In a post-Christmas blog post my indefatigable American Enterprise Institute colleague Jim Pethokoukis points to a study that shows that no economy in the world rewards smart, skilled workers more than the United States. the study, by economists Eric Hanushek, Guido Schwerdt, Simon Wiederhold and Ludger Woessmann, and published by the National Bureau for Economic Research, quantifies the return on numeracy skills for the U.S. at 28 percent, significantly ahead of Ireland, Germany, Spain and the U.K., which range between 21 percent and 23 percent. Korea, Canada, Poland and Japan hover below 20 percent.
Pethokoukis argues that the higher returns come in “economies with more open, private-sector-based labor markets.” He goes on to ask, “Wouldn’t this seem to argue that higher U.S. inequality — based on pre-tax, pre-transfer market incomes — reflects 21st century market forces rewarding ability rather than some sort of breakdown in social norms.”
Sign Up for the Michael Barone newsletter!
To this (seemingly rhetorical) question I would answer “yes,” and would go on to say that it tends to confirm the thesis of my 2004 book Hard America, Soft America. In it, I contrasted Hard America — the parts of American society in which there is competition and accountability, and Soft America, the parts of American society in which there isn’t. K-12 education, in my view, is part of Soft America; the competitive market economy is part of Hard America.
Kansas Lawmakers Await Court Ruling on School Funding
After passing some of the most aggressive tax cuts in the nation, Kansas lawmakers are watching the state’s top court for a ruling that could force education spending to skyrocket.
The Kansas Supreme Court will determine whether the state must comply with a lower-court ruling requiring the GOP-led legislature and Republican Gov. Sam Brownback to increase annual funding for K-12 education by an estimated $450 million, or 14% above the previous year’s level. The timing of the ruling is unclear, but it could come to dominate the state legislative session that opens Monday.
The court battle, which came after school districts challenged how much money the state sends to towns and cities for K-12 education, is one of several across the U.S. that have pulled judges into the fights over how much states should spend on public education.
In Kansas, lawmakers started to push back against the courts last year. The Senate passed a bill to amend the state constitution so that such decisions on education spending would be up to the legislature. To go into effect, the proposed amendment would have to win approval in the House by a two-thirds majority and pass in a statewide vote.
Commentary on the Madison School Board’s Uncontested Election
“The test of any particular voting scheme is the quality of the candidates who are elected under it,” Hughes told me. “We currently have seven good board members. After the spring election we’ll continue to have seven good board members. I don’t see a problem.”
And here I thought that in a democracy the best test of a voting “scheme” was how well it represented the desires of the democracy’s citizens.
Silly me.
Here’s the truth about Shanghai schools: they’re terrible
The western world watches China’s rise as a formidable world-power with a mixture of awe and apprehension. Sci-fi films depict a futuristic world where Baidu.com is the new Google and Mcdonalds has been replaced by Grandma Wang’s Dumpling Emporium. And yet again Shanghai is number one on the Programme for International Student Assessment’s (Pisa) 2012 ranking list of international education, and the US is once again at a low rank, this time 36th place. The US is desperate, and naturally the Chinese educational system seems like an answer. But let me tell you – this is not the case. I know; for two years I attended a local Shanghainese high school and this is the truth: they are terrible.
The biggest problem with Chinese education? It’s medieval. Shanghainese education is just like the stories my grandmother tells about high school in the 1940’s. Footage of military parades in Fascist Italy share an unnerving resemblance to the morning assemblies from my school in Shanghai. Chinese education would be a poison for America, not a remedy.
The problem is that there are too many Chinese students. Shanghainese classrooms have about 40 students and in the countryside classes have over 60. The most efficient way to organize all these children is by testing, categorizing and grading them – Chinese education is essentially elitist. Students that excel in school are rewarded with prizes and encouragement, but struggling students are abandoned. I once served as a translator for the principal of my school when seven Swedish principals came to visit Shanghai. The Swedes asked what the school did for students with “special needs” and the principal answered:
Trends from 2013: the higher education bubble
This concept, which I began to track in early 2012, built across multiple fronts in 2013. The bubble idea holds that colleges are overpriced, that student demand is questionable, and both could drop together. I have tested this concept throughout 2013 through social media and in-person presentation, using multiple trends and analyzes, and even developed an alternative model (peak higher education). My verdict now is… the bubble might be happening.
A series of major trends supported the bubble concept in 2013:
College and university tuition and fees continued to rise, despite several tuition freeze experiments. This is consistent with a rising bubble, among other interpretations.
Student debt rose throughout 2013, inspiring widespread anxiety. This is also consistent with a bubble (as well as other models: consumer behavior in a captive market, and also consumers reacting to media panic, etc.)
A number of institutions took drastic steps to stave off financial crisis, including merging with other campuses, ending academic programs, and laying off faculty (I dubbed the latter two “sacrificing the queen”). These events could be advance signs of a bubble about to pop.
The number of students taking classes went down across many sectors (see “Enrollment decline” above). If this continues, then that’s a sign of a bubble popping.
Some graduate programs suffered badly in 2013, most notably law schools, who saw declining revenues, applicants, graduates, and jobs.
Outside of campuses, political pressures remained steady. Some of this occurred in partisan terms, as Republicans extended their criticism of public K-12 to all of higher education, sometimes with an anti-union dimension.
Indeed, I find bubble arguments most often made by conservatives. However, 2013 also saw Democrats joining in for a full-court bipartisan press on higher education, from a presidential charge to build a new institutional assessment system to high-profile governors and mayors calling for reduced higher education fees.
GED Test Overhauled, Some States opt for New Exam
The GED test, for decades the brand name for the high school equivalency exam, is about to undergo some changes.
On Thursday, an upgraded GED exam and two new competing equivalency tests offered in several states will usher in a new era in adult education testing.
The GED (General Educational Development) exam was created in 1942 to help World War II veterans who dropped out of high school use college benefits offered under the GI Bill. This will be its first face-lift in more than a decade.
The revamped test is intended to be more rigorous and better aligned with the skills needed for college and today’s workplaces. The new test will only be offered on a computer, and it will cost more. What consumers pay for the test varies widely and depends on state assistance and other factors.
Even before its launch, officials in many states have balked at the cost increase and at doing away with paper-and-pencil testing. At least nine states — New York, New Hampshire, Missouri, Iowa, Montana, Indiana, Louisiana, Maine and West Virginia — severed ties with the GED test and adopted one of the two new tests that are entering the market. Three others — Wyoming, New Jersey and Nevada — will offer all three. Tennessee will offer the GED test and one other, and other states are expected to decide what to do in the coming months.
Much at stake in Obama’s proposed ranking of colleges
Name a factoid about a college — best party school, most military-friendly, et cetera — and a magazine or website somewhere is probably ranking it.
The implication of those measures is usually some publicity.
But a new ratings system proposed by President Barack Obama would put more than a college’s reputation at stake.
The nation’s colleges would be pitted against one another on measures such as graduation rates, student debt and cost of attendance under the president’s proposed system, aimed at putting a rating to the value colleges provide for their tuition dollars.
Obama said the plan is intended to hold down the cost of college and steer federal loans and grants toward those schools that rate the best. The schools that come out on top could eventually be rewarded with a bigger piece of the federal funding pie.
The Awesomest 7-Year Postdoc or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Tenure-Track Faculty Life
As a young faculty member at Harvard, I got asked such questions a lot. Why did you choose this career? How do you do it? And I can’t blame them for asking, because I am scared by those myths too. I have chosen very deliberately to do specific things to preserve my happiness, lots of small practical things that I discovered by trial and error.
So when asked by graduate students and other junior faculty, I happily told them the things that worked for me, mostly in one-on-one meetings over coffee, and a few times publicly on panels. Of course, I said all these things without any proof that they lead to success, but with every proof that they led me to enjoy the life I was living.
Most people I talked to seemed surprised. Several of my close friends challenged me to write this down, saying that that I owed it to them. They told me that such things were not done and were not standard. That may be true. But what is definitely true, is that we rarely talk about what we actually do behind the scenes to cope with life. Revealing that is the scariest thing of all.
I’ve enjoyed my seven years as junior faculty tremendously, quietly playing the game the only way I knew how to. But recently I’ve seen several of my very talented friends become miserable in this job, and many more talented friends opt out. I feel that one of the culprits is our reluctance to openly acknowledge how we find balance. Or openly confront how we create a system that admires and rewards extreme imbalance. I’ve decided that I do not want to participate in encouraging such a world. In fact, I have to openly oppose it.
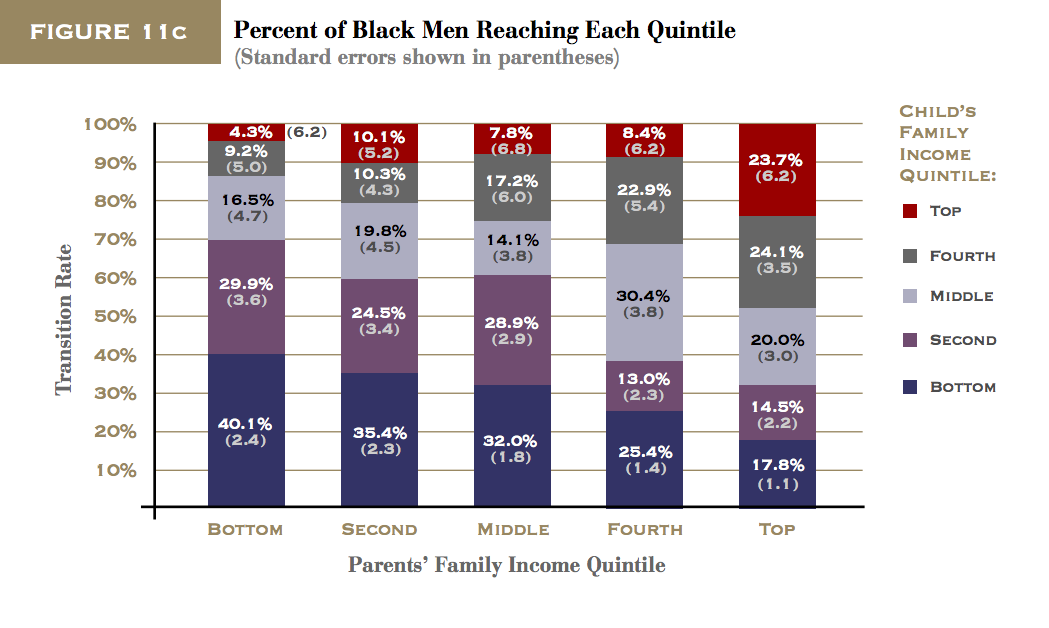
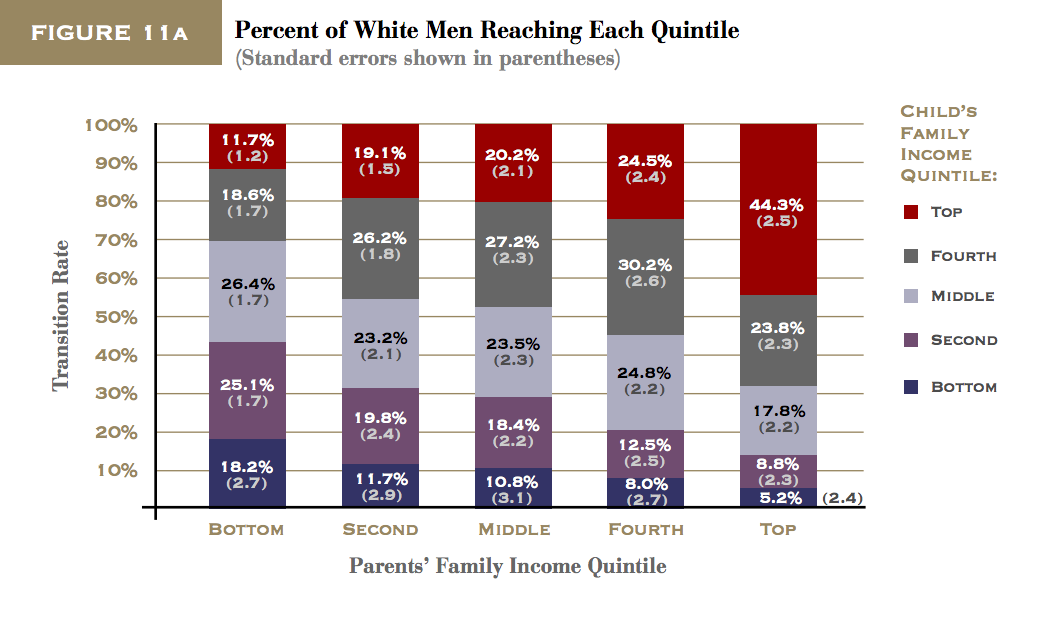
Intergenerational Economic Mobility
In an era of rising income inequality, understanding the extent of economic mobility from one generation to the next in America has never been more important. Only if there is considerable opportunity for children from disadvantaged backgrounds to move beyond their parents’ place in the income distribution, may economic inequality be viewed as tolerable. This report introduces two new and flexible measures to examine upward relative mobility–the extent to which children can rise above their parents’ position when compared to their peers. The report also explores various factors that might account for racial differences in upward economic mobility rates.
Using the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth and measuring family income averaged over several years, the report discusses the following key findings:
The vast majority of individuals, 71 percent, whose parents were in the bottom half of the income distribution actually improved their rankings relative to their parents. However, the amount of their movement was not large.
- Only about 45 percent of those who started in the bottom half moved
up the income distribution by more than 20 percentiles relative to their
parents’ ranking.- Many of those who did manage to exceed their parents’ income started near the very bottom, where exceeding one’s parents is not a very steep hurdle.
As a result, only 38 percent of individuals who started in the bottom half of the income distribution moved to the top half of the distribution as adults
Tech’s Gender and Race Gap Starts in High School
When people talk about how to diversify the tech field, a common solution is, “Start earlier.” Rather than focus on getting women and minorities hired at tech startups or encouraging them to major in computer science in college, there should be a push to turn them on to the discipline when they’re still teenagers–or even younger.
