was one item on which the Oversight Group was unable to reach agreement, the hiring process for the support units. Pursuant to the handbook development process, this item was presented to me for review and recommendation to the Board. There was discussion around this item during the meeting and, the Board requested that members of the Oversight Group meet again in an attempt to reach consensus.
Per the Board’s direction, District and employee representatives on the Oversight Group came together to work on coming to consensus on the one remaining item in the Handbook. The group had a productive dialog and concluded that with more time, the group would be able to work together to resolve this issue. Given that the Handbook does not go into effect until July1, 2016, the group agreed to leave the issue regarding the hiring process for the support units unresolved at this point and to include in the Handbook the phrase “To Be Determined” in the applicable sections. As such, there is no longer an open item. When you vote on the Handbook on Monday, the section on the “Selection Process” in the various addenda for the applicable support units will state “To Be Determined” with an agreement on the part of the Oversight Group to continue to meet and develop final language that the Board will approve before the Handbook takes effect in the 2016-17 school year.
Current Collective Bargaining Agreement (160 page PDF) Wordcloud:

Proposed Employee Handbook (304 Page PDF – 9.21.2015 slide presentation) Wordcloud:

Background:
1. The Wisconsin Institute for Law and Liberty has filed suit to vacate the Madison government schools collective bargaining agreement with Madison Teachers, Inc.
2. Attorney Lester Pines has spent considerable time litigating Act 10 on behalf of Madison Teachers, Inc. – with some success.
3. The collective bargaining agreement has been used to prevent the development of non-Madison Government school models, such as independent charter, virtual and voucher organizations. This one size fits all approach was manifested by the rejection [Kaleem Caire letter] of the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB charter school.
4. Yet, Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results, despite spending more than $15,000 per student annually. See also “What’s different, this time?”
5. Comparing Madison, Long Beach and Boston government school teacher union contracts. Current Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham has cited Boston and Long Beach government schools as Districts that have narrowed the achievement gap. Both government districts offer a variety of school governance models, which is quite different than Madison’s long-time “one size fits all approach”.
6. Nearby Oconomowoc is paying fewer teachers more.
7. Minneapolis teacher union approved to authorize charter schools.
8. Madison Teachers, Inc. commentary on the proposed handbook (Notes and links). Wordcloud:
9. A rather astonishing quote:
“The notion that parents inherently know what school is best for their kids is an example of conservative magical thinking.”; “For whatever reason, parents as a group tend to undervalue the benefits of diversity in the public schools….”
– Madison School Board member Ed Hughes.
10. 1,570,000 for four senators – WEAC.
11. Then Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 speech to the Madison Rotary Club:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Schwerpunkt via wikipedia.
Fortunately, the tides in education policy are finally pushing the system to realize the importance of its teachers. Test-based accountability is forcing districts to look past their myopic focus on enrollments, course offerings, and graduation rates and to take students’ academic performance more seriously. And because modern research has shown that teachers are the most important school-level factor influencing student achievement, many of today’s most prominent reform efforts focus on ensuring there is an effective, expert teacher in every classroom.
If schools and districts intend to fulfill the mandate to boost student achievement, they will need to adopt new strategies that place paramount emphasis on recruiting and retaining the best teachers. This shift in district strategy should then put individual teachers in a position to negotiate their salaries and working conditions based on the value their individual expertise brings to their schools.
But unfortunately, even in this era of increased accountability, many districts still operate as if teachers are commodities. Instead of recruiting strategically from the best teacher preparation programs in the country, they take the teachers that the nearest regional state school has to offer. Instead of putting together competitive and attractive salary and benefit packages and then working in the early spring to attract the best teachers to their schools, they wait until just before the start of the school year to frantically fill their open teaching slots. Instead of giving principals control over staffing so that they can build great faculty teams across multiple years, they move teachers around capriciously from one year to the next—and sometimes during the middle of the school year—and prioritize allocation targets over effectiveness. Instead of working with individual teachers to find roles where their particular areas of expertise are most relevant, districts often shift teachers at the last minute to grade levels or subject areas that are technically within their certification but realistically outside the domains where those teachers are most experienced, passionate, and able to excel.
Related: a focus on adult employment.
Just in time for the new school year, today guest host Mike Wagner talks with UW professor Robert Asen on his new publication, “Democracy, Deliberation, and Education,” on the difficult decisions school boards have to make the democratic process behind it.
From Penn State University Press, “Democracy, Deliberation, and Education” looks at three Wisconsin school boards and democracy at the local level that occurs to make decisions for school districts.
Asen is a Professor of Communication Arts at the University of Wisconsin- Madison Robert, with a focus in public policy debate, public sphere studies, and rhetoric and critical theory, and the way political and economic inequalities interact with relations of power to shape public discourse.
I believe Professor Asen overstates the role and applied power of most school boards. While they are certainly capable of great change, Madison’s experiences is illustrative. In general, the Madison School Board has operated as a go along, get along governing body. One example: Madison’s long term disastrous reading results: 2005, 2013 editions…
A “focus on adult employment“.
Possible de-regulation of Wisconsin charter school authorizations has lead to a bit of rhetoric on the state of Madison’s schools, their ability to compete and whether the District’s long term, disastrous reading results are being addressed. We begin with Chris Rickert:
Madison school officials not eager to cede control of ‘progress’:
Still, Department of Public Instruction student achievement data suggest independent charter schools overseen by UW-Milwaukee since 1999 provide better educations than Milwaukee public schools.
And if the UW System gets the authority to create a new office for approving charter schools in Madison, it wouldn’t be the first time a local or state government function was usurped by unelected and allegedly unaccountable people at higher levels of government who are aiming to eliminate injustice. U.S. presidents sent federal authorities to the South during the civil rights era. Appointed state and federal judges have been asked to overturn local and state abortion-related ordinances and laws. Last year, a federal judge struck down Wisconsin’s voter-approved gay marriage ban.
The injustice in the Madison School District is, of course, its decades-long failure to close achievement gaps between white students and students of color and between middle class and poor students.
Cheatham told this newspaper that “we are making progress on behalf of all children.”
Apparently, the district feels it should be the only educational organization in Madison with the opportunity to make such progress.
That’s because control over education might be as high a priority for the district as improving education.
It is a worthy debate, for there is little doubt that the full school board, its superintendent, its teachers union, the Democratic Party, Mayor Soglin, and probably the majority of Madisonians share Ed’s sentiments. For the festive rest of us, the white lab coats at the Blaska Policy Research Werkes have developed an alternative Top Ten, dedicated to the late Larry “Bud” Melman.
1) Attack the motives of your adversaries. “What’s tougher is buying into [the] interpretation that the Joint Finance Committee Republicans are the good guys here, struggling mightily to do what’s right for our kids,” Ed Hughes says. “My much different interpretation is that the Joint Finance proposal is simply another cynical attack on our neighborhood public schools and is motivated both by animus for Madison and by an unseemly obsession with privatizing public education, particularly in the urban areas of our state.”
Unseemly! Particularly in urban Milwaukee, where the public school district as a whole has received a failing grade from the Department of Public Instruction, and in Madison, with a yawning chasm between black and white student achievement.
2) Nobody asked our permission. Ed complains that nobody consulted MMSD about its “strategies for enhancing student achievement, promising practices, charter school philosophy, or anything else.” Um, sometimes results speak louder than pretty words on paper, Ed.
Madison School Board Member Ed Hughes:
So we have two contrasting interpretations of the proposal. As it happens, I am right and Rickert is wrong. To help Rickert see the error of his ways, here’s a Letterman-like list of the top ten reasons why the Joint Finance proposal to establish a so-called “Office of Educational Opportunity” within the office of the UW System President is a cynical ploy to stuff Madison with charter schools for the sake of having more charter schools rather than a noble effort to combat injustice:
This points up one of the frustrating aspects of trying to follow school issues in Madison: the recurring feeling that a quoted speaker – and it can be someone from the administration, or MTI, or the occasional school board member – believes that the audience for an assertion is composed entirely of idiots.
Finally, then Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman, in 2009:
Zimman’s talk ranged far and wide. He discussed Wisconsin’s K-12 funding formula (it is important to remember that school spending increases annually (from 1987 to 2005, spending grew by 5.10% annually in Wisconsin and 5.25% in the Madison School District), though perhaps not in areas some would prefer.
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Madison has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
In an irony typical of politics, then, the right’s intellectual critique of public-sector unions is illustrated by the ease with which police unions have bridled and ridden actual right-wing politicians. Which in turn has left those unions in a politically enviable position, insulated from any real pressure to reform.
Yet reform is what they need. There are many similarities between police officers and teachers: Both belong to professions filled with heroic and dedicated public servants, and both enjoy deep reservoirs of public sympathy as a result. But in both professions, unions have consistently exploited that sympathy to protect failed policies and incompetent personnel.
A focus on “adult employment“.
For the past four months, a group of Kentucky teenagers has been working to make a one-sentence change to a state law. In the history of student activism, this is not a big ask. They want local school boards to have the option—just the option—of including a student on the committees that screen candidates for superintendent jobs.
That’s it. They aren’t asking to choose the superintendent; the elected school board does that. They just want to have one student sit among the half-dozen adults (including two teachers, a parent, and a principal) who help vet candidates and make recommendations to the board.
“I thought everyone would view it as a no-brainer,” said Nicole Fielder, 18. She said this on Tuesday from Frankfort, the state’s capital, where she was missing classes in order to advocate—for the sixth time—for this bill.
Policymakers should be begging students to serve on committees and school boards, not the other way around. That’s because students are their secret weapons: Kids can translate abstract policy into real life with a speed and fluency that no adult can match.
