I’m less interested in blame than in the useful reminder that not all politics is American politics. Vaccination rates have dipped worldwide and not in response to U.S. politics or RFK Jr. In fact, despite RFK Jr. the U.S. is doing better than some of its North American and European peers. Outbreaks here may be triggered by cross-border exposure, not failures in U.S. public health alone. Not all politics is American—and not all American outcomes are made in America.
A call for professional maturity
Despite decades of educational research, evidence-based practices remain marginalised in teacher training, curriculum design, & classroom implementation. Instead, unproven fads continue to dominate. This article argues that education’s failure to mature into a profession grounded in empirical research (unlike medicine, accounting, or engineering) is the root cause. We examine ideological resistance, weak research standards, & structural failures in English Language Teaching (ELT) as a case study. Finally, we propose a pathway toward a more evidence-informed educational profession.
Street-Fighting Mathematics
This course teaches the art of guessing results and solving problems without doing a proof or an exact calculation. Techniques include extreme-cases reasoning, dimensional analysis, successive approximation, discretization, generalization, and pictorial analysis. Applications include mental calculation, solid geometry,
K-12 Tax & $pending Climate: Against Land Value Taxes
However, these proposed fixes fail to address a deeper and more fundamental issue: adding such patches to the LVT fundamentally undermines its ability to function as a substantial source of tax revenue.
Even in its simplest “naive” form, the LVT has a narrow tax base. The reality is that the vast majority of global wealth is created through human labor and innovation, not through the inherent value of natural or undeveloped land. If this sounds counterintuitive to you, perhaps imagine being transported to Earth millions of years ago, before humans evolved. Being the only human on Earth, you’d “own” all the natural resources on the planet, but you’d be unable to access almost any of the value tied up in those resources, because unlocking that value requires human labor and tools that haven’t been invented yet.
DIE and the University of Wisconsin Administration
As of the beginning of Wednesday, the division had approximately 100 full-time employees, John Lucas, UW-Madison spokesperson, said. Lucas said UW-Madison sent the employees who were laid off a notice Wednesday.
The restructuring of the diversity division is one of several recommendations a working group consisting of administrators identified over the past year, Mnookin said. She said she charged the working group with completing a review of how UW-Madison is supporting its undergraduate students.
The changes to the diversity division come after the UW Board of Regents in 2023 reached an agreement with Republican lawmakers to freeze hiring for diversity, equity and inclusion positions for three years and restructure related roles in exchange for receiving millions of dollars in state aid.
UW Regents approve tuition hikes for third consecutive year
Tuition for most undergraduate students at the Universities of Wisconsin will increase this fall.
The UW Board of Regents at a meeting Thursday approved raising in-state undergraduate tuition at the UW system’s 13 public universities by at least 4%. All universities also opted into an additional 1% tuition increase except UW-Green Bay.
The tuition change is the third consecutive increase students will see after a 10-year-long freeze that ended in 2023. The Regents voted for a 3.75% tuition increase last year for the 2024-25 school year and a 5% raise the year prior.
The Crumbling Boundary Between High School and College
By all appearances, students in the honors program at the University of Iowa should make a seamless adjustment to their college courses. These students, who applied and were selected by the program in a holistic process, have long been on the academic fast track. Many came in with college credits, often from Advanced Placement.
Related: Dual Enrollment across Wisconsin (very little in the taxpayer funded Madison K-12 system…)
Gary Payton II’s basketball camp provides support to children with dyslexia
A basketball camp by Warriors guard Gary Payton II is providing skills for children who love the game, while also serving a bigger purpose.
The GPII Foundation is hosting its third annual basketball summer camp at Oakland Hills Campus, formerly known as Holy Names University. On Tuesday morning, roughly 130 children gathered for the clinic to work on skills and rotations, and support children with dyslexia.
“Summer morning at 9 o’clock, you got to have a love for the game to be here,” Payton said. “I’m glad that they have that passion in them for basketball, just like I do.”
The camp is made possible by the GPII Foundation. It was established in 2021 and raises dyslexia awareness and offers support. The non-profit is run by his mother, Monique Payton, and his sister, Raquel Payton-Childs.