“It’s already too late,” Paul Graham, founder of the tech entrepreneur boot camp Y Combinator, said last month in a controversial interview. “What we should be doing is somehow changing the middle school computer science curriculum or something like that.”
Right now, the “start early” strategy doesn’t seem to be working: The students doing advanced computer science work in high school remain overwhelmingly white and male. According to data from the College Board compiled by Georgia Tech’s Barbara Ericson, only a small percentage of the high-schoolers taking the Advanced Placement Computer Science exam are women. Black and Latino students make up an even lower percentage of the test-takers.
More Students Subsidize Classmates’ Tuition
Well-off students at private schools have long subsidized poorer classmates. But as states grapple with the rising cost of higher education, middle-income students at public colleges in a dozen states now pay a growing share of their tuition to aid those lower on the economic ladder.
The student subsidies, which are distributed based on need, don’t show up on most tuition bills. But in eight years they have climbed 174% in real dollars at a dozen flagship state universities surveyed by The Wall Street Journal.
During the 2012-13 academic year, students at these schools transferred $512,401,435 to less well-off classmates, up from $186,960,962, in inflation-adjusted figures, in the 2005-06 school year.
Enlarge Image
Maria Giannopoulos, a 20-year-old junior at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, relies on the tuition help. Darren Hauck for The Wall Street Journal
At private schools without large endowments, more than half of the tuition may be set aside for financial-aid scholarships. At public schools, set-asides range between 5% and 40% according to the Journal’s survey.
The Open Office (Classroom) Trap
In 1973, my high school, Acton-Boxborough Regional, in Acton, Massachusetts, moved to a sprawling brick building at the foot of a hill. Inspired by architectural trends of the preceding decade, the classrooms in one of its wings didn’t have doors. The rooms opened up directly onto the hallway, and tidbits about the French Revolution, say, or Benjamin Franklin’s breakfast, would drift from one classroom to another. Distracting at best and frustrating at worst, wide-open classrooms went, for the most part, the way of other ill-considered architectural fads of the time, like concrete domes. (Following an eighty-million-dollar renovation and expansion, in 2005, none of the new wings at A.B.R.H.S. have open classrooms.) Yet the workplace counterpart of the open classroom, the open office, flourishes: some seventy per cent of all offices now have an open floor plan.
The open office was originally conceived by a team from Hamburg, Germany, in the nineteen-fifties, to facilitate communication and idea flow. But a growing body of evidence suggests that the open office undermines the very things that it was designed to achieve. In June, 1997, a large oil and gas company in western Canada asked a group of psychologists at the University of Calgary to monitor workers as they transitioned from a traditional office arrangement to an open one. The psychologists assessed the employees’ satisfaction with their surroundings, as well as their stress level, job performance, and interpersonal relationships before the transition, four weeks after the transition, and, finally, six months afterward. The employees suffered according to every measure: the new space was disruptive, stressful, and cumbersome, and, instead of feeling closer, coworkers felt distant, dissatisfied, and resentful. Productivity fell.
Madison’s Thoreau Elementary School was originally built with “open classrooms“.
Academe quits me
Tomorrow I will step into a classroom to begin the last semester of a 24-year teaching career. Don’t get me wrong. I am not retiring. I am not “burned out.” The truth is rather more banal. Ohio State University will not be renewing my three-year contract when it expires in the spring. The problem is tenure: with another three-year contract, tenure becomes an option. In an era of tight budgets, there is neither money nor place for a 61-year-old white male professor who has never really fit in nor tried very hard to. (Leave aside my heterodox politics and hard-to-credit publication record.) My feelings are like glue that will not set. The pieces fall apart in my hands.
This essay is not a contribution to the I-Quit-Academe genre. (A more accurate title in my case would be Academe Quits Me.) Although I have become uncomfortably aware that I am out of step with the purposeful march of the 21st-century university (or maybe I just never adjusted to Ohio State), gladly would I have learned and gladly continued to teach for as long as my students would have had me. The decision, though, was not my students’ to make. And I’m not at all sure that a majority would have voted to keep me around, even if they had been polled. My salary may not be large (a rounding error above the median income for white families in the U.S.), but the university can offer part-time work to three desperate adjuncts for what it pays me. A lifetime of learning has never been cost-effective, and in today’s university–at least on the side of campus where the humanities are badly housed–no other criterion is thinkable.
Former Omaha teacher gives $2.5 million to Council Bluffs library
Ann Cook loved the library.
She spent hours upon hours during her 70 years there, reading about faraway lands, visions of the future and dramas about life and love.
As a gift to the institution that gave her so much joy, the former school teacher left $2.5 million to the Council Bluffs Public Library.
“I’m not surprised,” said Mildred Smock, head librarian from 1957 until her retirement in 1992.
“She was a great reader,” said Smock, who first met Cook when the library patron was a young girl. “She was in the library checking out books about once a week, very frequently. This was a long time ago, but in my recollection she read mostly fiction for pleasure.”
Cook supported the library financially throughout her life, thanks in part to money inherited from her parents, who also passed on their love of books and learning to their daughter. As an adult, Cook would stop by after school let out. She taught from 1964 to 1997 at Norris and the now-closed Bancroft Junior Highs in the Omaha Public Schools system. After retirement she spent even more time at the library, volunteering with the Friends of the Library organization.
Pay Our Teachers or Lose Your Job
My son Ben’s language arts teacher emailed one morning this winter to tell me she is leaving Ben’s school. I feel sick, but I don’t blame her. Three of Ben’s middle school teachers have left in the past year. North Carolina’s intentional assault on public education is working. It is pushing our best teachers out.
Ten years ago my family moved to Chapel Hill. A relatively low cost of living and bipartisan commitment to public education made North Carolina immensely attractive. There is plenty of historic precedent for devaluing public education in the South, and for many years North Carolina was not much different from its neighbors. In 1997 the state ranked 42nd in teacher pay. The year before, Gov. Jim Hunt had run on a platform to invest in public education. After he was elected, he worked with Republican House Speaker Harold Brubaker to focus on excellence in teaching and raised teacher salaries up to the national average in just four years. That bipartisan investment paid off. In the 1990s our public student test scores rose more than any other state’s. North Carolina became known as “the education state.” As recently as 2008, North Carolina paid teachers better than half the nation.
Things can change quickly, especially if you’re not looking. Now, the brand that attracted us–“the education state”–sounds like a grim joke. After six years of no real raises, we have fallen to 46th in teacher pay. North Carolina teachers earn nearly $10,000 less than the national average. And if you look at trends over the past decade, we rank dead last: After adjusting for inflation, North Carolina lowered teacher salaries nearly 16 percent from 2002 to 2012, while other states had a median decline of 1 percent. A first-year teacher in North Carolina makes $30,800. Our school district lost a candidate to a district in Kentucky because its starting salary was close to $40,000. It takes North Carolina teachers more than 15 years to earn $40,000; in Virginia it may take only four. Gap store managers on average make about $56,000.
Comprehensive on Completion
Maryland’s public colleges are six months into complying with one of the nation’s most ambitious college completion bills. The state-mandated push puts Maryland in a class with Tennessee, Indiana and Georgia.
“It represents a defining moment for public higher education in the state of Maryland,” said Charlene M. Dukes, president of Prince George’s Community College. “It sets a whole new tone.”
A few educators said they were uneasy about the state’s Legislature getting so deep in the weeds with legislation that touches on everything from dual enrollment to remediation and completion plans for each student. (See below for more details about the measure.)
Making the many required changes has been a heavy lift at times. But several college leaders said the comprehensive nature of the legislation was a virtue.
That’s because Maryland’s completion law, which was enacted in July, deals simultaneously with K-12, community colleges and four-year institutions. Experts say attempted completion fixes, such as improving remedial course success rates, can benefit from reaching across the various stages of public education.
“If we really want to deal with developmental education,” said Bernie Sadusky, executive director of the Maryland Association of Community Colleges, “we have to go to the source of the problem. That is K-12.”
AFT’s Weingarten Backtracks on Using Value-Added Measures for Teacher Evaluations
American Federation of Teachers President Randi Weingarten has announced that she’ll call for the end of using “value added” measures as a component in teacher-evaluation systems.
Politico first reported that the AFT is beginning a campaign to discredit the measures, beginning with the catchy (if not totally original) slogan “VAM is a sham.” We don’t yet know exactly what this campaign will encompass, but it will apparently include an appeal to the U.S. Department of Education, generally a proponent of VAM.
Value-added methods use statistical algorithms to figure out how much each teacher contributes to his or her students’ learning, holding constant factors like student demographics.
In all, though, Weingarten’s announcement is less major policy news than it is something of a retreat to a former position.
When I first interviewed Weingarten about the use of test scores in evaluation systems, in 2008, she said that educators have “a moral, statistical, and educational reason not to use these things for teacher evaluation.”
Much more on “value added assessment”, here.
School Climate

Los Angeles library to offer high school diplomas
A Los Angeles library plans to take its role as a place of learning a step farther and will start offering residents the opportunity to get an accredited high school diploma.
The Los Angeles Public Library announced Thursday that it is teaming up with a private online learning company to debut the program for high school dropouts, believed to be the first of its kind in the nation.
It’s the latest step in the transformation of public libraries in the digital age as they move to establish themselves beyond just being a repository of books to a full educational institution, said the library’s director, John Szabo.
Since taking over the helm in 2012, Szabo has pledged to reconnect the library system to the community and has introduced a number of new initiatives to that end, including offering 850 online courses for continuing education and running a program that helps immigrants complete the requirements for U.S. citizenship.
No, the ‘College Bubble’ Isn’t Popping
When newspaper editors are in the mood to run a good old-fashioned screed about the collapsing value of college, they inevitably turn to Richard Vedder, an Ohio University economist who runs the Center for College Affordability and Productivity. Vedder likes to argue that the financial return on a B.A. is falling, graduates are chronically underemployed, and that our profligate universities are in for a reckoning once everyone wises up and stops throwing their money away. (For what it’s worth, I tend to disagree).
Today Vedder and one of his students, Christopher Denhart, have upped the ante a bit for The Wall Street Journal, where they’ve published an op-ed titled, “How the College Bubble Will Pop.” The reckoning, they say, is already upon us, as total college enrollment has fallen 1.5 percent since 2012.
“What’s causing the decline?” they ask. “While changing demographics–specifically, a birth dearth in the mid-1990s–accounts for some of the shift, robust foreign enrollment offsets that lack. The answer is simple: The benefits of a degree are declining while costs rise.”
It’s an alluring theory. But their evidence falls apart under even the lightest inspection.
Madison Schools’ 2014-2015 Budget Forecast 1; “Same Service” or “Cost to Continue”; “intends to go beyond marginal refinements”.

Madison School District (PDF):
This budget forecast and those that will follow are intended to keep the board informed as the budget development process unfolds. The forecasts also provide an opportunity for board discussion and input into important budget development issues.
MMSD’s Strategic Framework establishes the direction of the school district. The framework is supported by the annual budget, which is simply the resource strategy behind the Strategic Framework. The budget process begins with a thorough review of district priorities, current spending patterns, and outcomes. The zero- based budget process requires a critical examination of all budget practices and how those practices influence resource deployment.
Based upon our budget work thus far, we believe there are opportunities to make the staffing process more responsive to individual school needs, to shift non- personnel resources from central office budgets to school budgets, and to improve budget accuracy by clarifying and simplifying account structures. We’re excited to explore these and other opportunities throughout the 2014-15 budget process.
Zero-based Approach to Budget Development:
A zero-based approach is being used to develop the expenditure budget. Unlike an ‘historical cost’ budget or a ‘cost to continue’ budget, the zero-based process is intended to go beyond marginal refinements of existing budgets and existing structures.
For example, MMSD has used essentially the same staffing allocation process for over ten years under the ‘cost to continue’ approach, with only minor modifications along the way. While the existing allocation process is uniform and consistent, it can be improved by making it more responsive to the challenges presented by individual schools. The senior leadership team, with input from the principals, is assessing the staffing allocation process this month before any allocation decisions are put into motion in February.
The existing staff allocation process consists of a series of departmental layers, with separate staffing allocations for regular education, special education, Title 1, OMGE, pupil services, PBS, etc. We are hopeful that a more integrated and responsive staffing allocation process, beginning this year and refined continuously in subsequent years, will produce a more tailored fit for each school. The zero-based approach is designed to uncover such opportunities.
The zero-based process also includes in-depth reviews of each central office department. We are particularly interested in identifying inter-departmental overlaps, gaps, and even redundancies. We are optimistic that this effort will produce new efficiencies and help push resources from the district office into the schools.
Strategic Priorities Drive the Budget:
The resource decisions contained in the annual budget are subject to continuous review, either directly through the zero-based budget process, or indirectly through the SIP process, district surveys, targeted studies (such as the Principal Pipeline study [PDF] and High School Reform study), and several active advisory committees. These are the sources which inform the budget development process.
The Strategic Framework identifies five key priorities which are aimed at providing schools with the tools, processes and resources they need to serve children and their families better than ever before. The five priorities are: (1) Coherent Instruction, (2) Personalized Pathways, (3) Family and Community Engagement, (4) A Thriving Workforce, and (5) Accountability at All Levels.
Each of the priorities in the Strategic Framework includes a set of high-leverage actions that have cost implications. A preview of some of the major actions with cost implications, organized by Priority Area, will be developed and refined throughout the budget development process. A preview of the major actions will be presented to the Operations Work Group along with this Budget Forecast.
The word cloud is interesting, particularly in light of the District’s job number one, addressing its long term disastrous reading results.
Related: numerous links on the District’s 2013-2014 budget, here. Madison spends about twice the national average per student ($15k).
The Degree Is Doomed
The credential — the degree or certificate — has long been the quintessential value proposition of higher education. Americans have embraced degrees with a fervor generally reserved for bologna or hot dogs. Everyone should have them! Many and often! And their perceived value elsewhere in the world — in Asia in particular — is if anything even higher.