Related: an emphasis on adult employment.
This is not the end of the story for vouchers, however. In both Milwaukee and Washington, voucher schemes get similar results to the public schools but with much less money. Under the DC scheme, each voucher is worth $8,500 a year, compared with $17,500 to educate a child in the public school system. In Milwaukee the difference is smaller but still amounts to several thousand dollars. Another consistent finding from voucher schemes is that parents like being given a choice, which explains why vouchers, once granted, are hard to take away.
Though Milwaukee’s experience overall has been mixed it still has lessons for elsewhere. If one includes private schools, charter schools and open enrolment at public schools (which means parents may enroll their children in a school that is not in the neighbourhood where they live), around 40% of parents in Milwaukee exercise some kind of choice over their children’s education, an unusually high share. With so much competition, it is hard for any school to grow complacent. There are good public, private and charter schools and bad ones, too. Some private schools do very well with poor black and Hispanic children, others fail them and yet manage to stay in business, which suggests that even with lots of parents choosing there is a need for an authority than can close the bad schools down.
The proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School, rejected by a majority of the Madison School Board.
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
An interview with Henry Tyson.
A focus on adult employment.
“That charter authorizer is without accountability, if you will, to the voter in any way,” she said. “And so why would we want to do that? That’s what I would like explained to me. Why would that be a good thing for the state of Wisconsin? Honestly, I can’t fathom what the justification would be other than if I’m one of the big chains (of charter schools) that wants leverage into Wisconsin.”
Madison School Board member Ed Hughes wrote against the proposal on his education blog last week, saying the proposal allows new authorizers to “operate with a free hand in the state’s largest urban areas.”
Walker included a similar proposal in his 2013-15 budget but it was pulled out. Sen. Alberta Darling, R-River Hills, also has proposed similar legislation in the past. She said in an interview Tuesday that more communities than Milwaukee and Racine should have the option of an independent charter school.
She pointed to Madison Preparatory Academy, an independent charter school proposed by the Urban League of Greater Madison geared toward low-income, minority students that was voted down by the School Board in 2011.
“In some cases there will be opportunities where school boards say, ‘No, we don’t want that,’ as Madison did, and it seems there should be another option for those families,” she said.
Related:
The proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School, rejected by a majority of the Madison School Board.
Madison’s long term, disastrous reading results.
An interview with Henry Tyson.
A focus on adult employment.
Talk about putting your best foot forward only to get it stomped on.
Last week, in response to an open records request from this newspaper, the UW System released internal emails that showed System President Ray Cross throwing UW-Eau Claire chancellor James Schmidt under the bus for sending him “candid” ideas for how to cope with Gov. Scott Walker’s plan to cut $300 million from the System’s state aid in exchange for giving the System more autonomy.
“Incredible logic!!” Cross writes in an email forwarding Schmidt’s ideas to two other System administrators. “I find this most troubling!!! I thought Jim was a bit more thoughtful than this.”
As a mere civilian, I thought Schmidt’s ideas had merit. And after spending 25 minutes talking to him on the phone, I think the System would do well to hire more people like him.
Schmidt laid out 10 suggestions in all, with five more concerning initiatives specific to his campus.
They range from seeking different employee health care insurers, to creating links between four-year campuses and their nearby two-year campuses, to cutting down on administrative overhead, to shrinking and decentralizing System administration.
Cross, who declined my interview request, was particularly irked by what he called Schmidt’s proposed “elimination of the System” and his call for even greater autonomy for System campuses.
Schmidt didn’t back down from the value of his ideas or from the importance of coming up with them, although he acknowledged that on second look, some, like combining administrative functions at four-year campuses and their nearby two-year feeder schools, might not provide as much savings as he initially thought.
A focus on “adult employment“.
This is Madison. I learned that phrase when I moved here from Green Bay in 1992.
It means that the elites who drive the politics and the predominate culture are more liberal or “progressive” than backward places out state.I knew I was in Madison as a reporter when parents and activists were fighting over whether to have “Sarah Has Two Mommies” posters in a grade school library. Concerned parents weakly stated at a public hearing that first-graders were too young to understand sexuality of any kind.
Activists at the public meeting said the children needed to understand tolerance. One conservative parent said: “Why don’t we vote by secret ballot?” An activist said, “No, we want a consensus.”
The Madison School District official who was presiding agreed, and the controversial posters stayed on the library walls. This is Madison.
Now we have the Madison School Board. It has been historically run by the teacher’s union. The same was true after Gov. Scott Walker’s Act 10 was passed, strictly limiting collective bargaining for public employees.
Three weeks before the state Supreme Court would rule on the constitutionality of the law, the union-owned School Board rushed through a teacher’s contract that largely ignored Act 10. Unlike any other school district in the state, the contract made sure Madison teachers were not required to share the cost of their health insurance premiums. Unlike any other school district, Madison collects union dues from teacher paychecks for its leader, John Matthews.
By the way, I would not want him in a dark alley with me.
The problem is the Madison School District has a projected budget shortfall for 2015-2016 of $12 million to $20 million, according to last week’s State Journal. About $6 million could be saved by making aggressive health care costs, including requiring staff to contribute toward insurance premiums, renegotiating contracts with health care providers, and making plan changes. That’s according to Michael Barry, assistant superintendent of business services.
In fact, the district spends about $62 million on employee health care costs, which are expected to grow by 8.5 percent next school year. Shockingly, Madison School Board member Ed Hughes said: “If we’re talking about taking not a scalpel, but a machete to our programs given the cuts we’ll make because we’re the only school district in the state that’s unwilling to ask employees to contribute to their health insurance, I think that would be an impression that we would deservedly receive ridicule for.”
Even board member Mary Burke said: “We would be irresponsible to the community where basically 99 percent of the people pay contributions to health care” if the board made up the savings with cuts to staff and heath care.
So now what? The contract expires in June 2016. Conservative blogger David Blaska sued to force Madison to live under Act 10. A local judge ruled last week Blaska did have standing as a taxpayer to carry out his lawsuit as he is joined by The Wisconsin Institute of Law and Liberty.
Madison teacher’s union leader John Matthews said by making employees contribute to health care premiums, the district is effectively asking them to pay for iPads and administrators. Huh?
Todd Berry of the Wisconsin Taxpayers Alliance told me 90 percent of state cuts to education were covered by savings offered to school districts under Act 10 by changing work rules, by employee contributions to retirement and health insurance premiums, and by altering health plans.
That might fly for the rest of the state, but then again, this is Madison.
Much more on benefits and the Madison School District and Act 10.
A focus on “adult employment“.


Tap to view larger versions.
Deirdre Hargrove-Krieghoff:
In support of the continued work of developing a thriving workforce, the HR team conducted a survey of the 10 largest districts in the State of Wisconsin as well as districts in Dane County to provide a picture of our current compensation standing. It is our intent to develop and maintain a competitive salary structure for all of our employees, and we are committed to creating a structure that attracts the highest performers and is equity based.
The following information was developed for a specific budget-related purpose – to help determine, on a macro level, where the district stands relative to comparables for principal and teacher salaries, and whether a significant budget allowance (additional funding) is needed in 2015-16 for the specific purpose of adjusting to market comparables.
Please note:
When reviewing the data for Principals and Assistant Principals, it is illustrating the range that a candidate could make entering the district. For the Teacher base it shows the starting range for a beginning teacher. Maximum salaries are not listed, as most districts that reported are in the process of restructuring their salary schedules for teachers.Approximately 80 out of the 320 of teachers hired annually actually come in at the base step of $37,263.The data suggests that compared to other districts represented, MMSD is mid to low in salary placement for Assistant Principals and Teachers and mid to high for salary placement for Principals.
Some districts represented, have moved away from the traditional approach of funding salary steps and tracks within their schedules and are front loading their schedule to be more competitive, this shift may cause their ranges to be higher than MMSD.
Presumably, a real comparison might include total compensation and outcomes, not to mention qualification differences.
Notes and links:
Madison School Board Member Ed Hughes, writing in 2005:
“This points up one of the frustrating aspects of trying to follow school issues in Madison: the recurring feeling that a quoted speaker – and it can be someone from the administration, or MTI, or the occasional school board member – believes that the audience for an assertion is composed entirely of idiots.”
Comparing Madison and other District approaches to teacher benefits. Staffing compared: Madison, Long Beach & Boston.

In 2013, Madison Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham said “What will be different, this time“? The Superintendent further cited Long Beach and Boston as beacons in her Rotary speech.
However, based on recently released 2015-2016 budget slides (PDF) and Molly Beck’s summary, it appears that the same service, status quo governance model continues, unabated.
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situatio
I am so sick and tired of hearing that “xyz” person doesn’t have teaching experience, or is a “non-educator” and therefore can’t possibly have a worthwhile view on the education of our kids.
We are not applying for teaching jobs. We are not writing curriculum (standards are not curriculum). We do however, pay for education and that comes with the responsibility to ensure our money is spent effectively.
Every single person in this country helps to pay for education. Every single person has the right to question if their money is being spent properly, when the results they see are not ideal.
Related: A focus on adult employment.
The arrival of Thanksgiving means local homeowners will soon see their annual property tax bills. The chart below compares Madison area homes sold in 2012, ranging in price from $239,900 to $255,000
Tap to view a larger version. Excel. A Middleton home’s property tax burden is about 13% less than a similar property in Madison (based on 2012 sales and 2013 assessments and payments). The Madison home noted in this analysis was assessed $1100 higher than the Middleton property. Taxes, spending growth and academic achievement over time are surely worth a much deeper dive.
SIS notes and links on Madison area property taxes.