Visiting two public charter schools in California’s poor Central Valley, note dual enrollment
It’s more than just talk. Many of the older students told us about the college level courses they had taken at WCPA as part of the school’s Pathways program, and how they appreciated the different style of teaching and demands of coursework. Professors from nearby Bakersfield College teach Pathway classes at WCPA; 100% of students take some of their courses, and 50% earn enough credits for an Associates degree by the time they graduate. This is a huge jumpstart in time and money toward a BA, which means a lot to large numbers of students and their families.
One by one, the older students walked-and-talked with us as we toured the campus. Here are some of the highlights we saw and heard about:
Soldiers of Change: The school sponsors a shark-tank like program for projects addressing social change. The students organize themselves into small groups, survey the other students for ideas, collect topics, and make their pitches. Judges listen, award winners, and approve budgets. A recent winner used food (always a hit). Their project was to present new cuisines as intros to new cultures, in the school cafeteria. One boy raved about Indian food, and his first-ever bites.
It’s more than just talk. Many of the older students told us about the college level courses they had taken at WCPA as part of the school’s Pathways program, and how they appreciated the different style of teaching and demands of coursework. Professors from nearby Bakersfield College teach Pathway classes at WCPA; 100% of students take some of their courses, and 50% earn enough credits for an Associates degree by the time they graduate. This is a huge jumpstart in time and money toward a BA, which means a lot to large numbers of students and their families.
One by one, the older students walked-and-talked with us as we toured the campus. Here are some of the highlights we saw and heard about:
Soldiers of Change: The school sponsors a shark-tank like program for projects addressing social change. The students organize themselves into small groups, survey the other students for ideas, collect topics, and make their pitches. Judges listen, award winners, and approve budgets. A recent winner used food (always a hit). Their project was to present new cuisines as intros to new cultures, in the school cafeteria. One boy raved about Indian food, and his first-ever bites.
…….
Learning Farm and Harvest Hall: At the school’s on-site garden, called the Learning Farm, students learn to grow and harvest crops. The results show up frequently in the school cafeteria, to the delight of the young farmers. One of our guides reported an overheard conversation, “Hey, those are my tomatoes you’re eating. I’ve been growing those and now they’re on your flatbread! Check out my tomatoes!”
Beginning in 7th grade, in the classrooms and kitchen, students learn how to build and cook meals, and even take home ideas to their families. On any given day, high schoolers may be prepping the food, serving the meals, doing the checkout. Besides imparting these practical, lifelong skills, there is a higher purpose for the emphasis on nutritious food. Here in the Central Valley, which provides about 25 % of America’s food supply, WCPA is developing and nurturing a sophisticated sense of the ecosystem of agriculture, nutrition, and business. But also, here in Kern County, home to both Lost Hills and Delano, the rate of obesity is 49% and of diabetes, nearly 9%. So, WCPAs are starting early to build good foundations and break bad cycles. The adults emphasized to us that they’re “stamping” the kids with an understanding and experience in managing every aspect of this place-based asset of the food culture that surrounds them. “That’s a piece that we see as vital.”
———
more.
———
Notes and links on dual enrollment.
Madison High Schools & University of Wisconsin-Madison Enrollment: A Recent History
Civics: Almost every single policy they rolled out has failed
Geiger summary:
Jamie Dimon on Democrats today:
“I have a lot of friends who are Democrats today, and they’re idiots. I always say they have big hearts and little brains. They do not understand how the real world works. Almost every single policy they rolled out has failed.”
——-
More and more people are realizing that the old Dem/Rep parties are both dead…
Moving forward it’s:
Nationalism vs. Communism
Stephen Miller vs. Zohran Mamdani
——
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $25,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Children under 16 can no longer go to Madison’s Goodman pool without an adult
Children under 16 years old no longer will be allowed at Goodman pool without a parent or adult guardian under new rules implemented by the city.
The previous age of children who require an adult chaperone was 10, but Madison Parks officials voted Wednesday night to raise that to 15 years old. The new rule takes effect Thursday, July 17.
The change was in response to a recent fight involving a large group of kids at the South Side facility, the city’s only public swimming pool.