From the evaluator’s standpoint, credentials provide signals that allow one to make quick assumptions about a candidate’s potential contribution to an organization and their ability to flourish on the job. To a prospective student (or parent), the value lies in assuming these signals will be accepted in employment markets and other times of social evaluation. These signals have long been known to be imperfect, but they were often the only game in town. Thus, a degree from a top university has been seen to contain crucial information about a person’s skills, networks, and work habits.
The university has become a rogue institution in need of root-and-branch reform
Two factors have so far shielded the American university from the sort of criticism that it so freely levels against almost every other institution in American life. (1) For decades a college education has been considered the key to an ascendant middle-class existence. (2) Until recently a college degree was not tantamount to lifelong debt. In other words, American society put up with a lot of arcane things from academia, given that it offered something — a BA or BS degree — that almost everyone agreed was a ticket to personal security and an educated populace.
Not now. Colleges have gone rogue and become virtual outlaw institutions. Graduates owe an aggregate of $1 trillion in student debt, borrowed at interest rates far above home-mortgage rates — all on the principle that universities could charge as much as they liked, given that students could borrow as much as they needed in federally guaranteed loans.
School Wasn’t Canceled for Bad Weather in 1882
Record-low temperatures caused by the Polar Vortex have forced schools across the country to close this week. Weather-related school cancellations tend to raise anxieties about whether we’re a nation of wimps. During President Obama’s first winter in Washington, he complained when his daughters’ school closed for bad weather: “We’re going to have to apply some flinty Chicago toughness to this town.” In response to this latest round of school closings, a Virginia mom sighed, “Hasn’t anyone heard of gloves, scarf and a hat when it’s cold?? Just bundle up–people do it all over the world. We are such wimps to cancel school.”
A story about a teacher assigned to a one-room schoolhouse in South Dakota in the 1880s will confirm suspicions that America has gone soft when it comes to dealing with the cold. The story is from These Happy Golden Years, the second-to-last book in Laura Ingalls Wilder’s beloved “Little House” series about growing up on the American frontier. It describes the protagonist, a 15-year-old teacher named Laura, traveling a half a mile in the snow to get to school:
How the College Bubble Will Pop In 1970, less than 1% of taxi drivers had college degrees. Four decades later, more than 15% do.
Richard Vedder & Christopher Denhart:
The American political class has long held that higher education is vital to individual and national success. The Obama administration has dubbed college “the ticket to the middle class,” and political leaders from Education Secretary Arne Duncan to Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke have hailed higher education as the best way to improve economic opportunity. Parents and high-school guidance counselors tend to agree.
Yet despite such exhortations, total college enrollment has fallen by 1.5% since 2012. What’s causing the decline? While changing demographics–specifically, a birth dearth in the mid-1990s–accounts for some of the shift, robust foreign enrollment offsets that lack. The answer is simple: The benefits of a degree are declining while costs rise.
A key measure of the benefits of a degree is the college graduate’s earning potential–and on this score, their advantage over high-school graduates is deteriorating. Since 2006, the gap between what the median college graduate earned compared with the median high-school graduate has narrowed by $1,387 for men over 25 working full time, a 5% fall. Women in the same category have fared worse, losing 7% of their income advantage ($1,496).
A college degree’s declining value is even more pronounced for younger Americans. According to data collected by the College Board, for those in the 25-34 age range the differential between college graduate and high school graduate earnings fell 11% for men, to $18,303 from $20,623. The decline for women was an extraordinary 19.7%, to $14,868 from $18,525.
November school board elections in N.J. could keep costs down
Okay, maybe he’s no shrinking violet, but it’s worth taking note that almost exactly two years ago today Christie signed A-4394/S-3148, a law that gives school districts the right to bypass school budget votes if they move school board member elections to November.
After years of dissent from the New Jersey Education Association and the NJ School Boards Association, the bill, mostly sponsored by Democrats in the Statehouse, passed quietly, forever changing the dynamics of school board politics and fiscal strategy. Final vote tallies were 34-3 in the Senate and 62-11 in the Assembly.
Wait: you mean school board elections used to be in April?
PISA’s China Problem Continues: A Response to Schleicher, Zhang, and Tucker
In October 2013, I posted an essay, “PISA’s China Problem,” that called on the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) to fully disclose its arrangement with China regarding Shanghai’s participation in the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA). The latest PISA scores were to be released in December, offering an excellent opportunity for the OECD to dispel the mystery surrounding Shanghai’s 2009 involvement with PISA. I noted that Shanghai, the wealthiest, most educated province in China, was the only mainland province officially participating in PISA 2009 and PISA 2012. Other data from rural areas of China had been talked about by PISA officials over the years, but never released to the public domain. I called on PISA to release those data.
When the latest PISA scores came out in December, nothing had changed. I followed up with a second essay. I again urged full transparency. I also challenged PISA’s portrayal of Shanghai as a “high equity” school system. An extensive literature–including excellent journalism and both qualitative and quantitative scholarship–documents the cruel effects of the hukou system on migrants in Shanghai. Hukou is an internal registration system in China that limits rural migrants’ access to urban public services, in particular, to schools. These migrants are Chinese citizens, mind you, not immigrants from other countries. They have simply moved from rural areas to China’s big cities, or, because the hukou is inherited, they were born in one of China’s big cities but because of their family’s rural hukou, have become second generation migrants in the eyes of the state.
Can Unions Save Adjuncts?
Last week, I wrote that collectively, faculty need to deal with the terrible market for professorships by producing fewer potential professors: admitting a lot fewer students to graduate school. Graduate school doesn’t exploit students the way that, say, a third-tier law school program does — the students are paid, not paying vast sums for degrees they can’t use. But by wildly overproducing graduate students, academia is doing something just as bad, in a different way: encouraging overoptimistic (OK, maybe arrogant) kids to spend their formative years in the labor market pursuing jobs they aren’t so likely to get, then hiring the excess students as essentially casual labor at low wages.
There are two criticisms I’ve received that seem worth responding to. The first is that I myself work in a profession that looks a lot like a tournament: a lucky few at the top, and a lot of hopefuls who don’t make it. That’s absolutely true. But I don’t encourage young people to seek jobs in the profession; I tell them the math is terrible and getting worse, and they should do something else. The economics of the industry are very bad, unless you are lucky enough to work for a place like Bloomberg News, which doesn’t depend on advertising. I certainly don’t get paid to train them for journalism jobs that they probably won’t get.
That said, most people don’t spend five or six or eight years just preparing to be eligible to get a job in journalism, and an additional four years or so cycling through post-docs before it becomes clear that that journalism job isn’t going to happen. Nor, when they are six years into their first permanent job, do they have a committee that meets to decide whether to fire them and put them back on the job market, quite possibly with very poor prospects. They don’t have to move to towns in the middle of nowhere or give up relationships because their partners will never be able to find work in the Ozarks. Female journalists do not have to put off starting a family until they’re pushing 40 because it would be insane to reproduce before the tenure committee approves them. The opportunity costs of trying to become a journalist are quite a bit lower than the opportunity costs of trying to become an academic.
How to Help College Students Graduate
AMERICAN students are enrolling in college in record numbers, but they’re also dropping out in droves. Barely half of those who start four-year colleges, and only a third of community college students, graduate. That’s one of the worst records among developed nations, and it’s a substantial drain on the economy. The American Institutes for Research estimates the cost of those dropouts, measured in lost earnings and taxes, at $4.5 billion.
Incalculable are the lost opportunities for social mobility and the stillborn professional careers.
There’s a remedy at hand, though, and it’s pretty straightforward. Nationwide, universities need to give undergraduates the care and attention akin to what’s lavished on students at elite institutions.
If that help is forthcoming, graduation rates more than double, according to several evaluations of an innovative program at the City University of New York’s community colleges.
Youth Misery Index Hits all time High
A Youth Misery Index that measures young Americans’ woes has skyrocketed under President Barack Obama and hit an all-time high.
The index, released Wednesday, was calculated by adding youth unemployment and average college loan debt figures with each person’s share of the national debt. While it has steadily grown over the decades, under Obama the figure has shot up dramatically, from 83.5 in 2009 to 98.6 in 2013.
The index has increased by 18.1 percent since Obama took office, the highest increase under any president, making Obama the worst president for youth economic opportunity, according to the nonprofit that released the figure.
“Young people are suffering under this economy,” said Ashley Pratte, program officer for Young America’s Foundation, which developed the index and calculates it annually using federal statistics. “They’re still living in their parent’s basements, unable to find full-time jobs that pay them what they need in order to pay back their debt.”
Youth unemployment in 2013 was 16.3 percent, and student loan debt came in at a record-breaking average of $29,400 last year, the foundation points out; what’s more, each person’s share of the roughly $17 trillion dollar national debt stands at its highest level ever: $52,948.
Madison Teachers Union “Fair Share” Members
Madison Teachers, Inc. Solidarity eNewsletter (PDF), via a kind Jeannie Kamholtz email:
MTI represents nearly 3,000 teachers in the Madison Metropolitan School District. Of that number, over 96% are members of their Union. That number has been rising since Governor Walker, as he described it, “dropped the bomb” on public employees and collective bargaining almost three years ago.
However, there are currently several hundred MMSD employees in the teacher bargaining unit who are not members of MTI. They choose to be “fair share” contributors – that is, they pay a maintenance fee to the Union for all of the rights and benefits MTI has negotiated for them and provides to them, even though they are not members of their Union. These individuals have no voice in what issues MTI pursues; how MTI is governed; and can’t vote on MTI contracts, or in the election of MTI officers.
Faculty Representatives in each school and work location receive, on a monthly basis, updated lists of members and fair share contributors. What can you do? Share this article with fair share teachers at your work location, and have a discussion about the many rights and benefits MTI has negotiated on their behalf over the last 45 years, e.g., a never-ending salary schedule, health, dental and life insurance, due process, retirement, TERP, leaves of absence, paid sick leave, paid holidays and FMLA integration, to name a few.
Patronage for Plutocrats: Why elite colleges with the fewest low-income students get the most work-study money.
Greg Noll, a senior at Columbia University, balances his engineering major with a federally subsidized “work-study” job at the university’s fitness center, where he fills spray bottles, wipes sweat off the machines, and picks up towels for twenty hours a week. The $9-an-hour wage he’s paid is underwritten by the federal work-study program, which was launched in 1964 to support low-income students who would not otherwise be able to afford college.
While Noll and his counterparts at Columbia and other pricey, top-tier private colleges and universities no doubt benefit from the program–Noll says he uses the money to buy books and food and to go out with his friends on the weekends–they are not necessarily the intended recipients of aid from the $1.2 billion federal program. Noll’s family, for instance, makes $140,000 a year, which he says, rightly, puts them squarely in the upper-middle class. In fact, researchers at the Community College Research Center at Teachers College, Columbia University, have found that only 43 percent of students who receive work study meet the federal definition of financial need as determined by whether they also receive Pell Grants. Work study “disproportionately benefits the students who need it the least,” says Rory O’Sullivan, research and policy director at the youth advocacy organization Young Invincibles.
A major source of the problem stems from the fact that the work-study program uses a fifty-year-old formula to determine how federal funds are allocated. Unlike other federal financial aid programs that distribute money according to how many students at a university actually need aid, money for the work-study program is based instead on how much a university received the previous year, and how much it charges for tuition.
How College Pricing Is Like Holiday Retail Sales
Higher education may seem like a different world, but universities in many ways have been working from the same playbook.
Savvier college-bound consumers know that the so-called “sticker price” of tuition and fees at a given college or university isn’t what many – or even most – students pay.
Take American University, where 74 percent of full-time freshmen got a grant or scholarship – essentially, a discount off the list price – for the 2011-2012 school year. Or Drexel University, where that figure was 98 percent.
At nearly 200 schools, 100 percent of full-time freshmen got a scholarship, as DePaul University’s Jon Boeckenstedt points out.
The Loneliness of the Long-Distance Reader
“TO read a novel is a difficult and complex art,” Virginia Woolf wrote in a 1925 essay, “How to Read a Book.” Today, with our powers of concentration atrophied by the staccato communication of the Internet and attention easily diverted to addictive entertainment on our phones and tablets, book-length reading is harder still.
It’s not just more difficult to find the time and focus that a book demands. Longstanding allies of the reader, professionals who have traditionally provided guidance for those picking up a book, are disappearing fast. The broad, inclusive conversation around interesting titles that such experts helped facilitate is likewise dissipating. Reading, always a solitary affair, is increasingly a lonely one.
A range of related factors have brought this to a head. Start with the publishing companies: Overall book sales have been anemic in recent years, declining 6 percent in the first half of 2013 alone. But the profits of publishers have remained largely intact; in the same period only one of what were then still the “big six” trade houses reported a decline on its bottom line. This is partly because of the higher margins on e-books. But it has also been achieved by publishers cutting costs, especially for mid-list titles.
Much at stake in Obama’s proposed ranking of colleges
Name a factoid about a college — best party school, most military-friendly, et cetera — and a magazine or website somewhere is probably ranking it.
The implication of those measures is usually some publicity.
But a new ratings system proposed by President Barack Obama would put more than a college’s reputation at stake.
The nation’s colleges would be pitted against one another on measures such as graduation rates, student debt and cost of attendance under the president’s proposed system, aimed at putting a rating to the value colleges provide for their tuition dollars.
Obama said the plan is intended to hold down the cost of college and steer federal loans and grants toward those schools that rate the best. The schools that come out on top could eventually be rewarded with a bigger piece of the federal funding pie.
10 Words to Cut From Your Writing
As Mark Twain famously wrote, “I didn’t have time to write a short letter, so I wrote a long one instead.” His point? Strong writing is lean writing.
When you want to make your writing more powerful, cut out words you don’t need–such as the 10 included in this post:
1. Just: The word “just” is a filler word that weakens your writing. Removing it rarely affects meaning, but rather, the deletion tightens a sentence.