Worth reading: Wisconsin Taxpayers Alliance:
The property tax is Wisconsin’s largest, oldest, and most confusing tax. At least five governments use the tax, and two different methods of valuing property are used to distribute taxes among property owners. One source of confusion arises when tax rates and levies move in opposite directions, a common occurrence over the past 20 years. In addition, property owners are often unaware of how changing property values, both within a municipality and among municipalities, can cause individual property tax bills to rise, even when levies are “frozen.”
Madison Mayor Paul Soglin:”(Property Tax) Delinquencies 30% more than we expect“.
Spending and adult employment.
Property tax growth (along with other tax sources) is a manifestation of the challenges we see in our k-12 school districts.
Kevin Roose interviews Wisconsin native Marc Andreesen:
But let’s just project forward. In ten years, what if we had Math 101 online, and what if it was well regarded and you got fully accredited and certified? What if we knew that we were going to have a million students per semester? And what if we knew that they were going to be paying $100 per student, right? What if we knew that we’d have $100 million of revenue from that course per semester? What production budget would we be willing to field in order to have that course?
You could literally hire James Cameron to make Math 101. Or how about, let’s study the wars of the Roman Empire by actually having a VR [virtual reality] experience walking around the battlefield, and then like flying above the battlefield. And actually the whole course is looking and saying, “Here’s all the maneuvering that took place.” Or how about re-creating original Shakespeare plays in the Globe Theatre?
Latest spending increase plans while long term disastrous reading results continue.
And, a focus on adult employment.
Democrat Mary Burke told education officials Friday she would fight as governor to stop the expansion of voucher schools but would leave alone the long-standing program in Milwaukee.
“This is something that may sound like a good political sound bite, but it is bad public policy,” she said of expanding the voucher program.
“I think it is the thing that most threatens a vision of a public school system and an education for students in Wisconsin to be the leaders in our country.”
Her comments drew applause from her audience at a Wisconsin Association of School District Administrators conference at the Concourse Hotel in Madison.
For more than 20 years, the state has run a program in Milwaukee that allows certain students to attend religious schools and other private institutions at taxpayer expense.
In recent years, a similar program was created for eastern Racine County and a more limited one for the rest of the state. Republican Gov. Scott Walker has championed those programs and said he wants to expand the statewide one.
Burke said she would leave alone the Milwaukee program, but indicated she wanted to halt the statewide voucher program.
“For the rest of the state, vouchers have no place and they are a drain on our public school system at a point at which we have very, very limited resources,” she said. “So I do not see the research after 20 years in Milwaukee that says this is a way of improving student learning throughout the state.
Related:
Milwaukee Public Schools Spend More on a Vacant Building.
I have been asked for my “single best idea for reforming K-12 education”. When you only have one shot, you want to make it count. So I thought I would share my idea here, in case anyone has a brighter insight.
Root cause: factory model of management
To decide what is the single best idea for reforming K-12 education, one needs to figure out what is the biggest problem that the system currently faces. To my mind, the biggest problem is a preoccupation with, and the application of, the factory model of management to education, where everything is arranged for the scalability and efficiency of “the system”, to which the students, the teachers, the parents and the administrators have to adjust. “The system” grinds forward, at ever increasing cost and declining efficiency, dispiriting students, teachers and parents alike.Given that the factory model of management doesn’t work very well, even in the few factories that still remain in this country, or anywhere else in the workplace for that matter, we should hardly be surprised that it doesn’t work well in education either.
But given that the education system is seen to be in trouble, there is a tendency to think we need “better management” or “stronger management” or “tougher management”, where “management” is assumed to be the factory model of management. It is assumed to mean more top-down management and tighter controls, and more carrots and sticks. It is assumed to mean hammering the teachers who don’t perform and ruthlessly weeding out “the dead wood”. The thinking is embedded in Race to the Top and No Child Left Behind.
These methods are known to be failing in the private sector, because they dispirit the employees and limit their ability to contribute their imagination and creativity; they frustrate customers, and they are killing the very organizations that rely on them. So why should we expect anything different in the education sector?
Much more on a focus on adult employment, here.
Teachers are some of our most dedicated public servants. Many inspiring educators have changed lives for the better in Madison’s public schools. But their union is a horror.
Madison Teachers Inc. has been a bad corporate citizen for decades. Selfish, arrogant, and bullying, it has fostered an angry, us-versus-them hostility toward parents, taxpayers, and their elected school board.
Instead of a collaborative group of college-educated professionals eager to embrace change and challenge, Madison’s unionized public school teachers comport themselves as exploited Appalachian mine workers stuck in a 1930s time warp. For four decades, their union has been led by well-compensated executive director John A. Matthews, whom Fighting Ed Garvey once described (approvingly!) as a “throwback” to a different time.
From a June 2011 Wisconsin State Journal story:
[Then] School Board member Maya Cole criticized Matthews for harboring an “us against them” mentality at a time when the district needs more cooperation than ever to successfully educate students. “His behavior has become problematic,” Cole said.
For years, Madison’s school board has kowtowed to Matthews and MTI, which — with its dues collected by the taxpayer-financed school district — is the most powerful political force in Dane County. (The county board majority even rehearses at the union’s Willy Street offices.)
Erin Richards & Patrick Marley
Joe Zepecki, Burke’s campaign spokesman, said in an email Wednesday that he couldn’t respond officially because Burke has made clear that her campaign and her duties as a School Board member are to be kept “strictly separate.” However, on the campaign trail, Burke says she opposes Act 10’s limits on collective bargaining but supports requiring public workers to pay more for their benefits, a key aspect of the law.
John Matthews, executive director of Madison Teachers Inc., said the contracts were negotiated legally and called the legal challenge “a waste of money and unnecessary stress on district employees and the community.”
The lawsuit came a day after the national leader of the country’s largest union for public workers labeled Walker its top target this fall.
“We have a score to settle with Scott Walker,” Lee Saunders, the union official, told The Washington Post on Tuesday. Saunders is the president of the American Federation of State, County and Municipal Employees. A spokeswoman for Saunders did not immediately return a call Wednesday.
AFSCME has seen its ranks in Wisconsin whither since Walker approved Act 10. AFSCME and other unions were instrumental in scheduling a 2012 recall election to try to oust Walker, but Walker won that election by a bigger margin than the 2010 race.
“When the union bosses say they ‘have a score to settle with Scott Walker,’ they really mean Wisconsin taxpayers because that’s who Governor Walker is protecting with his reforms,” Walker spokeswoman Alleigh Marré said in a statement.
Kenosha School District over teacher contracts after the board approved a contract with its employees.
In Madison, the School District and School Board “are forcing their teachers to abide by — and taxpayers to pay for — an illegal labor contract with terms violating Act 10 based upon unlawful collective bargaining with Madison Teachers, Inc.,” a statement from WILL said.
Blaska, a former member of the Dane County Board who blogs for InBusiness, said in addition to believing the contracts are illegal, he wanted to sue MTI because of its behavior, which he called coercive and bullyish.
“I truly believe that there’s a better model out there if the school board would grab for it,” Blaska said.
MTI executive director John Matthews said it’s not surprising the suit was filed on behalf of Blaska “given his hostile attacks on MTI over the past several years.”
“WILL certainly has the right to challenge the contracts, but I see (it as) such as a waste of money and unnecessary stress on district employees and the community,” said Matthews, adding that negotiating the contracts “was legal.”
In August, the Wisconsin Supreme Court ruled Act 10 constitutional after MTI and others had challenged its legality. At the time, union and district officials said the contracts that were negotiated before the ruling was issued were solid going forward.
Under Act 10, unions are not allowed to bargain over anything but base wage raises, which are limited to the rate of inflation. Act 10 also prohibits union dues from being automatically deducted from members’ paychecks as well as “fair share” payments from employees who do not want to be union members.
Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham said Wednesday the district has not yet received notification of the suit being filed.
“If and when we do, we’ll review with our team and the Board of Education,” she said.
School Board vice president James Howard said the board “felt we were basically in accordance with the law” when the contracts were negotiated and approved.
A lawsuit targeting the Madison School District and its teachers union is baseless, Madison School Board member and Democratic gubernatorial candidate Mary Burke said Thursday.
The lawsuit filed Wednesday by the conservative nonprofit Wisconsin Institute for Law & Liberty on behalf of well-known blogger David Blaska alleges the school district, School Board and Madison Teachers Inc. are violating Act 10, Republican Gov. Scott Walker’s signature law that limits collective bargaining.
The union has two contracts in effect through June 2016. Burke voted for both of them.
“I don’t think there is a lot of substance to it,” Burke said of the lawsuit. “Certainly the board, when it negotiated and approved (the contracts), it was legal then and our legal counsel says nothing has changed.”
At any rate, Esenberg said, he doesn’t consult with Grebe, Walker or anyone else in deciding what cases to take on.
“The notion that we think Act 10 is a good idea because it frees the schools from the restraints of union contracts and gives individual employees the right to decide whether they want to support the activities of the union — that shouldn’t surprise anyone,” Esenberg said.
WILL is not likely to prevail in court, Marquette University Law School professor Paul Secunda told the Wisconsin State Journal. “They negotiated their current contract when the fate of Act 10 was still up in the air,” said Secunda, who also accused Esenberg of “trying to make political points.”
Esenberg contends the contract always was illegal.
The school board, district and union knew they could not negotiate anything more than wage increases based on inflation under the law, the lawsuit alleges. Despite the institute’s warnings, they began negotiations for a new 2014-15 contract in September 2013 and ratified it in October. What’s more, they began negotiating a deal for the 2015-16 school year this past May and ratified it in June, according to the lawsuit.