————
Former Madison Mayor Paul Soglin:
Credentialism and k-12 Governance
The Madison School District said Thursday that it is working with the man it hired to be the new principal at Lori Mann Carey Elementary School to make sure he gets the state educator’s license he needs to take the job.
The district on Tuesday announced the appointment of longtime educator and activist Percy Brown Jr. as the new principal at the South Side school, but it wasn’t clear from the Department of Public Instruction’s online licensing database that he has the license that under state law he needs to be a principal at a public school in Wisconsin.
The database shows a Percy L. Brown has had teacher and administrator licenses in the past, but none of them were current. Instead, it shows that teacher and administrator licenses applied for in June 2019 and June 2020, respectively, were currently invalid because background checks had not been completed.
———
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $25,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
An open letter from educators who refuse the call to adopt GenAI in education
Current GenAI technologies represent unacceptable legal, ethical and environmental harms, including exploitative labour, piracy of countless creators’ and artists’ work, harmful biases, mass production of misinformation, and reversal of the global emissions reduction trajectory.
GenAI is a threat to student learning and wellbeing. There is insufficient evidence for student use of GenAI to support genuine learning gains, though there is a massive marketing push to position these products as essential to students’ future livelihoods. Young people using anthropomorphised chatbots are vulnerable to psychological and emotional addiction. GenAI “relationships” continue to trigger mental health crises, human relationship breakdowns, and in the worst cases, attempted and completed suicides.
Further, GenAI adoption in industry is overwhelmingly aimed at automating and replacing human effort, often with the expectation that future “AGI” will render human intellectual and creative labor obsolete. This is a narrative we will not participate in.
civics: Why Won’t Socialism Die?
Why are so many young people today turning to socialism?
By socialism I mean an economic system where the government nationalizes the means of production—if not in all industries, at least in some critical ones. But as we shall see, many of those attracted to socialism these days may be more attached to negative vibes about the status quo than any particular economic system.
This is most evident in the recent New York City electoral results of Zohran Mamdani, who did very well in the Democratic primary for mayor and is polling well ahead of sitting mayor Eric Adams and former governor Andrew Cuomo. Among other things, Mamdani has called forgovernment-run grocery stores, rent freezes, and free buses.
The Sputnik vs. DeepSeek Moment: Why the Difference?
America’s response to rising scientific competition from China—symbolized by DeepSeek’s R1 matching OpenAI’s o1—has been very different. The DeepSeek Moment has been met not with resolve and competition but with anxiety and retreat.
Trump has proposed slashing the NIH budget by nearly 40% and NSF by 56%. The universities have been attacked, creating chaos for scientific funding. International collaboration is being strangled by red tape. Foreign scientists are leaving or staying away. Tariffs have hit highs not seen since the Great Depression and the US has moved away from the international order.
Some of this is new and some of it is an acceleration of already existing trends. In Launching the Innovation Renaissance, for example, I said that by the Federal budget numbers, America is a warfare-welfare state not an innovation state. However, to be fair, there are some bright spots. Market‑driven research might partially offset public cuts. Big‑tech R&D now exceeds $200 billion annually—more than the entire federal government spending on R&D. Not everything we did post-Sputnik was wise nor is everything we are doing today foolish.
Nevertheless, the contrast is stark: Sputnik spurred investment and ambition. America doubled down. DeepSeek has sparked defensiveness and retreat. We appear to be folding.
Question of the hour. Why has America responded so differently to similar challenges? Can understanding that pivot help to reverse it? Show your work.
Rethinking Higher Education in the age of “ai”
But for English departments, and for college writing in general, the arrival of A.I. has been more vexed. Why bother teaching writing now? The future of the midterm essay may be a quaint worry compared with larger questions about the ramifications of artificial intelligence, such as its effect on the environment, or the automation of jobs. And yet has there ever been a time in human history when writing was so important to the average person? E-mails, texts, social-media posts, angry missives in comments sections, customer-service chats—let alone one’s actual work. The way we write shapes our thinking. We process the world through the composition of text dozens of times a day, in what the literary scholar Deborah Brandt calls our era of “mass writing.” It’s possible that the ability to write original and interesting sentences will become only more important in a future where everyone has access to the same A.I. assistants.