2. Really: Using the word “really” is an example of writing the way you talk. It’s a verbal emphasis that doesn’t translate perfectly into text. In conversation, people use the word frequently, but in written content it’s unnecessary. Think about the difference between saying a rock is “hard” and “really hard,” for example. What does the word add? Better to cut it out to make your message stronger.
Eric Cantor vows fierce protection of school choice
Stephanie Simon & Maggie Severns:
House Majority Leader Eric Cantor vowed Wednesday to protect and promote school choice programs and attacked Democratic politicians, including New York Mayor Bill de Blasio, for seeking to block the growth of charter schools and voucher programs.
Long an advocate of school choice, Cantor used a speech at the Brookings Institution to vow that Republicans would defend what he called an “education revolution” that has shifted power away from traditional public schools and put it in the hands of parents. Many states now allow parents to get tax-funded vouchers to send their children to private or parochial schools or chose from an array of charter schools, which are publicly funded but privately run.
How Students Are Forced to Prop Up the Education Bubble
If there was going to be major action to reduce the $1 trillion in student debt–or at least the rate at which it’s increasing–it probably should have happened by now.
The conventional wisdom going into the election was that President Obama and the Democrats would have to galvanize the youth vote if they wanted a repeat of 2008. With nearly 20 percent of families, and 40 percent of young families, owing a slice of the education debt, the issue affects a large and growing constituency. And because existing student loan policy is so anti-student and pro-bank, Democrats could have proposed a number of commonsense, deficit-neutral reforms, even reforms that would have saved the government money. The stars were aligned for a major push.
Remarkably, it didn’t happen. Instead we saw dithering, half-measures, and compromises meant to reassure voters that politicians were aware of their suffering and that something was going to be done. The moves that were implemented did not address the core problem: the amount of money debtors will have to pay. For example, President Obama claimed credit for delaying a doubling of interest rates on federal loans from 3.4 to 6.8 percent, while, at the same time, ending interest grace periods for graduate and undergraduate students. The first measure is temporary and is expected to cost the government $6 billion; the second is permanent and will cost debtors an estimated $20 billion in the next decade alone. Despite his campaign rhetoric, President Obama has overseen an unparalleled growth of student debt, with around a third of the outstanding total accruing under his watch.
California students sue state over ineffective teachers
Mary C. Tillotson, via a kind reader:
California’s laws surrounding teacher tenure, dismissal, and layoffs violate the state’s constitution — specifically, students’ right to an equal opportunity to access quality education — say nine students suing the state. The trial is set to begin Jan. 27.
If they win, the effects could ripple across the country.
“I think any time that you see a genuine reform in California, you empower reformers everywhere in the country who realize if you can actually fix something like that in California, you can fix it anywhere,” said Ed Ring, executive director of the California Public Policy Center.
Plaintiffs argue that minority and poor students are most in need of effective teachers and least likely, in California, to be taught by them.
“Research has shown that inside the school building, nothing matters more than the quality of the teachers,” said Sandi Jacobs, vice president for National Council on Teacher Quality. “An effective teacher and a highly effective teacher make a really significant difference in the trajectory of their students, and the same is true in the negative capacity for an ineffective teacher.”
Other factors, like parents’ level of education, are also correlated with student performance, but as far as factors schools can control, teacher quality matters more than any other variable, she said.
“Wisconsin Together” – Merger Details Revealed
Having asked their national affiliates for permission, the Wisconsin Education Association Council and AFT-Wisconsin finalized the founding documents of a new merged state teachers’ union, to be called Wisconsin Together.
The representative bodies of both unions will vote on a new constitution and by-laws in April. If approved, the merger will go into effect on September 1.
AFT-Wisconsin has posted the full text of the documents on its web site, but here are a few of the highlights:
While Wisconsin Together will come into being in September 2014, it will have a two-year transition period during which the current WEAC president and the AFT-Wisconsin president will act as co-presidents.
One of the major differences between NEA affiliates and AFT affiliates is that the former practice term limits for executive officers while the latter do not. The new representative body of Wisconsin Together will decide the issue after September 2016.
Digest of Education Statistics 2012
Thomas Snyder & Sally Dillow (PDF):
The data in this volume were obtained from many different sources–including students and teachers, state education agencies, local elementary and secondary schools, and colleges and universities–using surveys and compilations of administrative records. Users should be cautious when comparing data from different sources. Differences in aspects such as procedures, timing, question phrasing, and interviewer training can affect the comparability of results across data sources.
Most of the tables present data from surveys conducted by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) or conducted by other agencies and organizations with support from NCES. Some tables also include other data published by federal and state agencies, private research organizations, or professional organizations. Brief descriptions of the surveys and other data sources used in this volume can be found in Appendix A: Guide to Sources. For each NCES and non-NCES data source, the Guide to Sources also provides information on where to obtain further details about that source.
Data are obtained primarily from two types of surveys: universe surveys and sample surveys. In universe surveys, information is collected from every member of the population. For example, in a survey regarding certain expenditures of public elementary and secondary schools, data would be obtained from each school district in the United States. When data from an entire population are available, estimates of the total population or a subpopulation are made by simply summing the units in the population or subpopulation. As a result, there is no sampling error, and observed differences are reported as true.
Finding New Meaning in Life Through PowerPoint
Lourdes del Castillo de Rumié, 77 years old and practically vibrating (because there is so much left to do!), thinks she may have found the secret to joyous old age: PowerPoint.
Yes, that PowerPoint: legendary time drain of consultants, bureaucrats and generals — the software that never fails to make simple things more complicated. But Mrs. del Castillo de Rumié has found that what makes it tedious for the young makes it marvelous for the ripened. After all, when you are old, though you lack for years ahead, you have all the hours in the world.
Mrs. del Castillo de Rumié wants to tell any older person she can to take the path she did a year and a half — and 175 or so PowerPoint presentations — ago, after many fulfilling decades baking wedding cakes and teaching informal art history classes to adults from her home in this lush Caribbean city. “You’re going to find so much happiness before you die,” she said.
She traces her late blossoming as a PowerPoint evangelist to bank visits in which the teller would ask for her email address. It was humiliating to confess she didn’t have one.
That bitter feeling is where the encounter with technology so often ends for the well-aged. It might have for Mrs. del Castillo de Rumié, too, had it not been for a friend whom she considered truly old.
25 sources of free public domain books
An updated list of sites that offer free public domain books in electronic and audio format.
Every year new publications enter public domain. That means their intellectual property rights have expired or are not applicable any longer.
The content of these works becomes available for public use. Anyone is free to use it – but also to reuse it, for instance publish a new edition. Therefore you may find in major ebookstores (Kindle, Nook, Kobo, iBook Store, or Google Play Books) public domain books that are not free.
Friday Interview: Government Fuels Higher Education ‘Arms Race
People of all political persuasions have identified significant problems plaguing the American system of higher education. President Obama outlined some reform ideas during a back-to-school tour of New York and Pennsylvania colleges. But Ohio University economist Richard Vedder, director of the Center for College Affordability and Productivity, believes the president’s proposals fall short in some important ways. During a visit to the Triangle, Vedder discussed higher education challenges with Mitch Kokai for Carolina Journal Radio. (Click here to find a station near you or to learn about the weekly CJ Radio podcast.)
Kokai: We have heard quite a bit about this issue of what’s wrong with higher ed, especially [when] the president made a big deal out of this. … First of all, you think that some of his ideas made some sense.
Vedder: Yeah, the president said one or two very sensible things. He said we need more transparency in higher education. That is to say people should have better information about the decisions they make. I don’t see how one could reasonably disagree with that. Indeed the federal government does have some data available that it could make available, such as earnings data on graduates. There’s a decent argument that can be made that that should be provided. So that part of his remarks didn’t bother me at all.
Another Unopposed Madison School Board Election
Madison School Board filings are in: Michael Flores and Wayne Strong in race for Seat 6. Board president Ed Hughes runs unopposed for 7.
— Molly Beck (@MollyBeckWSJ) January 7, 2014
Much more on Michael Flores, Wayne Strong & Ed Hughes three unopposed elections (!).
Diminished in wake of Act 10, 2 teachers unions explore merger
acing reduced membership, revenue and political power in the wake of 2011 legislation, Wisconsin’s two major state teachers unions appear poised to merge into a new organization called Wisconsin Together.
The merger would combine the Wisconsin Education Association Council, the state’s largest teachers union, and AFT-Wisconsin, a smaller union that includes technical college, higher education and state employees, according to new draft documents.
At the same time, a national educators group that promotes itself as an alternative to unions — and has the backing of some conservative-leaning organizations — is picking up new members in Wisconsin.
The developments underscore the changing landscape for Wisconsin teachers unions since the passage of Act 10, which limits collective bargaining and makes it more difficult for unions to collect dues.
After Act 10, WEAC has lost about a third of its approximately 98,000 members and AFT-Wisconsin is down to about 6,500 members from its peak of approximately 16,000, leaders of both organizations have reported.
According to their most recent federal tax filings, WEAC collected about $19.5 million in dues in 2011, and AFT-Wisconsin collected about $2 million. Both have downsized staff and expenses.
The initial governance documents of Wisconsin Together, which include a transition document, constitution and bylaws, have been posted on AFT-Wisconsin’s website for members of both organizations to peruse. A final vote on whether to merge will be taken at a special joint assembly in Green Bay on April 26.
Darien Top 10 of 2013: No. 1 — Special education
David DesRoches, via a kind reader:
Darien’s issues have highlighted a special education flaw that exists across the state and nation. The question over what is appropriate has drawn a deep divide among residents. Parents from several states and Connecticut towns have contacted The Times, saying that Darien’s problems happen everywhere, and in most cases, the problems are worse.
Sue Gamm, the Chicago attorney hired by the Board of Education to investigate how deep the special education problems went, told The Darien Times that her work in town was the most difficult job in her 40-plus year career. Gamm formerly was a top administrator for Chicago Public Schools and a division director for the U.S. Office of Civil Rights. She has performed similar duties in more than 50 school districts across the United States.
John Verre, the man charged with overhauling Darien’s special education program, has also noted the difficult challenge Darien presents.
“Darien is a particularly challenging combination of problems,” Verre told The Times shortly after he was hired in October. “It compares to the most challenging situation I’ve ever found.”
A number of people have resigned from their top-earning positions, including the schools’ superintendent, Steve Falcone, along with Matt Byrnes, a former assistant superintendent, Dick Huot, the finance director, and Antoinette Fornshell, the literacy coordinator. Most recently, one of the people who has been consistently named as having contributed to the illegal special education program, Liz Wesolowski, announced to fellow staff members she was leaving Darien for a position with Shelton Public Schools.
Fornshell and Wesolowski played key roles in the implementation of the district’s SRBI program, which Gamm criticized for its lack of data and poor implementation due to staff being poorly trained. There was also no manual for SRBI, which is an intervention program designed to give children extra help if they fall behind in their class work. It’s intended to prevent children from needing more expensive special education services, but critics say it is more often used to delay providing special ed to children with legally-defined disabilities.
Four ways for low-income schools to thrive, according to a remarkable study
For the past 31 years, since I stumbled across amazing things happening at Garfield High School in East Los Angeles, my main topic as an education writer has been schools whose low-income students have been raised to unexpected heights of academic achievement. There are many schools in the Washington area that have done that. What about those that haven’t?
By my count, in about 20 predominantly low-income high schools in the District and Prince George’s County, the passing rates on Advanced Placement exams have been stuck below 10 percent. Yet other high schools full of impoverished kids in those same two school districts have done better on the challenging college-level tests.
Why are some succeeding and others not?
The Eli and Edythe Broad Foundation has released a remarkable study answering these questions from a national perspective. It found six districts among contenders for its annual Broad Prize for Urban Education where black students in AP “were improving passing rates quickly enough to gain on their white peers while increasing or keeping participation levels steady.” They were: Cobb County and Fulton County in Georgia, the Garland Independent district in Texas, Jefferson County in Kentucky, Orange County in Florida and the San Diego Unified district in California. The researchers identified four reasons for their success:
1. Searching for more academic talent: In many cases, this meant enlarging gifted programs for younger students far beyond the designations based on high IQ scores that most districts use. In Fulton County, the settlement of a court-ordered desegregation plan in the early 2000s included a big expansion. The district went from two to 58 elementary schools with gifted-education teachers, and from 300 to almost 2,000 elementary school students getting gifted services.
2. Giving more high school students access to challenging courses: A surprising finding, at least to me, was that the move to smaller high schools in some urban districts reduced the variety of course offerings, including AP. I know of some small charter high schools that have plenty of AP courses, but I can see how smaller schools in big districts might be shortchanged. The researchers said: “San Diego has opened several small schools and is now moving back to large ones in part because of the lack of opportunities for specialized courses.” The districts doing well with AP tend to give PSAT tests to all students to identify the many who are overlooked for AP but whose test scores show they are ready. The researchers said that approach is based on this fact: “A College Board study showed only a 0.28 correlation between AP exam passage and grade point average, while the correlation with PSAT scores was 0.5 to 0.7.”
Madison 4.10.2014: Wrightslaw Special Education Law and Advocacy Conference with Pete Wright, Esq.
Wrights Law, via a kind reader:
Wrightslaw Special Education Law and Advocacy Training Conference, a Wrightslaw training program featuring Pete Wright, Esq., is being sponsored and organized by ParSEC Wisconsin, LLC., with Co-sponsors Integrated Development Services (IDS), Walbridge School, The Law Center for Children & Families and Wisconsin Family Ties. This is the first Wrightslaw conference in the state of Wisconsin!
The education crisis spreads to the professions. Watch the universities crack.
Today we look at the first signs of collapse in the business model of America’s universities. The For More Information section has a wealth of information about the crisis in education (and links to posts about the crisis in journalism).
Structural Change
More education as a solution for America
The universities act like vampires, bleeding their students
The law of supply and demand strikes back
Articles about the collapse of universities
For More Information
More education as a solution for America
Decades of falling real wages has sparked a frantic scramble by youth (and increasing numbers of older people) for undergraduate and advanced degrees. In July 2009 I wrote that this made sense for an individual — but could not work for a nation, and would not end well.