Both deals go beyond base wage changes to include working conditions, teacher assignments, fringe benefits, tenure and union dues deductions, the lawsuit said.
Taxpayers will be irreparably harmed if the contracts are allowed to stand because they’ll have to pay extra, the lawsuit went on to say. It demands that a Dane County judge invalidate the contracts and issue an injunction blocking them from being enforced.
“The Board and the School District unlawfully spent taxpayer funds in collectively bargaining the (contracts) and will spend substantial addition(al) taxpayer funds in implementing the (contracts),” the lawsuit said. “The (contracts) violate the public policy of Wisconsin.”
2009 Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman speech to the Madison Rotary Club:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Related:
WEAC (Wisconsin Teacher Union Umbrella): 4 Senators for $1.57M.
Understanding the current union battles requires a visit to the time machine and the 2002 and the Milwaukee County Pension Scandal. Recall elections, big money, self interest and the Scott Walker’s election in what had long been a Democratic party position.
The 2000-2001 deal granted a 25% pension “bonus” for hundreds of veteran county workers. Another benefit that will be discussed at trial is the controversial “backdrop,” an option to take part of a pension payment as a lump-sum upon retirement.
Testimony should reveal more clues to the mysteries of who pushed both behind the scenes.
So what does it mean to take a “backdrop?”
“Drop” refers to Deferred Retirement Option Program. Employees who stay on after they are eligible to retire can receive both a lump-sum payout and a (somewhat reduced) monthly retirement benefit. Employees, upon leaving, reach “back” to a prior date when they could have retired. They get a lump sum equal to the total of the monthly pension benefits from that date up until their actual quitting date. The concept was not new in 2001, but Milwaukee County’s plan was distinguished because it did not limit the number of years a worker could “drop back.” In fact, retirees are routinely dropping back five years or more, with some reaching back 10 or more years.
That has allowed many workers to get lump-sum payments well into six figures.
Former deputy district attorney Jon Reddin, at age 63, collected the largest to date: $976,000, on top of monthly pension checks of $6,070 each.
And, Jason Stein:
The Newsline article by longtime legal writer Stuart Taylor Jr. alleges that Chisholm may have investigated Walker and his associates because Chisholm was upset at the way in which the governor had repealed most collective bargaining for public employees such as his wife, a union steward.
The prosecutor is quoted as saying that he heard Chisholm say that “he felt that it was his personal duty to stop Walker from treating people like this.”
The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel has requested to speak with the former prosecutor through Taylor and has not yet received an answer.
In a brief interview, Chisholm denied making those comments. In a longer statement, an attorney representing Chisholm lashed out at the article.
“The suggestion that all of those measures were taken in furtherance of John Chisholm’s (or his wife’s) personal agenda is scurrilous, desperate and just plain cheap,” attorney Samuel Leib said.
Matthew Richmond (PDF), via several kind readers:
Why do American public schools spend more of their operating budgets on non-teachers than almost every other country in the world, including nations that are as prosperous and humane as ours? We can’t be certain. But we do know this:
» The number of non-teachers on U.S. school payrolls has soared over the past fifty years, far more rapidly than the rise in teacher numbers. And the amount of money in district budgets consumed by their salaries and benefits has grown apace for at least the last twenty years.Underneath the averages and totals, states and districts vary enormously in how many non-teachers they employ. Why do Illinois taxpayers pay for forty staff per thousand pupils while Connecticut pays for eighty-nine? Why does Orange County, Florida (Orlando) employ eleven teacher aides per thousand students when Miami-Dade gets by with seven?
What accounts for such growth—and such differences? We don’t know nearly as much as we’d like on this topic, but it’s not a total mystery. The advent and expansion of special education, for example, obviously gave rise to substantial demand for classroom aides and specialists to address
the needs of youngsters with disabilities. The widening of school duties to include more food service, health care, and sundry other responsibilities accounts for more.But such additions to the obligations of schools are not peculiar to the United States and they certainly cannot explain big staffing differences from place to place within our country.
Retired Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 speech to the Madison Rotary Club:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
It’s not a good idea for the Madison School District to extend its labor contract with teachers through the 2015-2016 school year without renegotiating it, says school board member Ed Hughes.
Hughes wants Madison School District administrators — especially school principals — to have the ability to offer jobs to the best teacher candidates before they are snapped up by other districts.
One way to accomplish that would be to drop a labor contract provision giving Madison teachers the opportunity to transfer into open positions before external candidates can be offered those jobs, Hughes says.
“To take the collective bargaining agreement in its current form and just change the date without any discussion, to my mind, is creating a potential impediment to our important efforts to attract a highly qualified and diverse workforce,” Hughes said Tuesday.
Hughes said that a labor contract that includes a “last hired, first fired” provision also hampers efforts to hire teachers with experience in racially and ethnically diverse classrooms.
“Why would someone with 15 years experience in Janesville come to Madison and be the first one on the chopping block if there are layoffs?” he asked. “I’m not proposing a specific solution, but we need to address these issues in a collaborative way so we’re not handcuffing ourselves from bringing in the best teachers.”
Related: Act 10, Madison Teachers, Inc and Ed Hughes.
Emphasizing adult employment: Newark School Reform and retired Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman.
Mr Hughes wrote one of the more forthright quotes on local school matters in 2005:
This points up one of the frustrating aspects of trying to follow school issues in Madison: the recurring feeling that a quoted speaker – and it can be someone from the administration, or MTI, or the occasional school board member – believes that the audience for an assertion is composed entirely of idiots.
Tea leaves: Mr. Hughes was just replaced as President of the Madison School Board. Interestingly, he ran unopposed in three (!) elections. The candor is appreciated, but were there similar comments during the past few years?
The Madison School District (3MB PDF):
Five Priority Areas (just like the “Big 10”) but who is counting! – page 6:
– Common Core
– Behavior Education Plan
– Recruitment and hiring
– New educator induction
– Educator Effectiveness
– Student, parent and staff surveys
– Technology plan
2014-2015 “budget package” 3MB PDF features some interesting changes, beginning on page 92, including:
1. + $986,314 to other Wisconsin public school districts due to Outbound open enrollment growth and $160,000 for Youth Options (page 108)
2. + 5.3% Teacher & Staff Health insurance spending is $44,067,547, or 11% of total spending! (Page 92). Total teacher & staff benefits are $73,248,235 or 18% of total spending. Let’s compare (as best we can):
Madison: 18% budget web page. Note, Madison’s is likely higher than 18% as I did not count all “funds” beyond teachers and certain staff. I’ve sent an email to the District for a complete number.
Middleton: 15.7% 2013-2014 Budget (PDF) Middleton – Cross Plains School District Budget web page. Middleton’s document summarizes spending across all funds (Page 8), something that I did not find in the Madison document (Pages 110-123 summarize aspects of Madison’s spending).
Boston: 14.1% Boston Schools 2013-2014-2015 budget xls file) Boston schools’ budget information.
Long Beach: 15.9% (Long Beach Budget Document (PDF)) Long Beach budget information.
Madison Superintendent Cheatham cited the Boston and Long Beach Schools for “narrowing their achievement gap” during a July, 2013 “What Will be Different This Time” presentation to the Madison Rotary Club.
3. “Educational Services” (Page 96) benefits are $21,581,653 up 4.5%.
4. “Food Services” (Page 98) benefits are $2,446,305, up 4.2%.
5. 10.3%: MSCR’s health insurance cost increase (page 99). MSCR spending and property tax growth (“Fund 80”) has been controversial in the past.
The Madison School District’s per student spending has been roughly constant for several years at about $15,000. Yet, certain budget elements are growing at a rather high rate, indicating an ability to manage effectively by reallocating and raising tax dollars or the presence of a rather fluid budget.
“focused instead on adult employment”
Retired Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 Madison Rotary speech is always worth revisiting:
Zimman’s talk ranged far and wide. He discussed Wisconsin’s K-12 funding formula (it is important to remember that school spending increases annually (from 1987 to 2005, spending grew by 5.10% annually in Wisconsin and 5.25% in the Madison School District), though perhaps not in areas some would prefer.
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Zimman noted that the most recent State of Wisconsin Budget removed the requirement that arbitrators take into consideration revenue limits (a district’s financial condition @17:30) when considering a District’s ability to afford union negotiated compensation packages. The budget also added the amount of teacher preparation time to the list of items that must be negotiated….. “we need to breakthrough the concept that public schools are an expense, not an investment” and at the same time, we must stop looking at schools as a place for adults to work and start treating schools as a place for children to learn.”
The price of budget spaghetti manifests itself via little to no oversight – see legitimate questions on the District’s most recent $26,200,000 maintenance referendum (another tax increase looms). These documents, while reasonably detailed, are impossible to compare to recent budgets.
The demise of Lawrie Kobza’s 2 page “citizen’s budget” will lead to growing cost of living and achievement gaps, including nearby Districts such as Middleton where a comparable homeowner spends 16% less on property taxes.
Under the new contracts clerical and technical employees will be able to work 40-hour work weeks compared to the current 38.75, and based on the recommendation of principals, employees who serve on school-based leadership teams will be paid $20 per hour.
Additionally, six joint committees will be created to give employees a say in workplace issues and address topics such as planning time, professional collaboration and the design of parent-teacher conferences.
Kerry Motoviloff, a district instructional resource teacher and MTI member, spoke at the beginning of the meeting thanking School Board members for their collective bargaining and work in creating the committees that are “getting the right people at the right table to do the right work.”
Cheatham described the negotiations with the union as “both respectful and enormously productive,” adding that based on conversations with district employees the contract negotiations “accomplished the goal they set out to accomplish.”