DIE $pending and the University of Wisconsin-Madison
The University of Wisconsin–Madison announced that its DEI office will “sunset as a freestanding division” in an email to its students and employees on Wednesday. Unfortunately, DEI is dead in name only.
While UW–Madison’s Division of Diversity, Equity, and Educational Achievement (DDEEA) is no longer independent, most of its operations are merely being shifted to other places. Chancellor Jennifer Mnookin said its responsibilities and personnel would be divided between the Division for Teaching and Learning, the human-resources department, and the data collection office.
According to the Daily Cardinal, one of UW–Madison’s student newspapers, fewer than ten of the approximately 100 DDEEA employees …
Politicized courses are migrating, not disappearing
Eliminating these degree programs and rebranding them as minors does little to address the broader ideological imbalance on campus. Other programs—Political Science and Anthropology, to name two—also reflect a clear ideological bias.
Just as important are underlying structural problems in the university’s broader curriculum. The University of Wyoming offers dozens of Ph.D. programs, including in fields such as entomology, anthropology, and English. Many of these programs are not nationally competitive, offering modest stipends and limited job placement for graduates. They are largely a legacy of the university’s push to achieve R1 research status. It wouldn’t be surprising if many of them are soon labeled low-producing.
Without deeper, structural reforms, headlines about canceled degree programs will likely become more common.
Harvard Graduate School of Education shutters DEI office as federal funding stalls
The Graduate School of Education’s DEI shutdown is part of a broader trend at Harvard. Campus Reform has reported that the university has taken steps away from DEI during the Trump administration.
Earlier this year, for instance, Harvard Medical School renamed its DEI office to the Office for Culture and Community Engagement amid growing federal pressure.
Harvard has faced significant consequences over its support for DEI, including a freeze in $2 billion of federal funding.
“Harvard has in recent years failed to live up to both the intellectual and civil rights conditions that justify federal investment,” departments within the Trump administration stated in their April letter announcing the funding pause. “But we appreciate your expression of commitment to repairing those failures and welcome your collaboration in restoring the University to its promise.”
Politics and The Princeton “hedge fund”
Just this week, Barnard University settled a lawsuit stemming from widespread problems with antisemitism on campus. In that settlement, it reaffirmed that it would not use its endowment for political purposes, including sanctioning Israel. And last week, the University of Pennsylvania reached an agreement with the Trump administration to cease having men compete in women’s sports or to be in women’s locker rooms.
There are even reports that both Harvard and Columbia are close to reaching agreements with the Trump administration to remediate their civil rights violations and to unfreeze federal funds.
Soon, Princeton will find itself standing alone in its pursuit of an increasingly politicized university. If it continues to lose public subsidy and doesn’t eventually reverse course, it may find itself reduced to nothing more than a finishing school for wealthy young radicals. Under Eisgruber, it already looks a lot like that.
“Local Parents Fighting ‘Cesspool’ of Anti-Semitism in Philly Schools”
Philadelphia’s public school system has become an “absolute cesspool” of anti-Semitism and anti-American hatred, according to local parents, who say Gov. Josh Shapiro (D.) has “completely ignored” their pleas for help.
Since Hamas’s Oct. 7, 2023, attacks, Philadelphia school officials have publicly defended terrorism, called for the release of convicted cop killers, claimed Israel is an “apartheid theocracy,” and denounced the United States as a “criminal Amerikan empire.” The Philadelphia school district settled a federal discrimination case with the Department of Education last year after students allegedly taunted their Jewish classmates with Nazi salutes, swastika graffiti on doors, and threats to “kill the Jews.”
Frustrated parents told the Washington Free Beaconthat they have tried to raise these issues with the governor but that his staff has done nothing in response and eventually stopped taking meetings with them.
One mother of two Philadelphia public school students told the Free Beacon that she and other concerned parents met with Shapiro staffers several times during 2023 and 2024, including with Carrie Rowe, the current head of Pennsylvania’s Department of Education.
“We have met with people in his office, seven or eight of them on a few occasions, and nothing has happened,” the mother said. “[The governor’s office] heard firsthand the horrors that are going on, and what we’ve been dealing with, and nothing has happened to address or fix it.”