How Today’s Youth Navigate Identity, Intimacy, and Imagination in a Digital World
We’d all like to absolve our children of their bad behavior by blaming it on some pernicious influence or other. As Howard Gardner and Katie Davis document in “The App Generation,” there is plenty to forgive. They examine data showing that children have become less empathetic and more socially isolated, less imaginative and more hesitant to take risks.
Yet the authors make a common mistake. Like many others, they assume that because kids spend so much time with their gadgets, these are crucially important to children’s psychology and can explain all of their behavior. At times our phones (and not just our kids’) may indeed seem to reflect our quirks and our weaknesses, but if they do, the most natural explanation is that our weaknesses have shaped the technology’s development, not the other way around.
In Montgomery County schools, no answers yet for failed math exams
Montgomery County schools officials plan to survey students taking high school final exams in math next week about how they think about and prepare for the biggest test of the semester, as school leaders explore the causes of steep failure rates on the countywide tests.
The officials say they still have no clear answers for why a majority of 30,000 high school students in the high-performing district failed their finals in key math courses last year. The low grades came to public attention as data about the tests circulated in the spring, underscoring a problem that had gone on for years.
A work group studying the issue will make recommendations by March, said Erick J. Lang, associate superintendent for curriculum and instructional programs. A report was expected in November, but the issue has not been easy to unravel, he said.
Some parents and educators have suggested that the problem might be that students have been advanced too quickly in math courses or that they lack academic support. Many blame grading policies that leave students assuming that the test will not affect their course grades.
Online Teaching, Testing Spurs Calls for Faster School Connections, Revamp of Program
As public schools nationwide embrace instruction via iPads, laptops and other technologies, many are realizing they lack the necessary broadband speed to perform even simple functions. This is crimping classroom instruction as more teachers pull lesson plans off the Internet and use bandwidth-hungry programming such as video streaming and Skype.
An estimated 72% of public schools have connections that are too slow to take full advantage of digital learning, according to EducationSuperHighway, a nonprofit that tests school broadband speeds and works to upgrade Internet access. The average school has about the same speed as the average American home, while serving 200 times as many users, according to the Obama administration. Expanding high-speed Internet in schools involves upgrading wiring, expanding Wi-Fi capabilities or simply spending more money to purchase faster service.
Adding to the worries: 45 states and the District of Columbia adopted the new Common Core math and reading standards and most will take the new online assessments in the 2014-15 school year. The test results will be used to evaluate teachers, make student promotion and graduation decisions and rate schools.
“Just as people are getting excited about the power of what the Internet offers to students and teachers, they are running into the buzz saw of infrastructure,” said Evan Marwell, CEO of EducationSuperHighway.
Common Core Doesn’t Add Up to STEM Success
As a former member of the Common Core Validation Committee and the Massachusetts Board of Elementary and Secondary Education, I am one of the few mothers to have heard the full sales pitch for this latest educational reform, which has been adopted by 45 states.
I know the Common Core buzz words, from “deeper learning” and “critical thinking” to “fewer, clearer, and higher standards.” It all sounds impressive, but I’m worried that the students who study under these standards won’t receive anywhere near the quality of education that children in the U.S. did even a few years ago.
President Obama correctly noted in September 2012 that “leadership tomorrow depends on how we educate our students today–especially in science, technology, engineering and math.” He has placed a priority on increasing the number of students and teachers who are proficient in these vital STEM fields. And the president’s National Math and Science Initiative is strongly supported by people like Suzanne McCarron, president of the Exxon Mobil XOM -0.24% Foundation, who has said she wants to “inspire our nation’s youth to pursue STEM careers by capturing their interest at an early age.”
Yet the basic mission of Common Core, as Jason Zimba, its leading mathematics standards writer, explained at a videotaped board meeting in March 2010, is to provide students with enough mathematics to make them ready for a nonselective college–“not for STEM,” as he put it. During that meeting, he didn’t tell us why Common Core aimed so low in mathematics. But in a September 2013 article published in the Hechinger Report, an education news website affiliated with Columbia University’s Teachers College, Mr. Zimba admitted: “If you want to take calculus your freshman year in college, you will need to take more mathematics than is in the Common Core.”
Tale of two Kentucky schools: Barbourville gets $8,362 per student; Anchorage gets $19,927
Public schools in this Appalachian town pocked with shuttered factories and vacant storefronts got an average of $8,362 to spend on each student’s education in 2013, the least they had gotten in five years.
Several hours away, at the public K-8 school in the wealthy Jefferson County suburb of Anchorage, revenue rose slightly to $19,927 per student, more than twice as much as Barbourville’s.
Everything looks better in Anchorage: teachers’ salaries and experience levels, class sizes, textbooks, computer access, test scores and the future in general. After eighth grade, Anchorage students can go to a number of fine private academies. Or, if their parents desire, they can bypass Louisville’s sometimes troubled urban classrooms for public high school in affluent Oldham County, 10 miles down the road.
“The model we have here is really working,” said Anchorage school superintendent Kelley Ransdell.
In Barbourville, the locals are proud of their independent “city school,” as they call it, a small campus enrolling about 700 mostly poor children from preschool to 12th grade. But they don’t fool themselves about where it ranks.
There’s no money for pay raises and little for arts programs unless parents raise it themselves. There are a handful of desktop computers, outdated in the iPad era. There’s no state aid for textbooks, so the books on hand are few, old and worn. When new books became essential last year to teach modern “division math” at the elementary school, officials lifted $19,276 from the building repair fund.
Locally, Madison plans to spend about $15k/student during the 2013-2014 school year.
Teaching to the Big Questions – Changing the Framework of Higher Education
So much about education, from the classroom to the textbook has changed, largely due to educators setting a clear vision for the future. What initially began as a lecture-based style of teaching in the days of Greek philosophers has moved past teaching solely from the question and answer format. Engagement and creativity have found their way into the classroom, pushing students to think critically rather than just absorb knowledge. And in a world of iPads and Google Glass, educators too have had to find new ways to teach and adapt over the years, but the box can be pushed further if we allow it. We know the goal of all educators is to enhance the learning process, but can that goal be furthered by looking at new ways to approach classroom learning? The tried-and-true principles that have created the fundamentals of what a classroom education means are vital, but can also drive us into new ways to examine the educational process, rethink the concept of learning and forge new pathways for higher education success.
So how do we get to that next step of educational innovation? We as educators must build upon the current framework that drives our teaching and create a new space for innovation to take place. Consider today’s higher education framework, which revolves around the goal of engaging students in critical thinking, inquiry and thoughtful discussion. The method itself opens the door to creativity, illuminates ideas and stimulates conversation that may have never been considered. But are we satisfied with stopping there, or are we ready to take the next step in engaging students in the classroom, from where they live, where they work and in perspective to how they learn?
2013 Madison Summer School Report
The district provided a comprehensive extended learning summer school program, K-Ready through 12th grade, at ten sites and served 5,097 students. At each of the K-8 sites, there was direction by a principal, professional Leopold, Chavez, Black Hawk and Toki, and oral language development was offered at Blackhawk and Toki. The 4th grade promotion classes were held at each elementary school, and 8th grade promotion classes were held at the two middle school sites.
Students in grades K-2 who received a 1 or 2 on their report card in literacy, and students in grades 3-5 who received a 1 or 2 in math or literacy, were invited to attend SLA. The 6-7 grade students who received a GPA of 2.0 or lower, or a 1 or 2 on WKCE, were invited to attend SLA. As in 2012, students with report cards indicating behavioral concerns were invited to attend summer school. Additionally, the summer school criterion for grades 5K-7th included consideration for students receiving a 3 or 4 asterisk grade on their report card (an asterisk grade indicates the student receives modified curriculum). In total, the academic program served 2,910 students, ranging from those entering five-year-old kindergarten through 8th grade.
High school courses were offered for credit recovery, first-time credit, and electives including English/language arts, math, science, social studies, health, physical education, keyboarding, computer literacy, art, study skills, algebra prep, ACT/SAT prep, and work experience. The high school program served a total of 1,536 students, with 74 students having completed their graduation requirements at the end of the summer.
All academic summer school teachers received approximately 20 hours of professional development prior to the start of the six-week program. Kindergarten-Ready teachers as well as primary literacy and math teachers also had access to job embedded professional development. In 2013, there were 476 certified staff employed in SLA.
Jennifer Cheatham:
Key Enhancements for Summer School 2014
A) Provide teachers with a pay increase without increasing overall cost of summer school.
Teacher salary increase of 3% ($53,887).
B) Smaller Learning Environments: Create smaller learning environments, with fewer students per summer school site compared to previous years, to achieve the following: increase student access to high quality learning, increase the number of students who can walk to school, and reduce number of people in the building when temperatures are high. ($50,482)
C) Innovations: Pilot at Wright Middle School and Lindbergh Elementary School where students receive instruction in a familiar environment, from a familiar teacher. These school sites were selected based on identification as intense focus schools along with having high poverty rates when compared to the rest of the district. Pilot character building curriculum at Sandburg Elementary School. ($37,529)
D) Student Engagement: Increase student engagement with high quality curriculum and instruction along with incentives such as Friday pep rallies and afternoon MSCR fieldtrips. ($25,000)
E) High School Professional Development: First-time-offered, to increase quality of instruction and student engagement in learning. ($12,083)
F) Student Selection: Utilize an enhanced student selection process that better aligns with school’s multi-tiered systems of support (MTSS) so that student services intervention teams (SSIT) have time to problem solve, and recommend students for SLA. Recommendations are based on student grades and standardized assessment scores, such as a MAP score below the 25th percentile at grades 3-5, or a score of minimal on the WKCE in language arts, math, science, and social studies at grades 3-5. (no cost)
Estimated total cost: $185,709.00
Summer School Program Reductions
The following changes would allow enhancements to summer school and implementation of innovative pilots:
A) Professional development (PD): reduce PD days for teachers grades K-8 by one day. This change will save money and provide teachers with an extra day off of work before the start of summer school (save $49,344.60).
B) Materials reduction: the purchase of Mondo materials in 2013 allows for the reduction of general literacy curricular materials in 2014 (save $5,000).
C) Madison Virtual Campus (MVC): MVC is not a reimbursable summer school program as students are not in classroom seats. This program could be offered separate from summer school in the future (save $18,000).
D) Librarians: reduce 3 positions, assigning librarians to support two sites. Students will continue to have access to the expertise of the librarian and can utilize library resources including electronic equipment (save $12,903.84).
E) Reading Interventionists: reduce 8 positions, as summer school is a student intervention, it allows students additional learning time in literacy and math. With new Mondo materials and student data profiles, students can be grouped for the most effective instruction when appropriate (save $48,492).
F) PBS Coach: reduce 8 positions, combining the coach and interventionist positions to create one position (coach/interventionist) that supports teachers in setting up classes and school wide systems, along with providing individual student interventions. With smaller learning sites, there would be less need for two separate positions (save $24,408).
G) Literacy and Math Coach Positions: reduce from 16 to 5 positions, combining the role and purpose of the literacy and math coach. Each position supports two schools for both math and literacy. Teachers can meet weekly with literacy/math coach to plan and collaborate around curriculum and student needs (save $27,601.60).
Estimated Total Savings: $185,750.04
Strategic Framework:
The role of the Summer Learning Academy (SLA) is critical to preparing students for college career and community readiness. Research tells us that over 50% of the achievement gap between lower and higher income students is directly related to unequal learning opportunities over the summer (Alexander et al., 2007). Research based practices and interventions are utilized in SLA to increase opportunities for learning and to raise student achievement across the District (Odden & Archibald, 2008). The SLA is a valuable time for students to receive additional support in learning core concepts in literacy and math to move them toward MMSD benchmarks (Augustine et.al., 2013). SLA aligns with the following Madison Metropolitan School District (MMSD) Strategic Framework goals:
A) Every student is on-track to graduate as measured by student growth and achievement at key milestones. Milestones of reading by grade 3, proficiency in reading and math in grade 5, high school readiness in grade 8, college readiness in grade 11, and high school graduation and completion rate.
B) Every student has access to challenging and well-rounded education as measured by programmatic access and participation data. Access to fine arts and world languages, extra-curricular and co-curricular activities, and advanced coursework.
The School

UFT calls for new revenue
The United Federation of Teachers will make a push to raise taxes in New York City to fund universal pre-K “one of the main pieces in our legislative package this year,” the union’s president, Michael Mulgrew, told Capital. Republicans in the State Senate and Democratic Gov. Andrew Cuomo have so far declined to embrace the idea, citing an openness to the program but a reluctance to raise taxes. “There might be different ideas about this, but right now, this is the idea we are supporting,” said Mulgrew, adding that “an additional revenue source” is needed. “It should not come out of any revenue source that we currently have. The state budget is tight enough as it is; we are still not past the economic damage of this recession.”
College Football Recruiting
It was ayy very tuff decision but had to do wat was best for me #OnWisconsin#letsgetit#hann pic.twitter.com/FvkPsHD3Ld
— craig evans (@craigevans18) January 4, 2014
Central Valley California School District Develops Education Success Formula; Graduates 94% of Hispanic Students; Spends 50% less than Madison per student
When Yadir Sanchez arrived in this San Joaquin Valley agricultural town at age 5, she joined a well-traveled path to academic failure that children of other Mexican farmworkers had been on for years.
Students like Sanchez – poor, Hispanic and barely bilingual – routinely fell through the cracks in the Sanger Unified School District, which had one of the worst records in the state. Lacking basic math and English skills, students were pushed into trades or allowed to drop out.
Sanchez appeared to be no different, speaking only Spanish in kindergarten and struggling with English until fifth grade.
But something remarkable happened that lifted the fortunes of Sanchez and so many like her. The district reinvented itself, making huge strides by shaking up the way teachers worked with students, parents and each other.
In 2012, the district graduated 94 percent of its Hispanic students, 20 percentage points higher than the state average and similar districts. Its Hispanic dropout rate was just 3 percent, compared to 18 percent statewide.