“Madison is in the minority. Very few teachers are still under contract,” said Christina Brey, spokeswoman for the Wisconsin Education Association Council. Fewer than 10 of 424 school districts in the state have labor contracts with teachers for the current school year, she said Wednesday.
And while Brey said WEAC’s significance is not undermined by the slashed number of teacher contracts, at least one state legislator believes the state teacher’s union is much less effective as a resource than it once was.
Many school districts in the state extended teacher contracts through the 2011-2012 school year after Act 10, Gov. Scott Walker’s law gutting collective bargaining powers of most public employees, was implemented in 2011. The Madison Metropolitan School District extended its teacher contract for two years — through the 2013-2014 school year — after Dane County Judge Juan Colas struck down key provisions of Act 10 in September 2012.
The contract ratified by the members Monday will be in effect until June 30, 2015.
On Thursday, the Wisconsin Institute for Law and Liberty emailed a letter to Cheatham and the School Board warning that a contract extension could be in violation of Act 10.
Richard Esenberg, WILL president, said he sent the letter because “we think there are people who believe, in Wisconsin, that there is somehow a window of opportunity to pass collective bargaining agreements in violation of Act 10, and we don’t think that.”
If the Supreme Court rules Act 10 is constitutional all contracts signed will be in violation of the law, according to Esenberg.
Esenberg said he has not read the contract and does not know if the district and union contracts have violated collective bargaining agreements. But, he said, “I suspect this agreement does.”
The contract does not “take back” any benefits, Matthews says. However, it calls for a comprehensive analysis of benefits that could include a provision to require employees to pay some or more toward health insurance premiums if they do not get health care check-ups or participate in a wellness program.
Ed Hughes, president of the Madison School Board, said that entering into labor contracts while the legal issues surrounding Act 10 play out in the courts was “the responsible thing to do. It provides some stability to do the important work we need to do in terms of getting better results for our students.”
Hughes pointed out that the contract establishes a half-dozen joint committees of union and school district representatives that will take up issues including teacher evaluations, planning time and assignments. The contract calls for mediation on several of the issues if the joint committees cannot reach agreement.
“Hopefully this will be a precursor of the way we will work together in years to come, whatever the legal framework is,” Hughes said.
Matthews, too, was positive about the potential of the joint committees.
Wisconsin Institute for Law & Liberty:
WILL President and General Counsel Rick Esenberg warns, “The Madison School Board is entering a legally-gray area. Judge Colas’ decision has no effect on anyone outside of the parties involved. The Madison School Board and Superintendent Cheatham – in addition to the many teachers in the district – were not parties to the lawsuit. As we have continued to say, circuit court cases have no precedential value, and Judge Colas never ordered anyone to do anything.”
He continued, “If the Madison School District were to collectively bargain in a way that violates Act 10, it could be exposed to litigation by taxpayers or teachers who do not wish to be bound to an illegal contract or to be forced to contribute to an organization that they do not support.” The risk is not theoretical. Last spring, WILL filed a lawsuit against the Milwaukee Area Technical College alleging such a violation.
The Wisconsin Institute for Law & Liberty’s letter to Madison Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham (PDF).
The essential question, how does Madison’s non-diverse K-12 governance model perform academically? Presumably, student achievement is job one for our $15k/student district.
Worth a re-read: Then Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 speech to the Madison Rotary Club:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
To remember the loneliness, the fear and the insecurity of men who once had to walk alone in huge factories, beside huge machines. To realize that labor unions have meant new dignity and pride to millions of our countrymen. To be able to see what larger pay checks mean, not to a man as an employee, but as a husband and as a father. To know these things is to understand what American labor means.
— Adlai Stevenson, in a speech to the American Federation of Labor, New York City on 22 September 1952
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
The dichotomy that is Madison School Board Governance was on display this past week.
1. Board Member TJ Mertz, in light of the District’s plan to continue growing spending and property taxes for current programs, suggests that “fiscal indulgences“:
Tax expenditures are not tax cuts. Tax expenditures are socialism and corporate welfare. Tax expenditures are increases on anyone who does not receive the benefit or can’t hire a lobbyist…to manipulate the code to their favor.
be applied to certain school volunteers.
This proposal represents a continuation of the Districts’ decades long “same service” approach to governance, with declining academic results that spawned the rejected Madison Preparatory IB Charter School.
2. Madison’s new Superintendent, Jennifer Cheatham introduced her “Strategic Framework” at Wednesday’s Downtown Rotary Club meeting.
The Superintendent’s letter (jpg version) (within the “framework” document) to the Madison Community included this statement (word cloud): 
Rather than present our educators with an ever-changing array of strategies, we will focus on what we know works and implement these strategies extremely well. While some of the work may seem familiar, having the courage and determination to stay focused on this work and do it well is in itself a revolutionary shift for our district. This is what it takes to narrow and eliminate gaps in student achievement.
The Madison School Board’s letter (jpg version) to the community includes this statement:
Public education is under sustained attack, both in our state and across the nation. Initiatives like voucher expansion are premised on the notion that public schools are not up to the challenge of effectively educating diverse groups of students in urban settings.
We are out to prove that wrong. With Superintendent Cheatham, we agree that here in Madison all the ingredients are in place. Now it is up to us to show that we can serve as a model of a thriving urban school district, one that seeks out strong community partnerships and values genuine collaboration with teachers and staff in service of student success.
Our Strategic Framework lays out a roadmap for our work. While some of the goals will seem familiar, what’s new is a clear and streamlined focus and a tangible and energizing sense of shared commitment to our common goals.
The bedrock of the plan is the recognition that learning takes place in the classroom in the interactions between teachers and students. The efforts of all of us – from school board members to everyone in the organization – should be directed toward enhancing the quality and effectiveness of those interactions.
There is much work ahead of us, and the results we are expecting will not arrive overnight. But with focus, shared effort and tenacity, we can transform each of our schools into thriving schools. As we do so, Madison will be the school district of choice in Dane County.
Madison School Board word cloud:
North Carolina Gov. Pat McCrory, a Republican, signed a budget bill Friday that eliminates teacher tenure and–in a rare move–gets rid of the automatic pay increase teachers receive for earning a master’s degree.
The legislation targets a compensation mechanism that is common in the U.S., where teachers receive automatic pay increases for years of service and advanced degrees. Some research has suggested those advanced degrees don’t lead to improved teaching.
Although a few other states have talked about doing away with the automatic pay increase for advanced degrees, experts say North Carolina is believed to be the first state to do so.
The budget bill–which drew hundreds of teachers to the Capitol in protest earlier this week–also eliminates tenure for elementary and high-school teachers and freezes teacher salaries for the fifth time in six years.
It comes as states and districts across the country are revamping teacher evaluations, salaries and job security, and linking them more closely to student performance. These changes have been propelled, in part, by the Obama administration and GOP governors.
The challenge for Madison is moving away from long time governance structures and practices, including a heavy (157 page pdf & revised summary of changes) teacher union contract. Chris Rickert’s recent column on Madison’s healthcare practices provides a glimpse at the teacher – student expenditure tension as well.
Then Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 Madison Rotary speech offers important background on Madison’s dichotomy:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
“Budget Cuts: We Won’t Be as Bold and Innovative as Oconomowoc, and That’s Okay”.
Michael B. Horn And Meg Evans:
The past several decades have seen technology transform industry after industry. Nearly every sector in America has used new technologies to innovate in ways nearly unimaginable a generation before the change.
One sector, however, has remained nearly the same as it was a century ago.
The education system in place in urban school districts around the country was created in the early 1900s to serve a different time with different needs. In 1900, only 17% of all jobs required so-called knowledge workers, whereas over 60% do today.
Back then, the factory-model system that educators adopted created schools that in essence monolithically processed students in batches. By instituting grades and having a teacher focus on just one set of students of the same academic proficiency, the theory went, teachers could teach the same subjects, in the same way and at the same pace to all children in the classroom.
When most students would grow up to work in a factory or an industrial job of some sort, this standardization worked just fine. But now that we ask increasingly more students to master higher order knowledge and skills, this arrangement falls short.
Milwaukee and Wisconsin as a whole have felt this pressure acutely. Between 2011 and 2012, Wisconsin had the biggest six-month decline in manufacturing jobs in the nation after California. According to a Milwaukee Journal Sentinel special report, the city’s pool of college-educated adults ranks among the lowest of the country’s 50 biggest cities. To become an average city among the top 50, Milwaukee would need another 36,000 adults with college degrees. Since 1990, it has added fewer than 1,000 a year.
Spot on. Much more on our “Frederick Taylor” style K-12 system and its’ focus on adult employment, here.
There are sometimes days doing this watchdog work that are defeating, sad and frustrating. Today is one those. I’ll get to the issue at hand but a few thoughts first.
I’ve said this before – I do truly believe we have some good and decent people working in SPS. There are several up the food chain who are almost great but, like many a bureaucracy, have those whose work either drags them down or mires them in place.
I’ve also said this before – anyone who works in leadership at SPS who does not read and heed the words in the Moss-Adams report of 2002 is doomed to failure. Or, at least doomed to frustration.
The echo in my head from that brilliant report (and I paraphrase here) –
It does not matter what structural or systemic change you bring to an institution, if the culture of bureaucracy at an institution does not change, nothing changes.
The Madison School District has the money to improve low-income and minority student achievement but needs to reorganize its central administration to put more resources in the classroom, according to a group of local and national education experts who conducted a district review.
“We’re recommending the system turn on its head,” said Robert Peterkin, the former director of Harvard University’s Urban Superintendents Program who led the review team.