Madison High Schools & University of Wisconsin-Madison Enrollment: A Recent History
The Wisconsin Policy Forums’ recent brief look at Dual Enrollment (taking courses at a 2 or 4 year higher education institution while still enrolled in a high school) prompted me to update University of Wisconsin-Madison enrollment data by high school. The effort also reminded me of Janet Mertz’s tireless effort years ago on behalf of local high school students whose dual enrollment opportunities were largely aborted.
Most of the data for these charts is available at the UW-Madison Registrar’s web presence. The earlier years I somehow captured in an old spreadsheet.
UW-Madison enrollment has grown substantially in recent years, now around 50,000 students. The reasons for that are best left to another post, or better yet, others with a deeper understanding of higher ed finance & staffing choices.

Madison area high schools:










A 4/4 Teaching Load Becomes Law at Most of Wisconsin’s Public Universities
A 4/4 load is already common for many faculty members at teaching-focused institutions, such as regional public colleges. So is a 2/2 load at research institutions.
But Michael DeCesare, a senior program officer at the national American Association of University Professors, said state-mandated minimum course loads are at odds with AAUP standards, which recommend that faculty “participate fully in the determination of workload policy.”
Teaching requirements are best decided by individual colleges and departments, as they are in the UW system currently, since expectations vary widely among different types of staff, said Christa Olson, an English professor and chair of the English department at UW-Madison.
The budget’s “one-size-fits-all approach” applies equally to professors who focus on teaching as it does to employees in its extension program, who primarily do community outreach, Olson said.
……
While those mandates were not adopted, university officials tried to push back by improving transparency about how much faculty members work. Now the UW system publishes a database of thousands of instructors that details how many credit hours they teach, broken up by group and individual instruction.
Other state legislatures have previously discussed increasing faculty workloads, but the proposals haven’t come to fruition.
Dual Enrollment and AP Course Availability in Wisconsin High Schools; Madison….
The number of Wisconsin high school students who participate in dual enrollment programs continued its decade-long growth in the 2023-24 academic year, hitting a new record. A combined 78,703 students participated in the dual enrollment programs offered by the University of Wisconsin and Wisconsin Technical College systems, through which they could earn credit at higher education institutions as well as their high schools. This represents more than a quarter (26.6%) of the state’s secondary students across public, private, and home schools, and it is a 3.4% increase over the previous year (see Figure 1).
The Wisconsin Technical College System (WTCS) offers the largest dual enrollment program in the state, enrolling more than four times as many students as the one operated through the University of Wisconsin System (UW). From 2022-23 to 2023-24 (referred to in this brief as 2023 and 2024), however, the UW program grew at a faster rate – by 12.0% to 15,588 students – than the WTCS program, which increased by 1.5% to 63,115 students. Both systems offer an array of programs to meet the various needs of high school students, which sometimes results in similar, parallel programs in each system. In this analysis, individuals who took classes in both systems are counted twice but are unduplicated if they participated in multiple programs within one system.
In our previous report on dual enrollment, we examined participation in the programs using data provided by the state’s two public college systems. Since then, the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction has added postsecondary preparation programs to its annual report cards for high schools. These programs, which include dual enrollment and Advanced Placement (AP), equip students for higher education or the workforce. With this new information, we are now able to examine participation levels by high school in dual enrollment and other postsecondary opportunities.
…….
The 472 public high schools that reported providing dual enrollment opportunities in 2023 enrolled 259,286 students, and 68,151 of them (26.3%) took advantage of those opportunities.
Participation rates varied across these schools, however. Students from urban schools had the lowest rate of dual enrollment participation at 19.7%, while those in suburbs, towns, and rural communities had participation rates of 28.3%, 30.1%, and 27.6%, respectively — all higher than the state average.
Students from schools with high rates of poverty were less likely to participate in dual enrollment programs. Only 4.3% of students from schools in which more than 75% of the students identified as economically disadvantaged took a dual enrollment course. On the other extreme, schools where less than 25% of students are from economically disadvantaged families reported a dual enrollment rate of 30.5%.