Sanger’s success is still the exception across California. While Latinos are poised to become the state’s largest ethnic group in 2014, they continue to score lower on standardized tests, graduate at lower rates and drop out more often than other students.
Gov. Jerry Brown recently signed legislation that will funnel more money to help poorer schools, but Sanger’s success serves as a model for how a district made vast gains despite budget cuts.
Take Sanger Unified, for one. Six years ago, the achievement gap between whites in Sanger and whites in Fresno stood at 57 points on the API test. Today, the gap has widened to 78 points. Whites in Sanger score 892 points on the API compared to 814 points for whites in Fresno. The gap between Latinos, by far the majority population in both districts, is even wider. Latinos in Sanger score 811 on the API compared to 708 for Latinos in Fresno. The most stunning gap — a gulf really — can be seen in the black community. Blacks in Sanger score 821 while blacks in Fresno score 665. That’s a 156-point difference in two districts whose headquarters sit a few miles apart.
Sanger will spend $80,795,175 for 11,000 students during the 2013-2014 school year (PDF Budget document), or $7,345 per student. That is about half the amount Madison spends per student (!) and similar to the national average.
Sanger’s “Academic Performance Index“. Demographic comparison: Sanger | Madison.
Sanger high school offers 14 AP courses.
Madison’s substantial per student spending continues, despite long term disastrous reading results.
The Humanities Have Forgotten Their Humanity When Shakespeare lost out to ‘rubrics of gender, sexuality, race, and class’ at UCLA, something vital was harmed.
In 2011, the University of California at Los Angeles wrecked its English major. Such a development may seem insignificant, compared with, say, the federal takeover of health care. It is not. What happened at UCLA is part of a momentous shift that bears on our relationship to the past–and to civilization itself.
Until 2011, students majoring in English at UCLA had to take one course in Chaucer, two in Shakespeare, and one in Milton–the cornerstones of English literature. Following a revolt of the junior faculty, however, during which it was announced that Shakespeare was part of the “Empire,” UCLA junked these individual author requirements. It replaced them with a mandate that all English majors take a total of three courses in the following four areas: Gender, Race, Ethnicity, Disability and Sexuality Studies; Imperial, Transnational, and Postcolonial Studies; genre studies, interdisciplinary studies, and critical theory; or creative writing.
In other words, the UCLA faculty was now officially indifferent to whether an English major had ever read a word of Chaucer, Milton or Shakespeare, but the department was determined to expose students, according to the course catalog, to “alternative rubrics of gender, sexuality, race, and class.”
Cheating 101 at Middleton High School
Late last semester, as students were packing up their backpacks one final time before winter break, Middleton High School principal Denise Herrmann and assistant principal Lisa Jondle were co-authoring a note home to parents informing them of a widespread cheating scandal involving nearly 250 calculus students at the school. In the letter, they explain the scope of the incidents, including the taking, sharing and selling of cell phone photos of exam questions.
The administrators close their letter by saying, “We feel fortunate to have a wonderful student body (at Middleton High) whose academic record on multiple assessments is top-notch. We are hopeful that through our collaborative efforts we can determine the root cause of talented students choosing to participate in dishonest academic practices. In January, we will host a series of focus groups including staff, students and parents to problem-solve short- and long-term solutions.”
Ms. Herrmann and Ms. Jondle, I think I can save you lots of time on focus groups. I’m the parent of a high school student, albeit in Madison, and I have a pretty good inkling on the “root cause” of why “talented students” would choose to cheat.
It’s because these students are reminded every day that every test matters. These kids all have access to on-line forums like College Confidentialthat tell them, in no uncertain terms, that if they want to get into a top-ranked college or university, they better take the most rigorous high school curriculum available to them, which means calculus, perhaps even AP calc. But to get to calculus at all in high school, a year of math has to be skipped somewhere. The standard high school sequence has pre-calc as the 12th grade norm — so the jockeying for top dog status starts in elementary school.
Degrees of Value: Making College Pay Off; For Too Many Americans, College Today Isn’t Worth It
In the field of higher education, reality is outrunning parody. A recent feature on the satire website the Onion proclaimed, “30-Year-Old Has Earned $11 More Than He Would Have Without College Education.” Allowing for tuition, interest on student loans, and four years of foregone income while in school, the fictional student “Patrick Moorhouse” wasn’t much better off. His years of stress and study, the article japed, “have been more or less a financial wash.”
“Patrick” shouldn’t feel too bad. Many college graduates would be happy to be $11 ahead instead of thousands, or hundreds of thousands, behind. The credit-driven higher education bubble of the past several decades has left legions of students deep in debt without improving their job prospects. To make college a good value again, today’s parents and students need to be skeptical, frugal and demanding. There is no single solution to what ails higher education in the U.S., but changes are beginning to emerge, from outsourcing to online education, and they could transform the system.
Though the GI Bill converted college from a privilege of the rich to a middle-class expectation, the higher education bubble really began in the 1970s, as colleges that had expanded to serve the baby boom saw the tide of students threatening to ebb. Congress came to the rescue with federally funded student aid, like Pell Grants and, in vastly greater dollar amounts, student loans.
Related: UW Law School 2013 Graduation Speech by Judge Barbara Crabb.
Of (Former Teacher) Ronn Johnson, shattered trust and lessons learned
What really matters when it comes to the quality of education? It’s not whether a school is public, private or charter, said a speaker at a panel discussion I moderated.
“It’s about what happens with that personal relationship between that young person and that teacher when the door closes.”
The speaker said he had seen success at schools where he taught early in his career because of great leadership, and he aimed to be that kind of leader when he became a principal.
The best part of his job, he said, “was introducing myself and saying I was the proudest principal in America.”
His school didn’t have as much money as some schools, and it served students with a lot of needs. But, he said, “we did more with less because you had people who cared, and we were going to make it happen one way or the other.”
Oh, Ronn Johnson. What you said at that session 10 months ago was all true. As principal of Young Leaders Academy, an independent charter school in the YMCA branch at W. North and N. Teutonia avenues, you had accomplishments that deserved praise.
The school had a distinctive program, a lot of energy, solid structure and a record of decent, although not great, student achievement since it opened in 2002.
“Graph of the Year”
Knowledge may be priceless, but a higher education is clearly not. University administrators keep hiking tuition, the wages of graduates keep falling, and a whole generation of Americans is struggling under the crushing burden of debt as they postpone their dreams for a tomorrow that may never come.
‘Skin in the Game’ on Loans
A group of Senate Democrats announced Thursday a new push to provide student loan borrowers with more protections and hold colleges more accountable for loan defaults.
In a call with reporters, Senators Richard Durbin of Illlinois, Jack Reed of Rhode Island and Elizabeth Warren of Massachusetts highlighted a package of new and existing proposals aimed at reducing the burden of student debt. Durbin acknowledged that the senators had had “limited success” in getting Republican support for the measures, but said they will be a centerpiece of the Democratic agenda in the Senate in 2014.
One of the more controversial new proposals, to be introduced by Reed, would require colleges with high student loan default rates to pay a penalty to the government that is proportional to the defaulted debt.
Raising Children With an Attitude of Gratitude
At the Branstens’ modern white dining table, the family holds hands for their nightly ritual.
Arielle, 8 years old, says she’s thankful for her late grandfather, Horace, and how funny he was. “I’m missing him,” she says. Her third-grade pal, over for dinner, chimes in, “I’m grateful for the sausages.” Leela, who works for an education nonprofit, and her attorney husband Peter, burst into smiles. The San Francisco couple couldn’t have scripted this better. Appreciation for things big and small–that’s why they do this.
Giving thanks is no longer just holiday fare. A field of research on gratitude in kids is emerging, and early findings indicate parents’ instincts to elevate the topic are spot-on. Concrete benefits come to kids who literally count their blessings.
Gratitude works like a muscle. Take time to recognize good fortune, and feelings of appreciation can increase. Even more, those who are less grateful gain the most from a concerted effort. “Gratitude treatments are most effective in those least grateful,” says Eastern Washington University psychology professor Philip Watkins.
Among a group of 122 elementary school kids taught a weeklong curriculum on concepts around giving, gratitude grew, according to a study due to be published in 2014 in School Psychology Review. The heightened thankfulness translated into action: 44% of the kids in the curriculum opted to write thank-you notes when given the choice following a PTA presentation. In the control group, 25% wrote notes.
Academic research The useful science?
DO ACADEMIC economists focus too much on America? Yes: a sample of 76,000 papers published between 1985 and 2005 shows that econo-nerds are infatuated with the “land of the free”.
There were more papers focused on the United States than on Europe, Asia, Latin America, the Middle East and Africa combined (see chart). And for the world’s top-five economics journals–where publication of a paper can push a young researcher towards a full professorship–the imbalance is yet more marked. Even accounting for the fact that lots of economic research (and often the best) comes from American universities, the bias persists.
The world’s poorest countries are effectively ignored by the profession. From 1985 to 2005 Burundi was the subject of just four papers. The American Economic Review, the holy grail for many academics, published one paper on India, by some measures the world’s third-largest economy, every two years.
The US should encourage Arabic language students, not criminalise them
In August of 2009, Nicholas George boarded a flight from Philadelphia to Los Angeles. He was on his way back to university at Pomona College.
While he was going through airport security, a Transportation Security Administration (TSA) agent discovered Arabic language flashcards in his carry-on luggage.
He was pulled aside, detained and interrogated for five hours – two of which were allegedly spent in handcuffs.
“Do you know who did 9/11?” one of the TSA agents allegedly asked.
“Osama bin Laden,” George responded.
“Do you know what language he spoke?”
“Arabic”
“Do you see why these cards are suspicious?”
Nicholas George was released when it became clear that neither he nor his flashcards posed a threat to US national security. George went on to try to sue the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) for violating his first and fifth amendment rights. Last week -more than four years after the incident – the case was dismissed.
In other words, it is legal and legitimate to detain and interrogate a traveller on the grounds of suspicion from Arabic language flashcards alone.
As an Arab-American who came of age post-9/11, I am frustratingly resigned to the well-documented fact that airports are often hostile places for Arab and Muslim-Americans. Watching my white father effortlessly glide through airport security while my brown mother is frequently “randomly selected” to be stopped, searched and asked to show the contents of her bag is evidence of this in and of itself. However, detaining a traveller for Arabic language flashcards brings this flagrant racism and criminalization of all things Arab, Middle Eastern and Muslim (as the three are often conflated) to a whole new level.
2013 in Education
A week ago I published my list of top ten stories–highs and lows–in higher education in 2013. I was generously rewarded when Powerline picked it as #2 in its list of top ten top lists. But there are still some minutes left in the season of top ten lists, which ought to extend to January 6, the traditional date of Epiphany. Then we have the (lower case) epiphany that it is time to get on with things.
My new list is mainly about people who did something original, creative, noteworthy, or surprising in 2013 whose accomplishments deserve a little more attention. I set out to list only positive accomplishments, but unfortunately a few infamies sneaked in. What follows are the top ten best surprises: the gifts you didn’t know you wanted until you unwrapped the package. First up:
1. Thug Notes. This YouTube site debuted in June, with Sparky Sweets, Ph.D. explicating Dostoyevsky’s Crime and Punishment. Since then, Dr. Sweets has offered his taut plot summaries and explications de texte for Hamlet, The Great Gatsby, Pride and Prejudice, The Sun Also Rises, The Inferno, Heart of Darkness, Moby Dick, and many more canonical works of literature. The intro to each piece is a pastiche of Masterpiece Theater, the camera scanning across a shelf of beautifully bound volumes accompanied by Bach’s Brandenburg Concerto 3, then cutting to a book-lined study in which Dr. Sweets sits in a comfortable chair, in gold-chained muscle shirt and do-rag, announcing this week’s selection. “What’s happening, yo? This week on Thug Notes we get regal with Hamlet by William Shakespeare.”
This could have been a one-off parody, hitting the two birds of pretentious British TV and mass-marketed cheat sheets with one gangsta, but Dr. Sweets has developed the idea further. His wordplay (Hamlet serves up “Elizabethan hater-ade”) is smart and his rapid-fire analyses delivered in character as a street-smart thug really are smart.
The series has conferred minor celebrity on Dr. Sweets. He takes what he does seriously, telling one interviewer that he created Thug Notes because “literature is enshrouded by a veil of unnecessarily pedantic terminology and intellectual one-upmanship,” and that his calling is to bring it to “people on the opposite side of the social stratum.” Dr. Sweets holds that “the gift of literature is universal.”
2. Leaked! Harvard’s Grading Rubric. A+++ to Nathaniel Stein, who published this satire of Harvard’s grade inflation in The New York Times. Presented as a memorandum from the Dean of Harvard College, Leaked! purports to explain the criteria that qualify a term paper for an A+, including the stipulation that the “The paper contains few, if any, death threats.” Grades of A++ or A+++ are designated “A+ with garlands.”
3. Farewell. College presidents come and go and typically there is there is no reason to celebrate one’s leaving. The next is likely to be as bad or worse. But occasionally one comes and stays. And stays. And stays. In June Gordon Gee announced his retirement as president of Ohio State University. Gee became president of West Virginia University in 1981 at age 37, and then served in succession as president of the University of Colorado, Ohio State University, Brown University, Vanderbilt University, and then back to Ohio State again. He distinguished himself mainly by his soaring remuneration, becoming by 2003 the highest paid university president in the U.S. (and no doubt the world) with compensation of over $1.3 million.
It would difficult to understate Gee’s other accomplishments, though he did manage an uncommonly graceless departure by sneering at Roman Catholics and the University of Notre Dame (“those Damn Catholics”) and mocking other colleges. The remarks didn’t sit well with the Ohio State board of trustees. But let’s let Dr. Gee settle into his well-upholstered retirement. Few men have profited more from higher education than he.
College Students’ Thesis Topics Are Hilarious, Depressing
Even the most ardent academic must concede that there’s something darkly funny about devoting years of one’s life to a thesis question so abstruse that no one else had ever cared enough to ask it–and then answering it at such great length that few will ever care to read it.