New Madison schools superintendent Jennifer Cheatham, a graduate of the Harvard program, organized the team of experts as part of her transition. She plans to consult their recommendations before releasing next month a set of specific strategies and 2013-14 budget proposal.
According to the team’s analysis, students need to be at the top of the “power pyramid” rather than district administration, with the focused goal of turning out graduates ready to attend college or start a career.
Central office administrators need to spend more time in the classroom and cut down on new programs that contribute to what teachers call “initiative fatigue.”
Principals should have more input into hiring a more diverse staff. Teachers need more focused professional development. And all district employees need specific goals that can be measured and used to hold them accountable.
Students also need “demand parents” who take an active role, not only in school bake sales and sports, but in understanding the curriculum and educational goals for their students.
“Resources even in this environment can be brought to bear from existing dollars to your more focused set of goals and activities, rather than supporting proliferation of those activities,” Peterkin told the Madison School Board on Monday night.
Cheatham said the review team had not taken a deep enough look at district finances to conclude that funding is available, but based on her assessment of the budget so far, she said the conclusion was “fairly accurate.”
“The recommendations from the transition team warrant a deep look at the central office organization and our allocation of resources,” she said.
The “Transition Team” Report (3MB PDF) and Superintendent Cheathem’s “Entry Plan” summary.
Related:
Madison’s disastrous long-term reading results.
Deja Vu: A Focus on “Adult Employment” or the Impossibility of Governance Change in the Madison Schools.
Madison has long spent more per student than most districts. The most recent 2012-2013 budget, via a kind Donna Williams and Matthew DeFour email is $392,789,303 or $14,496.74 per student (27,095 students, including pre-k).
The list of administrators who are receiving a non-extension of contract is extensive due to the decision to move from rolling two-year contracts to straight two-year contracts and the desire to have approximately half of the administrators on odd-year contracts and half on even-year contracts. Other than the normal one-year contracted administrators, volunteers were solicited from the group of administrators who would have normally received a one-year contract extension to accept a non- extension this year and then accept a two-year contract for 2014-16. After the volunteers were accounted for, a lottery was held.
There is a group of 33 administrators in their first two years of employment with the district who are on one-year contracts. These contracts were approved in January 2013 and are not reflected on the attached lists (REVISED Appendix 000-12-5).
Fresh off a two-month tour to observe the operations of all 48 schools, various programs, and the Madison School District’s central administrative offices, Superintendent Jennifer Cheatham is promising to “ensure accountability at every level.”
Accountability as Cheatham describes it will include student achievement on standardized tests of the type that current school reform movements emphasize, but will go far beyond that to a new understanding of educators’ roles, the support they need to master them, and refined local measures of progress, she said.
“I worry that people perceive accountability as standardized test results, for example, and what I’m talking about is accountability for everybody playing well the function they are best positioned for in the service of children learning well,” Cheatham told me Thursday in an interview. “Educators at every level of the system lack clarity on what that particular function is for them.”https://www.schoolinfosystem.org/archives/2013/06/deja_vu_a_focus.php”>Accountability was one of five priority areas Cheatham identified in anEntry Plan Report released Wednesday. The others are: well-rounded, culturally responsive instruction; personal educational pathways for students; attracting, developing and retaining top-level talent; and engaging families and community members as partners.
As the dissatisfaction with the U.S. education system among parents grows, so does the appeal of homeschooling. Since 1999, the number of children who are being homeschooled has increased by 75%. Although currently only 4% of all school children nationwide are educated at home, the number of primary school kids whose parents choose to forgo traditional education is growing seven times faster than the number of kids enrolling in K-12 every year.
Any concerns expressed about the quality of education offered to the kids by their parents can surely be put to rest by the consistently high placement of homeschooled kids on standardized assessment exams. Data shows that those who are independently educated typically score between 65th and 89th percentile on such exams, while those attending traditional schools average on the 50th percentile. Furthermore, the achievement gaps, long plaguing school systems around the country, aren’t present in homeschooling environment. There’s no difference in achievement between sexes, income levels or race/ethnicity.Recent studies laud homeschoolers’ academic success, noting their significantly higher ACT-Composite scores as high schoolers and higher grade point averages as college students. Yet surprisingly, the average expenditure for the education of a homeschooled child, per year, is $500 to $600, compared to an average expenditure of $10,000 per child, per year, for public school students.
College recruiters from the best schools in the United States aren’t slow to recognize homeschoolers’ achievements. Those from non-traditional education environments matriculate in colleges and attain a four-year degree at much higher rates than their counterparts from public and even private schools. Homeschoolers are actively recruited by schools like the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, Stanford University and Duke.
Related: A focus on adult employment.
Indiana lawmakers are proposing huge increases in state education funding this year. Ditto those in Wisconsin.
Here in Illinois, The Deadbeat State? Just the opposite. Education funding is being strangled by the same python that is strangling the rest of state government’s finances: pension obligations. Every day that the Legislature delays the enactment of pension reform, the unfunded liability of the state’s five pension funds grows by $17 million, according to Gov. Pat Quinn’s office.
In this state, we’re not arguing about how to, say, give more money to schools because great schools drive growth and innovation, attract businesses, create jobs.
No, we’re arguing instead about which school kids will get cheated more than other school kids because state lawmakers dither on a pension fix — kids from richer districts or those from poorer districts? That’s the depressing debate we’re having.
Here’s why: In Illinois, the Legislature sets a “foundation” funding level that the state says every student needs for an adequate education. That’s the starting point for a calculation that determines how much state aid each district receives. The calculation considers each district’s local taxing ability to meet that foundation level, and also looks at how many students in the district need extra support because they’re from low-income families. Districts that have relatively lower revenue and educate relatively more higher-need students receive more state aid.
Related: Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman’s 2009 Madison Rotary Speech:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).

Tap or click for a larger version of the above chart.
Madison Superintendent Jane Belmore:
In investigating the options for data to report for these programs for 2011-12 and for prior years, Research & Program Evaluation staff have not been able to find a consistent way that students were identified as participants in these literacy interventions in prior years.
As such, there are serious data concerns that make the exact measures too difficult to secure at this time. Staff are working now with Curriculum & Assessment leads to find solutions. However, it is possible that this plan will need to be modified based on uncertain data availability prior to 2011-12.
Much more on Madison’s disastrous reading results, here. Reading continues to be job one for our $392,000,000 public schools.

Tap or click to view a larger version of the above image.
Measuring Madison’s Progress – Final Report (2.5MB PDF).
Given the results, perhaps the continued $pending and related property tax increases for Reading Recovery are driven by adult employment, rather than kids learning to read.
UPDATE: April 1, 2013 Madison School Board discussion of the District’s reading results. I found the curriculum creation conversation toward the end of the meeting fascinating, particularly in light of these long term terrible results. I am not optimistic that student reading skills will improve given the present structure and practices. 30 MB MP3.
UPDATE: December, 2017…. ….
The teachers are angry because we are being held accountable for things that we didn’t do at the high school level. Of those 24 students, 21 of them have been enrolled in Madison for four or more years.
Of those 24 students one is Caucasian the rest of them identify as some other ethnic group.
I am tired of the district playing what I called whack-a-mole, (in) another words a problem happens at Cherokee boom we bop it down and we we fix it temporarily and then something at Sherman or something at Toki or something at Faulk and we bop it down and its quiet for awhile but it has not been fixed on a system-wide level and that’s what has to change.
Here’s a novel way to address the problems caused by rising income inequality: give children the vote.
One virtue of this iconoclastic idea, recently advanced by the Canadian economist Miles Corak, is that it sidesteps the usual partisan debates. After all, the right and left have profound moral disagreements about economic inequality. But whatever your political stripe, you almost certainly believe in equality of opportunity.
Unfortunately, some of Corak’s most celebrated work has been to show that rising income inequality and declining social mobility go together. This relationship, which Alan B. Krueger, the head of President Barack Obama’s Council of Economic Advisers, has dubbed the Great Gatsby Curve, is one of the most powerful reasons to care about rising income inequality.
That’s where the kids come in. In a policy paper published last month by Canada 2020, a Canadian progressive research group, Corak points out that the group that suffers most from declining social mobility is the young. As it happens, this is also one of the last human constituencies that doesn’t have the right to vote. That relationship may not be coincidental.
“Older individuals, and those with more education working in higher-skilled occupations, are more likely to vote,” Corak writes in the paper. “But, in addition, there is a broad bias by virtue of the simple fact that children are disenfranchised. Children’s rights are not adequately recognized and they have a reduced political voice in setting social priorities.”
Corak has a simple and radical solution to that bias: Give children the vote. “When you first hear about it, it sounds like a crazy idea, and that was my first reaction,” Corak told me, speaking by phone from Ottawa.
Yes.
Related: “the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment”
Kaleem Caire, via a kind email
March 6, 2013
Dear Madison Leaders.
As the 2013 Madison school board race continues, we (the Urban League) are deeply concerned about the negative politics, dishonesty and inaccurate discussions that have shaped the campaign. While I will not, as a nonprofit leader, speak about the merits of individual candidates, we are concerned about how Madison Prep has become a red herring during the debates. The question of all the candidates has been largely narrowed to, “Did you support Madison Prep or did you not?”…as if something was horribly wrong with our charter school proposal, and as though that is the most important issue facing our school children and schools.
While the Urban League has no interest in partaking in the squabbles and confusion that has unfortunately come to define public conversation about our public schools, we do want to set the record straight about deliberations on Madison Prep that have been falsely expressed by many during this campaign, and used to dog individuals who supported the school proposal more than one year ago.
Here is how things transpired.