———
Related: A long running issue in the taxpayer funded Madison School District: Credit not for non MMSD Courses
Madison’s high schools compared, using taxpayer funded Wisconsin DPI “report cards”:Madison East (tap for the “report card”:

Madison LaFollette (tap for the “report card”:

Madison Vel Phillips Memorial (tap for the “report card”:

Madison Shabazz (tap for the “report card”:

Madison West (tap for the “report card”:

Economic literacy and public policy perspectives
Jared Barton and Cortney Rodet:
The authors measure economic literacy among a representative sample of U.S. residents, explore demographic correlates with the measure, and examine how respondents’ policy views correlate with it. They then analyze policy view differences among Republicans and Democrats and among economists and non-economists. They find significant differences in economic literacy by sex, race/ethnicity, and education, but little evidence that respondents’ policy views relate to their level of economic literacy. Examining heterogeneity by political party, they find that estimated fully economically literate policy views (i.e., predicted views as if respondents scored perfectly on the authors’ economic literacy assessment) for Democrats and Republicans are farther apart than respondents’ original views. Greater economic literacy among general survey respondents also does not result in thinking like an economist on policy.
——-
more.
Civics: On the exercise of patronage and its consequences
Sometimes that works out, and sometimes it doesn’t.
Patronage is thus inevitable, and it does come with costs. At its worst, patrons unthinkingly select their friends and relations, or their political allies, selected for loyalty and allegiance, demonstrated in some very different domain to that of the role in question. But it can also come with benefits. Confronted with our five promising lieutenants, the decision-maker at the Admiralty might recall that one of them is that nephew of his who, as a lad, never backed down from scraps and often won fights against much bigger boys. This sort of private but very useful information can be easily factored into decisions in a world where patronage is allowed to operate in a fairly unfettered manner. And indeed evidence suggests that naval officers with powerful friends at the Admiralty performed substantially better in battle, indicating that the patrons – especially in wartime – were judiciously using their power to select on important but low-visibility criteria.
Patronage can be viewed, therefore, as a mechanism to both improve average outcomes, but also increase the variance: on the whole things are better, and you get more top performers, but you also get more disasters. Clearly a mechanism will be needed to remove the underperformers. The Royal Navy, for instance, court-martialled every single post-captain who lost a ship. Most were of course exonerated, but for those who were judged not to have fought well enough, the penalties were severe: a permanent ban from naval command in many cases, death in a few.
Admiral John Bnyg was one of the unlucky ones. Judged to have not fought aggressively enough in the Battle of Minorca (1756) he was convicted to death under the Articles of War, although it was widely expected that George II would commute the sentence. The King declined and Byng was duly executed. Byng had lost no ships and was in many ways a victim of blunders at the Admiralty he was not responsible for. Nonetheless, the Articles of War constituted a strict incentive structure, applying to all ranks equally, that aimed to cajole naval officers to fight to the death rather than withdraw from battle (something that was and is much easier to do at sea than on land).
Notes on Canadian mass curricula sausage making
I’ve been reviewing Canadian math curricula (standards) this week. Here’s a BC grade 5 outcome titled “multiplication & division facts to 100.” As if this all weren’t bad enough, we have “memorization of facts is not intended at this level.” Grade 5! Wish I could unsee this.
——
2014: 21% of University of Wisconsin System Freshman Require Remedial Math
How One Woman Rewrote Math in Corvallis
Singapore Math
Discovery Math
K-12 Tax & $pending Climate: Redistributed State & Federal Taxpayer Funds vs Local Property Tax Growth
Gothard used a press conference Wednesday to call on state and federal legislators to provide a bigger chunk of the money local districts need to educate students — or local property taxpayers will be left shouldering even more of the cost of public education.
———
Madison taxpayers have long supported far above average (now > $25,000 per student) K-12 tax & spending practices. This, despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
The American Federation of Teachers plans to utilize the $23 million, including $500,000 from the A.I. startup Anthropic, to establish a national training center.
But some researchers have warned that generative A.I. tools are so new in schools that there is little evidence of concrete educational benefit — and significant concern about risk.