Enter lolmythesis.com, a Tumblr started by a Harvard senior procrastinating on her own undergraduate thesis. The blog encourages fellow undergrad and graduate students to distill all their hard-won knowledge into a single sentence–a sort of self-mocking tl;dr of their years-long labor of love/hate. The concept is reminiscent of #overlyhonestmethods, the brilliant hashtag game that swept science-Twitter earlier this year. If lolmythesis is a little less piercingly witty than its forebear, it’s also more accessible to non-academics. And it’s been flooded with submissions: Three weeks after it launched, the blog stands at 54 pages’ worth of academic one-liners.
How College Pricing Is Like Holiday Retail Sales
You know all those seemingly great sales during the holidays? It turns out, they are often a “carefully engineered illusion.” A recent piece in the Wall Street Journal defines what it calls “retail theater,” noting that often the discounts being offered to bargain-conscious consumers are carefully planned out by retailers from the start:
2014: The year of universal proficiency
– No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, section 1111(2)(F)
Those of us who fail to heed the lessons of history are destined to repeat it. So let us take this moment, as we enter the New Year, to remember the hubris that caused reformers, policy elites, members of Congress, and the George W. Bush Administration to set the goal of attaining “universal proficiency” in reading and math by 2014.
The next time someone says that we must ensure that all students are college and career ready…remember “universal proficiency by 2014.”
The next time someone says that we must place a highly effective teacher in every classroom…remember “universal proficiency by 2014.”
The next time someone says that we must eradicate childhood poverty…remember “universal proficiency by 2014.”
At-risk youth offered DJ and music production skills
Terrence lives at The Optimist Youth Homes & Family Services center in Highland Park. He’s trying to scratch a record for the first time.
Josh Winkler, an Atlanta DJ better known as Klever, says Terrence was impressive for his first attempt at DJing.
“He’s doing good. I think the most important thing right now is being on beat, the rhythm part,” he said. “And confidence really, man. Because at first all the guys were kind of looking, and scared. But now, look at ’em, they’re all wanting to do it, so overcoming all that stuff means more to me than trying to learn a scratch.”
Klever was one of about a dozen prominent DJs and music producers stationed at five tables set up around the gym, offering lessons in scratching, beat making, and other basic tricks of the trade.
Online Education Commentary & Expectations
One year ago, many were pointing to the growth of massive open online courses, or MOOCs, as the most important trend in higher education. Many saw the rapid expansion of MOOCs as a higher education revolution that would help address two long-vexing problems: access for underserved students and cost.
In theory, students saddled by rising debt and unable to tap into the best schools would be able to take free classes from rock star professors at elite schools via Udacity, edX, Coursera and other MOOC platforms.
But if 2012 was the “Year of the MOOC,” as The New York Times famously called it, 2013 might be dubbed the year that online education fell back to earth. Faculty at several institutions rebelled against the rapid expansion of online learning — and the nation’s largest MOOC providers are responding.
Earlier this year, San Jose State University partnered with Udacity to offer several types of for-credit MOOC classes at low cost. The partnership was announced in January with lots of enthusiastic publicity, including a plug from California Gov. Jerry Brown, who said MOOC experiments are central to democratizing education.
Substantive change takes more than a year, but will likely happen faster than Oda expects.
Recommended Parent Reading
Is your teenage son camped out in the basement surrounded by pizza boxes and Red Bull, playing video games 24/7 ? Does your daughter lie around ‘reading’ tabloid magazines or watching the Kardashians on her laptop until it’s time to eat when she graciously comes in to pick at the food you’ve spent the day making? Is your fridge completely empty because the TV-watching boy has eaten everything before noon and is now complaining of hunger?
Was your holiday gift-opening tranquility sabotaged by your girl who became enraged that her BFF (who she texted nonstop while opening every painstakingly wrapped item) got the iPad while she’s going to have to make do with an iPhone 5S FOR GOD’S SAKE?
Take solace mums and dads: Gigi Levangie Grazer has written just the book for you.
Seven Deadlies: A Cautionary Talea is a book of short stories set in the Los Angeles Mark Frost Academy, where kids and parents embody every tabloid, reality show or gossip column attribute you know. It’s a view of humanity (if that could possibly be the right word) seen through the eyes of narrator, Perry Gonzales, a 14-year-old Hispanic scholarship student. Perry gets right inside the mansions of her academic peers thanks to her tutoring skills. Like most of the regulars of these homes, she’s a paid Latina. But the joke is, she has something all of these kids seem to lack: brains.
Here she is on the moms at Mark Frost Academy:
Age of Ignorance
Widespread ignorance bordering on idiocy is our new national goal. It’s no use pretending otherwise and telling us, as Thomas Friedman did in the Times a few days ago, that educated people are the nation’s most valuable resources. Sure, they are, but do we still want them? It doesn’t look to me as if we do. The ideal citizen of a politically corrupt state, such as the one we now have, is a gullible dolt unable to tell truth from bullshit.
An educated, well-informed population, the kind that a functioning democracy requires, would be difficult to lie to, and could not be led by the nose by the various vested interests running amok in this country. Most of our politicians and their political advisers and lobbyists would find themselves unemployed, and so would the gasbags who pass themselves off as our opinion makers. Luckily for them, nothing so catastrophic, even though perfectly well-deserved and widely-welcome, has a remote chance of occurring any time soon. For starters, there’s more money to be made from the ignorant than the enlightened, and deceiving Americans is one of the few growing home industries we still have in this country. A truly educated populace would be bad, both for politicians and for business.
It took years of indifference and stupidity to make us as ignorant as we are today. Anyone who has taught college over the last forty years, as I have, can tell you how much less students coming out of high school know every year. At first it was shocking, but it no longer surprises any college instructor that the nice and eager young people enrolled in your classes have no ability to grasp most of the material being taught. Teaching American literature, as I have been doing, has become harder and harder in recent years, since the students read little literature before coming to college and often lack the most basic historical information about the period in which the novel or the poem was written, including what important ideas and issues occupied thinking people at the time.
Gifted in Math, and Poor
New York Times
To the Editor:
Re “Even Gifted Students Can’t Keep Up” (“Numbers Crunch” series, editorial, Dec. 15): Educators know that when the curriculum is set at an optimal difficulty level, students learn to persist, attend carefully and gain self-confidence. For mathematically gifted students, the curriculum must move more quickly and in greater depth so that they can become disciplined, resilient students.
When the mathematically gifted sons and daughters of affluent, well-educated parents are not challenged, their parents spend considerable amounts of time and money finding tutors, summer programs and online courses. As a psychologist who has worked for more than 20 years with the families of gifted students, I have seen how much time and money is required for this effort.
For mathematically gifted students from poorer families, there is neither the time nor the money to seek educational opportunities outside the public schools. A weak public school system without flexibility or adequate challenge can seriously limit the educational experiences and lifetime employment opportunities of these students. A weak public school system ultimately limits quality education to those few whose parents can pay for it privately.
JULIA B. OSBORN
Brooklyn, Dec. 19, 2013
Related: “They’re all rich, white kids and they’ll do just fine — NOT!”
Many private college president make $1 million
Presidents at 42 private colleges scaled the $1 million annual mark in total pay and benefits in 2011–a slight bump from the year before, according to a survey based on the latest federal tax information from the 500 private schools with the largest endowments.
Total median compensation was $410,523, or 3.2 percent more.
A high salary can be a sign of prestige for presidents, but it also opens them to criticism. The Obama administration and consumers are pressuring schools to rein in tuition costs, increase graduation rates and strengthen the value of a diploma.
The Chronicle of Higher Education’s report released Sunday used federal tax information from 2011, the most recent available.
The top earner in the survey was Robert J. Zimmer, the president of the University of Chicago. His base pay was $918,000, but his total compensation was $3.4 million. About 40 percent of his total earnings stem from deferred compensation–a retention tool commonly used to keep college presidents on the job longer, according to the Chronicle.
We’re Constantly in Fear: The life of a part-time professor
Several weeks ago, I approached my friend Jenny (not her real name) for information on how to get hooked up with a teaching position at one of the local community colleges. Jenny currently works at five different schools — three community colleges, one private university, and one online university. My guess was that if anyone could point me in the right direction, it would be her.
I always figured I’d end up in academia. While in graduate school, I taught a semester of undergraduate creative writing, but then after a few years in elementary-school classrooms, I gave up on the idea of teaching. Still, I keep it in my back pocket as a go-to if I absolutely have to do it again.
I approached Jenny not because things have gotten dire, but that the scramble from one freelance writing job to another is beginning to take its toll. I figure why not take it easy for a while, supplement my income with a consistent, guaranteed paycheck and balance out the uncertainty of the freelance life. And, yes, after years of living hand-to-mouth, I have lofty dreams of tweed, sabbaticals, retirement plans, and picking up the check while drinking beer with graduate students.
But, halfway through our conversation, after we’ve covered whom to contact, what to do with my résumé, and which schools not to bother with, Jenny knocks my professorial fantasy on its ass.
Geography and American Destiny
Imagine that North America was somehow flipped, so that East was West and West was East. The continent’s West Coast, as we know it, would face the Atlantic and Europe. That would have greatly affected the history of this country.
Before the Industrial Revolution, bulk goods such as grain and lumber moved by water or they did not move. People and news also traveled fastest by boat.
The East Coast is rich in harbors large and small. Its many rivers are navigable, some for hundreds of miles inland.
The Pacific Coast of the U.S. is practically a blank wall, with high mountains that often hug the coastline. It has only three good natural harbors along its entire length–Puget Sound, San Francisco Bay, and San Diego Bay. Only one river that flows into the Pacific, the Columbia, has deep water for more than a few miles inland. Its mouth, however, is blocked by a sand bar that has brought many a ship to grief.
Settling along the West Coast would have been difficult, developing a viable economy there equally so. But because of the East Coast’s water communications, commerce thrived in the British colonies and the settlements served as bases for exploring and occupying the interior. A further advantage: The wide alluvial plains east of the Appalachians made farming easy.
How to get into UC Berkeley after failing in High School- Dorian’s Story
When I graduated high school, I had a cumulative grade point average of 2.1, hadn’t taken any advanced placement classes or the SATs, and didn’t apply to any colleges. Five years later, I graduated from the nation’s best public university: UC Berkeley. Here’s the story of what happened.
I grew up in Laguna Hills and Malibu with an older sister and loving parents. My father was a drywall contractor and my mother stayed home to take care of us while working part time as a nanny/ housekeeper. While growing up in El Salvador, my mom ended her schooling before graduating middle school. Similarly, my father dropped out of high school in San Diego to work and support his parents. They worked incredibly hard to support my sister and I.
College Football Coach Investigated for paying a Player’s Tutor
On Thursday, recently departed Huskies coach Steve Sarkisian told ESPNLosAngeles.com he was informed last week that Lupoi was being investigated for potential violations of NCAA rules after he allegedly paid for tutoring and online classes for a recruit. Sarkisian said the investigation likely will prevent Lupoi from getting a job on USC’s staff.
“I learned of the allegations this past Friday and I was obviously surprised by them,” Sarkisian said. “I think this potential allegation could affect not only Tosh’s future at USC but moving forward anywhere.”
The Times reported on Wednesday that Washington and USC were looking into the allegations against Lupoi, who is in his second year as the Huskies’ defensive line coach. He was hired in 2012 by Sarkisian, who was Washington’s head coach at the time of the potential violations. Sarkisian left the Huskies for the head-coaching job at USC earlier this month.
The year in education: Wins, losses and unsung heroes
Did not much happen? Consider the waves of flat data on how kids are doing.
It may take a while to sort out this year. But that won’t stop me from offering a few awards for, um, distinguished something or other.
Most jaw-dropping moment of the year: Adding into the state budget a statewide private school voucher program. Literally in the middle of the night, with no public hearings or advance word, this emerged from a backroom deal by key Republicans and voucher lobbyists. It is limited to a small number of students now. But if Gov. Scott Walker wins re-election in November and Republicans keep control of the Assembly and Senate, there is a strong possibility vouchers will become available widely in Wisconsin.
Education person of the year: Milwaukee Public Schools Superintendent Gregory Thornton. In his fourth year, Thornton and his powerful behind-the-scenes chief of staff, Naomi Gubernick, are at the center of so much. Thornton is both tough and a nice guy, each an asset in his work. He is good at spreading optimism. He’s got plans and goals that sound good and, in many ways, are. And he’s politically adept. But he is a perplexing figure who seems eager not to be challenged by subordinates or pesky people like reporters. A “gotcha” style of management by bosses seems to be pretty common in MPS, undermining morale.
The Same Old Same Old Award: Waves of test data and a second round of the new statewide school report cards told us that the Have kids are doing OK in Wisconsin and the Have Not kids are not. As for the Haves, they’re not doing so well that we shouldn’t be talking about how to give their schools a fresh burst of energy, and that seems to be happening in some places. As for the Have Nots, so little has changed, despite so much effort. There are a few bright spots on the scene, and we need to do more to grow them. Overall, we’ve got to find paths that are better than the ones we’ve been on.
The Gone-At-Last Award (Hopefully To Stay): Dr. Brenda Noach Choice School. This was one of a handful of voucher schools that was a model of what’s wrong with oversight of Milwaukee’s nationally important program to pay for children in private schools. The school was “an abomination,” as one strongly pro-voucher leader told me recently. But for years, it fended off attempts to cut off its funding. Finally, this year, after receiving $7,299,749 in public money over a dozen years, the Brenda Noach school ran out of options — it couldn’t find anyone to accredit it. But that doesn’t mean the school leaders aren’t shopping for accreditation to re-open for next year.
Millions of American Students Need to Learn English
“In the words of teachers themselves, they don’t feel qualified,” Gandara said.
About 40 percent of American teachers have ELL students in their classrooms, but only a third of these teachers have training for them. However, this training usually amounts to just four hours over five years, said Granada on Saturday, laying the ground for a panel of ELL experts and teachers discussing why intensive efforts have failed to close the gaps of ELL students.