On May 9, 2011, Steve Goldberg of the CUNA Mutual Foundation facilitated a meeting about Madison Prep, at my request, between Madison Teacher’s Incorporated President, John Matthews and me. The meeting was held in CUNA’s cafeteria. We had lunch and met for about an hour. It was a cordial meeting and we each discussed the Madison Prep proposal and what it would take for the Urban League and MTI to work together. We didn’t get into many details, however I was sure to inform John that our proposal of a non-instrumentality charter school (non-MTI) was not because we didn’t support the union but because the collective bargaining agreement was too restrictive for the school model and design we were proposing to be fully implemented, and because we desired to recruit teachers outside the restrictions of the collective bargaining agreement. We wanted to have flexibility to aggressively recruit on an earlier timeline and have the final say on who worked in our school.
The three of us met again at the Coliseum Bar on August 23, 2011, this time involving other members of our teams. We got into the specifics of negotiations regarding the Urban League’s focus on establishing a non-instrumentality school and John’s desire to have Madison Prep’s employees be a part of MTI’s collective bargaining unit. At the close of that meeting, we (Urban League) offered to have Madison Prep’s teachers and guidance counselors be members of the collective bargaining unit. John said he felt we were making progress but he needed to think about not having MTI represent all of the staff that are a part of their bargaining unit. John and I also agreed that I would email him a memo outlining our desire to work with MTI, and provide the details of what we discussed. John agreed to respond after reviewing the proposal with his team. That memo, which we have not released previously, is attached [336K PDF]. You will see clearly that the Urban League initiated dialogue with MTI about having the teacher’s union represent our educators.
John, Steve and I met for a third time at Perkins restaurant for breakfast on the West Beltline on September 30, 2013. This time, I brought representatives of the Madison Prep and Urban League Boards with me: Dr. Gloria Ladson Billings, John Roach and Derrick Smith. It was at the close of this meeting that John Matthews told all of us that we “had a deal”, that MTI and the Urban League would now work together on Madison Prep. We all shook hands and exchanged pleasantries. Our team was relieved.
Later that evening, I received calls from Matt DeFour, a reporter with the Wisconsin State Journal and Susan Troller of The Capital Times. They both asked me to confirm what John had told them; that we had a deal. I replied by confirming the deal. The next day, The Capital Times ran a story, Madison Prep and MTI will work together on new charter school. The State Journal ran an article too, Prep School agrees to employ union staff. All was good, or so we thought.
Unfortunately, our agreement was short-lived. The very next day after the story hit the newspapers, my team and I began receiving angry letters from social workers and psychologists in MMSD who were upset that we did not want to have those positions represented by MTI. We replied by explaining to them that our reasoning was purely driven by the fact that 99% of the Districts psychologists were white and that there were few social workers of color, too. For obvious reasons, we did not believe MMSD would have success hiring diverse staff for these positions. We desired a diverse staff for two reasons: we anticipated the majority of our students to be students of color and our social work and psychological service model was different. Madison Prep had a family-serving model where the school would pay for such services for every person in a family, if necessary, who needed it, and would make available to families and students a diverse pool of contracted psychologists that families and students could choose from.
That Monday evening, October 3, 2011, John Matthews approached me with Steve Goldberg at the School Board hearing on Madison Prep and informed me that his bargaining unit was very upset and that he needed to have our Physical education teacher be represented by MTI, too. Our Phy Ed model was different; we had been working on a plan with the YMCA to implement a very innovative approach to ensuring our students were deeply engaged in health and wellness activities at school and beyond the school day. In our plan, we considered the extraordinarily high rates of obesity among young men and women of color. However, to make the deal with MTI work, that evening I gave MTI the Phy Ed teaching position.
But that one request ultimately became a request by MTI for every position in our school, and a request by John Matthews to re-open negotiations, this time with a mediator. At first, we rejected this request because we felt “a deal is a deal”. When you shake hands, you follow through.
We only gave in after current school board president, James Howard, called me at home to request that the Urban League come back to the negotiating table. James acknowledged not feeling great about asking us to do this after all we had been through – jumping through hoop after hoop. If you followed the media closely, you would recall how many times we worked to overcome hurdles that were placed in our way – $200K worth of hurdles (that’s how much we spent). After meeting with MMSD leadership and staff, we agreed to come back to the table to address issues with MTI and AFSCME, who wanted our custodial and food service workers to be represented by the union as well. When we met, the unions came to the negotiation with attorneys and so did we. If you care to find out what was said during these negotiations, you can request a transcript from Beth Lehman, the liaison to the MMSD Board of Education who was taking official notes (October 31 and November 1, 2011).
On our first day of negotiations, after all sides shared their requests and concerns, we (ULGM) decided to let AFSCME represent our custodial and food service staff. AFSCME was immediately satisfied, and left the room. That’s when the hardball towards us started. We then countered with a plausible proposal that MTI did not like. When we couldn’t get anywhere, we agreed to go into recess. Shortly after we came back from recess, former MMSD Superintendent Dan Nerad dropped the bomb on us. He shared that if we now agreed to have our staff be represented by MTI, we would have to budget paying our teachers an average of $80,000 per year per teacher and dedicating $25,000 per teacher to benefits. This would effectively increase our proposal from $15M over five years to $28M over five years.
Why the increased costs? For months, we projected in our budgets that our staff would likely average 7 years of teaching experience with a Master’s degree. We used the MTI-MMSD salary schedule to set the wages in our budget, and followed MMSD and MTI’s suggestions for how to budget for the extended school day and year parts of our charter school plan. Until that day, MMSD hadn’t once told us that the way we were budgeting was a problem. They actually submitted several versions of budgets to the School Board, and not once raising this issue.
Superintendent Nerad further informed us that MMSD was going to now submit a budget to the Board of Education that reflected costs for teachers with an average of 14 years’ experience and a master’s degree. When we shockingly asked Nerad if he thought the Board of Education would support such a proposal, he said they likely would not. We did not think the public would support such a unusual request either. As you can imagine, we left the negotiations very frustrated. In the 23rd hour, not only was the run we thought we had batted in taken away from us in the 9th inning, we felt like our entire season had been vacated by commissioners.
When we returned to our office that afternoon, we called an emergency meeting of the Urban League and Madison Prep boards. It was in those meetings that we had to make a choice. Do we completely abandon our proposal for Madison Prep after all we had done to see the project through, and after all of the community support and interests from parents that we had received, or do we go forward with our original proposal of a non-instrumentality charter school and let the chips fall where they may with a vote by the Board? At that point, our trust of MMSD and MTI was not very high. In fact, weeks before all of this happened, we were told by Nerad in a meeting with our team and attorneys, and his staff and attorneys, that the Board of Education had voted in closed session to unilaterally withdraw our charter school planning grant from the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction. They reversed this decision after we informed them we would file a lawsuit against them. We were later told that a certain Board member was pushing for months to have this done. Then, after months of not being able to get certain board members to meet with us, Marj Passman, decided to meet with me alone in my office. During that meeting, she told me that we (ULGM) didn’t have the votes for Madison Prep and that we were never going to get the school approved. She the offered to donate her personal funds to Madison Prep, if we pulled our proposal and decided to do a private school instead. I told her that I appreciated her offer, but declined.
After finally meeting with all seven board of education members, both the Madison Prep and ULGM boards decided unanimously that we must in good conscience go forward, put the needs and future of our children first, and reintroduce the non-instrumentality proposal to the School Board. You know the rest of the story.
Over the next 45 days, we (ULGM) were categorically painted as an anti-union conservative outfit who proposed a flawed school model that divided Madison and threatened to join the Scott Walker effort to eliminate unions. We were made to be the great dividers (not the achievement gap itself) and me, “an Angry Black Man”. Lost in the debate were the reasons we proposed the school in the first place – because so many children of color were failing in our schools and there was no effective strategy in place to address it even though the school system has known about its racial achievement gap since it was first document by researcher Naomi Lede for the National Urban League in 1965. That gap has doubled since then.
Ironically, two of the people behind the attacks on ULGM were Ben Manski and TJ Mertz. They were uniquely aligned in their opposition to Madison Prep. John Matthews even weighed in on video with his comments against us, but at least he told a story that was 80% consistent with the events that actually transpired. Watch the video and listen to the reason he gave for why he didn’t support Madison Prep. He didn’t call us union haters or teacher bashers. He knew better. So why all the fuss now? Why have those who knew exactly what went on in these negotiations not told the true story about what really happened with Madison Prep? Why has a charter school proposal been made the scapegoat, or defining lever, in a school board race where there are so many other more important issues to address?
If all it takes to win a seat on the school board now is opposition to charter schools, rather than being someone who possesses unique experiences and qualifications to serve our now majority non-white and low-income student body and increasingly challenged schools, we should all worry about the future of our children and public schools.
So, for those who were unaware and those who’ve been misleading the public about Madison Prep and the Urban League, I hope you at least read this account all the way through and give all of the candidates in this school board election the opportunity to win or lose on their merits. Falsehoods and red herrings are not needed. They don’t make our city or our school district look good to the observing eye. Let’s be honest and accurate in our descriptions going forward.
Thank you for reading.
We continue to move forward for our children and are more determined than ever to serve them well.
Onward.
Strengthening the Bridge Between Education and Work
Kaleem Caire
President & CEO
Urban League of Greater Madison
Main: 608.729.1200
Assistant: 608.729.1249
Fax: 608.729.1205
www.ulgm.org
www.madison-prep.org
Invest in the Urban League
Urban League 2012 Third Quarter Progress Report
The Memorandum from Kaleem Caire to John Matthews (Madison Teachers, Inc)
MEMORANDUM
Date: August 23, 2011
To: Mr. John Matthews, Executive Director, Madison Teachers, Inc.
From: Kaleem Caire, President & CEO, Urban League of Greater Madison
cc: Mr. Steve Goldberg, President, CUNA Foundation; Mr. David Cagigal, Vice Chair, Urban League of Greater Madison (ULGM); Ms Laura DeRoche-Perez, Charter School Development Consultant, ULGM; Mr. David Hase, Attorney, Cooke & Frank SC
Re: Discussion about potential MTl-Madison Prep Relationship
Greetings John.
I sincerely appreciate your openness to engaging in conversation about a possible relationship between MTI and Madison Preparatory Academy for Young Men. We, ULGM and Madison Prep, look forward to determining very soon what the possibilities could be.
Please accept his memo as a means to frame the issues.
- The Urban League of Greater Madison initially pursued a non-instrumentality public charter school
focused on young men to, first and foremost, eliminate the academic and graduate gaps between young people of color and their white peers, to successfully prepare greater percentages of young men of color and those at-risk for higher education, to significantly reduce the incarceration rate among young adult males of color and to provide an example of success that could become a learning laboratory for
educators, parents and the Greater Madison community with regard to successful ly educating young men, regardless of th eir race or socio-economic status.- We are very interested in determining how we can work with MTI while maintaining independence with regard to work rules, operations, management and leadership so that we can hire and retain the best team possible for Madison Prep, and make organizational and program decisions and modifications as necessary to meet the needs of our students, faculty, staff and parents.
- MTl’s collective bargaining agreement with the Madison Metropolitan School District covers many positions within the school system. We are interested in having MTI represent our teachers and guidance counselors. All other staff would not be represented by MTI.
- The collective bargaining agreement between MTI and Madison Prep would be limited to employee wages and benefits. Madison Prep teachers would select a representative among them, independent of Madison Prep’s leadership, to serve as their union representative to MTI.
I look forward to discussing this with you and members of our teams, and hearing what ideas you have for the
relationship as well.
Respectfully,
Kaleem Caire,
President & CEO
CONFIDENTIAL
336K PDF Version
jpg version
Related Links:
Madison Preparatory Academy IB Charter School (Rejected by a majority of the Madison School Board).
Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman on “the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment.“.
John Matthews, Madison Teachers, Inc.
Kaleem Caire, Madison Urban League
The rejected Studio Charter School.
Union politics.
2013 Madison School Board Elections.
Update: Matthew DeFour’s article on Caire’s message:
Lucy Mathiak, who was on the board in 2011, also didn’t dispute Caire’s account of the board action, but couldn’t recall exactly what happened in the board’s closed sessions.
“Did (the Urban League) jump through many hoops, provide multiple copies of revised proposals upon request, meet ongoing demands for new and more detailed information? Yes,” Mathiak said. “It speaks volumes that Madison Prep is being used to smear and discredit candidates for the School Board and used as a litmus test of political worthiness.”
Matthews said the problems with Madison Prep resulted from Caire’s proposal to hire nonunion staff.
“What Kaleem seems to have forgotten, conveniently or otherwise, is that MTI representatives engaged in several discussions with him and several of his Board members, in attempt to reach an amicable resolution,” Matthews said. “What that now has to do with the current campaign for Board of Education, I fail to see. I know of no animosity among the candidates or their campaign workers.”
Passman and other board members who served at the time did not return a call seeking comment.
Teachers all over Wisconsin lost benefits after Bruce Vielmetti:Act 10 eliminated most collective bargaining by public employees.
But maybe none lost more than those in Neenah, where hundreds of veteran educators are now headed to court in a class-action lawsuit to try to win back $170,000 in stipends, which supplemented their regular pensions.
District officials said changes to the retirement plan were necessary in light of $185 million in unfunded retirement liabilities.
“Obviously, you care about what your neighbors think, but ultimately you have to look out for your family,” said Tim Hopfensperger, 49, who noted he passed up administrative jobs in other districts because the extra pay over 10 years still wouldn’t match what he thought he had coming from Neenah, where he’s been an elementary school teacher since he was recruited from Germantown schools in 1990.
For years, Neenah’s teachers enjoyed one of the most generous retirement plans in Wisconsin. Many who were hired in the 1990s could retire at age 55 if they had 15 years with the district and get big stipends on top of their regular state retirement, plus health care coverage until they were eligible for Medicare.
The payment was based on 10 annual payments of one-half the starting teacher salary in the district, which last year was $34,319, or about $170,000. Teachers hired after July 1, 1998, had to work 20 years and reach age 57 to collect eight annual payments. Those hired after 2003 were eligible for less lucrative retirement enhancements.
Related on the adult employment focus of school districts.
Congrats to new #MMSD Supt. Jennifer Cheatham.If she respects district employees (MTI), we can succeed.We teach the children.
— Madison Teachers Inc (@MtiMadison) February 9, 2013
Madison School Board Member Ed Hughes:
Leadership comes in different shapes and sizes. After spending time with 41-year-old Jen Cheatham and attending the community forum on Thursday, I kept thinking back to the winter day 23 years ago when 43-year-old Barry Alvarez was introduced to the Madison community and made his memorable statement about how fans interested in season tickets better get them now because they’d soon be hard to get.
Like Cheatham, Alvarez was an outsider, a rising star in a major program who was ready to take the reins of his own program and run with it. That certainly did not guarantee success, but he proved to have that rare and ineluctable something that inspired his players to raise their game, that drove them to succeed as a team because they couldn’t bear to let their coach or teammates down.
As with Barry, so with Jen. For those of us who have been able to spend time with Jen Cheatham and talk to her about her vision for our Madison schools, it is clear that whatever leadership is, she has it. What we heard time and again from those she’s worked with is that Jen is able to inspire principals and teachers to do their best possible work for the students they serve. But also like Alvarez, she’s doesn’t shy away from tough decisions when they’re necessary.
Related: Madison’s third grade reading results:
“The other useful stat buried in the materials is on the second page 3 (= 6th page), showing that the 3rd grade proficiency rate for black students on WKCE, converted to NAEP-scale proficiency, is 6.8%, with the accountability plan targeting this percentage to increase to 23% over one school year. Not sure how this happens when the proficiency rate (by any measure) has been decreasing year over year for quite some time. Because the new DPI school report cards don’t present data on an aggregated basis district-wide nor disaggregated by income and ethnicity by grade level, the stats in the MMSD report are very useful, if one reads the fine print.”
Madison School Board Needs to Address Search Fiasco:
That being the case, Cheatham would come to this position in a difficult circumstance. As Kaleem Caire, the president of the Urban League of Greater Madison, told the State Journal: “The perception of people in this community when we have one pick, they will always question the value of this woman. That’s not fair to her and not fair to our kids.”
The School Board has presided over a fiasco that board member Ed Hughes admits — in a major understatement — “has not gone as smoothly as we’d like.”
Now the board needs to get its act together.
If would be good if the board were to seek the return of the more than $30,000 in taxpayer money that was allocated for what can only charitably be referred to as a “search.” However, we don’t want the board to squander more tax money on extended legal wrangling.
The board should make it clear that it will not have further dealings with this search firm, as the firm’s vetting of applicants does not meet the basic standards that a responsible board should expect.
Perhaps most importantly, the board should engage in a serious rethink of its approach to searches for top administrators. The Madison Metropolitan School District is a great urban school district. It has challenges, especially with regard to achievement gaps and the overuse of standardized testing, that must be addressed.
Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman – August, 2009
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).
Zimman noted that the most recent State of Wisconsin Budget removed the requirement that arbitrators take into consideration revenue limits (a district’s financial condition @17:30) when considering a District’s ability to afford union negotiated compensation packages. The budget also added the amount of teacher preparation time to the list of items that must be negotiated….. “we need to breakthrough the concept that public schools are an expense, not an investment” and at the same time, we must stop looking at schools as a place for adults to work and start treating schools as a place for children to learn.”
In a report issued Monday, StudentsFirst ranks states based on how closely they follow the group’s platform, looking at policies related not only to tenure and evaluations but also to pensions and the governance of school districts. The group uses the classic academic grading system, awarding states A to F ratings.
With no states receiving an A, two states receiving B-minuses and 12 states branded with an F, StudentsFirst would seem to be building a reputation as a harsh grader.
Ms. Rhee said that the relatively weak showing reflected how recently statehouses had begun to address issues like tenure and performance evaluations. “We didn’t say in any way that we want to show people how bad it is,” she said in a telephone interview. “We wanted to show the progress that is being made, but in places where progress is slower to come, be very clear with leaders of that state what they could do to push the agenda forward and create a better environment in which educators, parents and kids can operate.”
Related: Ripon Superintendent Richard Zimman:
“Beware of legacy practices (most of what we do every day is the maintenance of the status quo), @12:40 minutes into the talk – the very public institutions intended for student learning has become focused instead on adult employment. I say that as an employee. Adult practices and attitudes have become embedded in organizational culture governed by strict regulations and union contracts that dictate most of what occurs inside schools today. Any impetus to change direction or structure is met with swift and stiff resistance. It’s as if we are stuck in a time warp keeping a 19th century school model on life support in an attempt to meet 21st century demands.” Zimman went on to discuss the Wisconsin DPI’s vigorous enforcement of teacher licensing practices and provided some unfortunate math & science teacher examples (including the “impossibility” of meeting the demand for such teachers (about 14 minutes)). He further cited exploding teacher salary, benefit and retiree costs eating instructional dollars (“Similar to GM”; “worry” about the children given this situation).

schoolinfosystem.org