“This is really difficult to do,” said Gandara, quoting a bilingual teacher who still struggles to keep ELL students on track despite speaking Spanish, the native language of three-fourths of America’s ELL students.
Expensive cities are killing creativity
On May 5, musician Patti Smith was asked what advice she had for young people trying to make it in New York City. The long-time New Yorker’s take? Get out. “New York has closed itself off to the young and the struggling,” she said. “New York City has been taken away from you.”
Smith was not the only New Yorker to reject the city that had nurtured artists for decades. In October, musician David Byrne argued that “the cultural part of the city – the mind – has been usurped by the top 1 percent”. Under Michael Bloomberg, New York’s first billionaire mayor, homelessness and rent both soared, making one of the world’s centres of creative and intellectual life unliveable for all but the richest.
At play, notes Byrne, was more than a rise in the cost of living. It was a shift in the perceived value of creativity, backed by an assumption that it must derive from and be tied to wealth. “A culture of arrogance, hubris and winner-take-all was established,” he recalls. “It wasn’t cool to be poor or struggling. The bully was celebrated and cheered.”
New York – and San Francisco, London, Paris and other cities where cost of living has skyrocketed – are no longer places where you go to be someone. They are places you live when you are born having arrived. They are, as journalist Simon Kuper puts it, “the vast gated communities where the one percent reproduces itself”.
ObamaCore Public Education, or “We Know Best”
With the nationalizing of the American healthcare system well underway, nationalizing public education pre-K through 12 is the next big thing on the progressive agenda. Wait for it.
It will be called ObamaCore Education, for short.
The original 2008 Obama campaign Blueprint for Change document included a “Plan to Give Every American Child a World Class Education” and linked to a 15-page, single-spaced document entitled “Barack Obama’s Plan For Lifetime Success Through Education.” It offered a litany of proposals as part of a broad, federal intervention into America’s public education system.
A case can be made that the regime would have been better off, in the long run, nationalizing public education before healthcare, because the fundamental transformation of education would have been easier.
How so? you ask.
The reasons for the relative ease — compared to ObamaCare — of installing ObamaCore Education were cited in the American Thinker back in June 2009.
Related: Up for re-election Madison School Board President Ed Hughes: “The notion that parents inherently know what school is best for their kids is an example of conservative magical thinking.”; “For whatever reason, parents as a group tend to undervalue the benefits of diversity in the public schools….”. Remarkable.
Craigslist ad claims to be from incoming Harvard student offering to pay someone $40k a year to attend class, graduate for them
An advertisement that appeared briefly on the classifieds website Craigslist claimed to be posted by an incoming Harvard University student offering to pay $40,000 a year to have someone pretend to be the student for four years.
Whoever posted the ad wrote that they had already been accepted to start in the fall of 2014 at Harvard, which sent acceptance notices to 992 early action applicants for the class of 2018 a few days ago.
The ad poster said that they would, of course, also pay for tuition, books, housing, transportation and other living expenses. And, a $10,000 bonus would be given if the student imposter graduated successfully.
Millions of American students need to learn English
More than 5.3 million American public school students would struggle to understand this sentence.
These students need to be taught the English language in addition to the usual material in math, science, and social studies. This presents a monumental challenge for educators nationwide, according to Patricia Gandara, a UCLA education professor whom President Barack Obama appointed to the Commission on Educational Excellence for Hispanics. She is also co-director of the Civil Rights Project at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Speaking at the Education Writers Association’s National Seminar, held in May at Stanford University, Gandara referenced a nationwide survey given to teachers already trained for the growing number of English-language learners, commonly called ELLs.
“In the words of teachers themselves, they don’t feel qualified,” Gandara said.
Illinois Pension Reform: An Interview With State Senator Daniel Biss
Chad Aldeman: First, can you say why you are interested in pension reform, and what made this bill important?
Daniel Biss: I’m interested in pension reform because the first two years of my service in the Illinois General Assembly were years that followed a very significant tax increase and yet saw extremely deep cuts in discretionary spending to areas of public service that I cared deeply about, the reasons that I entered public service in the first place.
The size of our pension payments was so large that if we tried to address our budget problems without looking at pensions, we would be signing ourselves up for deep and never-ending impacts on the rest of state government. I just couldn’t get to a place where that seemed acceptable. I sought out changes to the pension system that ultimately strengthened and preserved it for those who rely on it the most.
This bill makes significant changes to the pension system in a way that seeks to do three very important things. The first is to achieve significant budgetary savings. After this legislation, our state payments over the next 30 years will be $160 billion dollars lower. Number two, this bill achieves those savings in a way that is consistent with my policy priorities, namely sheltering those with the smallest pensions and those who are most reliant on their pensions, as well as those who have served the longest. Number three, for the first time in history, Illinois will be making its actuarially required payments in keeping with national actuarial standards. Not only do we get on an actuarial payment schedule, we put in place protections to ensure that we stay on that schedule going forward.
Commentary: The Idiot’s Guide to the Common Core Standards
How much do you know about the Common Core Standards? Choose all that apply. The Common Core is:
a) a new set of nationwide standards that will encourage deep thinking instead of rote memorization
b) a new round of edu-crap, like No Child Left Behind
c) replacing state standards in 45 states including California
d) causing surprisingly large numbers of students to freak out and start weeping uncontrollably during initial tests all across the East Coast
e) causing Arne Duncan to infuriate opponents by dismissing them as “white suburban moms”
f) going to push fiction out of English classrooms
g) going to have no effect on the teaching of fiction
h) going to change everything
i) going to change nothing
j) going to make testing companies billions of dollars
Closing the “Word Gap” Between Rich and Poor
In the early 1990s, a team of researchers decided to follow about 40 volunteer families — some poor, some middle class, some rich — during the first three years of their new children’s lives. Every month, the researchers recorded an hour of sound from the families’ homes. Later in the lab, the team listened back and painstakingly tallied up the total number of words spoken in each household.
What they found came to be known as the “word gap.”
It turned out, by the age of 3, children born into low-income families heard roughly 30 million fewer words than their more affluent peers.
Research since then has revealed that the “word gap” factors into a compounding achievement gap between the poor and the better-off in school and life. The “word gap” remains as wide today, and new research from Stanford University found an intellectual processing gap appearing as early as 18 months.
That study led to some increased calls for universal preschool, but some say that’s not early enough.
“I recognized that we need to really start in the cradle,” says Angel Taveras, mayor of Providence, R.I.
He says two-thirds of kindergarteners in the city show up on their first day already behind national literacy benchmarks.
Next month, with funding from Bloomberg Philanthropies, Taveras’ city will launch “Providence Talks,” a new effort to take on the “word gap.” Providence will distribute small recording devices — essentially word pedometers — that tuck into the vest of a child’s clothing. These will automatically record and calculate the number of words spoken and the number of times a parent and child quickly ask and answer each other’s questions.
“We are very hopeful that we can be the laboratory here in Providence, and as we have success we can share it with the rest of the country,” Taveras says.
The idea was inspired in part by a research program called 30 Million Words in Chicago.
Aneisha Newell says that program taught her to talk to her young daughter in new ways. She says she never realized bath time — with colors and shapes of bubbles and toys to describe — could be a teachable moment. She ended up breaking the program’s record for the most words spoken.
And then there was the moment her daughter — not yet 3 years old — used the word ‘ridiculous’ correctly. Newell was amazed.
“It was just something that made me feel good as a parent,” she says.
Progress like Newell’s stems from a special kind of parent-child interaction, says Dana Suskind, a professor of surgery and pediatrics at the University of Chicago, who started the 30 Million Words program.
“We can’t just have people saying 30 million times ‘stop it!’ It’s got to be much more,” she says.
The parent should “tune in” to what the child is looking at, talk about it and ask questions that can create a sort of “serve and return” between parent and child.
Suskind says that research shows overhearing a cell phone conversation or sitting in front of a television program doesn’t cut it when it comes to building a child’s brain.
She and others hope to expand their style of training to day care centers and beyond. She says she hopes to eventually have it be routine for parents to learn about this at their newborn’s first hearing screening. She wants them to understand that their talk matters well before their baby starts talking back.
Science, Math & History: the struggle to marry content & pedagogy
Entangled, impossible to separate, that is what content and pedagogy have been and are in U.S. schooling. But not to reformers.
For decades, in science, math, and history policymakers, researchers, teacher educators, practitioners, and parents have argued over what kind of content should be taught in classrooms, playing down the inevitable presence of pedagogy or how the subject should be taught. Amnesiac reformers, pumped full of certitude, have pushed forward with “new science,” “new math” and “new history” curricula many times over the past century believing that the content in of itself-particularly delivered by academic experts-will magically direct teachers how to put innovative units and lessons into practice in their classrooms.
Well-intentioned but uninformed, these reformers have ignored how knotted and twisted together they are. Knowing content is one strand and how to teach it is the other. Entwined forever.
Why the 2014 Newark mayoral race is so important to the teacher unions
Did you hear about last Monday’s “National Day of Action to Reclaim the Promise of Public Education?” Maybe not. Despite a media blitz from the American Federation of Teachers and the National Education Association, despite allocations of $1.2 million of teachers’ union dues, despite organized protests in 90 cities across the country, this event had little impact.
For New Jersey, the more meaningful signal was sent by the AFT’s decision to hold its “Day of Action” in Newark. (Pennsylvanians headed over to Gov. Corbett’s Philly office on Broad Street.)
Newark, after all, is the heart of N.J. education reform territory and boasts the state’s most progressive teacher contract (signed last year with great acclaim), an extensive and successful cadre of charter schools that educates one in four public school students, and a superintendent whose latest initiative embraces parental empowerment through a universal enrollment plan. Some of that progress is at stake as Newark residents get ready to pick a replacement for Senator Cory Booker.
Next Step, Exogamy?
Integration seems one of the great political issues of our era. That is, people express great concern about factional favoritism based on race, ethnicity, religion, class, gender, age, etc., and push for laws and policies to prevent it, or to encourage mixing and ties across factional boundaries. I’ve tended to assume that such policies have been sufficient, and perhaps even excessive.
But a student, Randall McElroy, wrote a paper for my grad law & econ class, that got me thinking. He wrote about how the Hopi indians dealt with mass immigration in part by defining newcomers as a new clan, and then forbidding within-clan marriage. Such “exogamy” has apparently been a common strategy in history: force mixing and friendly ties between factions by requiring all marriages to be between factions.
I was reminded of Cleisthenes redesigning the political system of ancient Athens to break up the power of region-based alliances that had caused endemic political conflict. He created ten equal tribes, where a third of each tribe was taken from a different type of region, plain, coast, or hills, and made these tribes the main unit of political organization.
Does reading on screen beat paper?
American Airlines completed its transition to “paperless cockpits” this year, after giving pilots iPads in place of the 3,000-plus pages of documents and manuals they used to carry.
At professional services group PwC, meanwhile, staff must walk to a printer and enter a passcode to produce their hard copy – an extra step that was designed to cut the waste created by uncollected printouts.
If the paperless workplace is finally arriving, as these examples suggest, it is worth asking whether there is a difference between reading on screens and on paper – and whether all screens are created equal.
Anne Mangen, an associate professor at the University of Stavanger in Norway who specialises in reading, says the answer depends on the complexity of the content and the type of screen.
For skimming a short message, the medium may not matter, adds Maryanne Wolf, director of the Center for Reading and Language Research at Tufts University in the US.
But a screen is not necessarily best suited to “deep” reading, where the aim is to pick up more insight and come up with novel thoughts. In this situation, she says: “Paper seems to offer some advantages.”
When the Economy Transcends Humanity
What will our economy, workplaces, and society look like when we can copy our brains and build virtual workers to do our jobs? An economist looks at the next great era, a world dominated by robots.
What might a world full of robots as smart as humans look like? Experts in robotics and artificial intelligence have given a lot of thought to when and if such robots might appear. Most say it will happen eventually, and some say it will happen soon.
Knowing when advanced robots will appear doesn’t tell us how they will change the world. For that, we need experts in social science, like economists.
Here, I outline a scenario of what a new robot-based society might look like. Some people say I shouldn’t do this, because it’s impossible, while others just say it is unscientific. Even so, I’m doing it anyway, because it seems useful and it’s fun.
Keep in mind, however, that I’m not arguing that this scenario is good; I’m just applying basic economics to make best guesses about what things would actually be like. While most of you have probably seen movies depicting worlds with smart robots, as an economist I intend to show you we can do a lot better by using careful economic analysis. We can actually say quite a lot about this new world.
Wisconsin Teacher Evaluation System Commentary
In 2009 when the federal government announced the requirements for states to compete for billions of dollars of school reform grants, Wisconsin’s name came up — but not in the context state leaders wanted.
Education Secretary Arne Duncan called a Wisconsin law on the books at the time “simply ridiculous” because it prohibited using student test scores as a factor in evaluating teacher performance. Wisconsin never won a grant through the $4.35 billion Race to the Top competition.
Nearly five years later, the state is on the brink of rolling out an evaluation system for educators in all K-12 public school districts, but the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction still hasn’t determined how to tie student outcomes into those ratings.
Wisconsin adopts a small part of MTEL
Middleton good enough, smart enough to get to bottom of cheating
The U.S. government has arguably run far afoul of international and national law by torturing terrorism suspects and collecting private citizens’ phone records.
We’re just coming out of a recession caused largely by heretofore respectable banking, real estate and other moneyed interests who played fast and loose with the rules.
And recent years have seen many a hero athlete nabbed for taking performance-enhancing drugs.
So I find it hard to heap too much abuse on Middleton High School students accused of widespread cheating. They wouldn’t be wrong to point to the front page of almost any day’s newspaper and reprise a line from that old war-on-drugs public service announcement: “I learned it by watching you!”
Still, while we grown-ups have set some pretty bad examples, it would be a shame if Middleton’s grown-ups perpetuate that recent tradition by declining to dig too deeply into the cheating allegations.
Much more on Middleton, here (including 16% lower property taxes).