Chatbots can produce plausible-sounding misinformation, which could mislead students. A recent study by law school professors found that three popular A.I. tools made “significant” errors summarizing a law casebook and posed an “unacceptable risk of harm” to learning.
Outsourcing tasks like research and writing to A.I. chatbots may also hinder critical thinking, a recent study from Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon University found.
“I do think that there is a risk,” said Brad Smith, the president of Microsoft, noting that he frequently cited the critical thinking study to employees. He added that more rigorous academic research on the effects of generative A.I. was needed. “The lesson of social media is don’t dismiss problems or concerns.”
A Review of College Ranking Systems
Soubhik Barari, Ph.D., Eric Newsom, M.S.Ed., Ji Eun Park, Ph.D. and Susan M Paddock, Ph.D.
Higher education has long been viewed as a stepping-stone for individuals to achieve professional and personal goals. To demystify the options within the higher education landscape, prospective students and their families often turn to college rankings. This is especially true in an era of increasingly expensive college costs (Franke, 2017). Several major college rankings providers have recently revised their methodology to better reflect these cost concerns, along with making other updates. While this effort may be laudable, any proposal for substantive changes in rankings raises the question of the underlying qualities encapsulated by the rankings and whether the ascribed methodology can accurately capture those qualities.
Given these potential issues, we conducted a methodological review of five prominent college rankings systems: U.S. News & World Report (USNWR), Wall Street Journal (WSJ), Forbes’ Top College list (Forbes), The Times Higher Education World University Ranking (THE), and the QS World University Ranking (QS).
Our overarching approach is to assess the construct validity of college rankings. Construct validity is a crucial property in the development of numerical scales, such as rankings, that aim to quantitatively describe otherwise abstract qualities of social entities such as ‘market value’ or ‘educational quality.’ Our assessment includes a review of conceptual, data, and methodological factors within this framework that are central to developing a methodologically sound ranking of colleges, drawing examples from our five illustrative ranking systems. Here, we summarize five key issues spanning the conceptual, data, and methodological aspects of construct validity along with an initial recommendation to address each (expanded further in Section 5)
The president of the University of Washington system has proposed a tuition increase for in-state undergraduate students
In-state undergraduate students at the Universities of Wisconsin would pay hundreds more in tuition in the 2025-26 academic year under a proposal President Jay Rothman announced Tuesday.
The plan to raise tuition by up to 5% for in-state undergraduate students would be the third consecutive increase since 2023 after the end of a 10-year freeze.
Tuition would increase by 4% in the UW system under the proposal, plus an optional 1% that all universities except UW-Green Bay plan to adopt.
At UW-Madison, tuition and fees for 2025-26 would be $12,166.
——-
If approved, this would be the third year in a row the UW system will increase tuition after a 10-year freeze.
New Federal Student Loan “caps”
The law will cap how much graduate students and parents can borrow starting July 2026.
Graduate students will be capped at $20,500 per year, with a lifetime maximum of $100,000. This falls below the total cost of a master’s degree, which typically ranges from $44,640 to $71,140, according to the Education Data Initiative.
Professional students in law and medical programs may borrow up to $50,000 per year, capped at $200,000 total. Earning a law degree in the U.S. costs an average of $206,000, while medical school students face a higher total average of approximately $230,000, according to Education Data Initiative.
Parents who borrow for their children’s education are limited to $20,000 per year with a $65,000 lifetime maximum using the Parent PLUS loan program.
Policy experts predict that these changes will shift borrowers toward private lenders.
“We’re going to see huge growth of the private student-loan market as a result of this bill,” said Bryce McKibben, senior director of policy and advocacy at the Hope Center for Student Basic Needs at Temple University, in an interview with MarketWatch.
“exactly the video you’d expect from a 24-year-old barre instructor and fitness influencer who studied political science and communications”
Ann Althouse summary:
This gets my tag “MSM reports what’s in social media.”
Here‘s the viral video the article is about. It’s exactly the video you’d expect from a 24-year-old barre instructor and fitness influencer who studied political science and communications. It’s what I’d have said at age 24.
By the way, I just watched a movie made by a 24-year-old woman, and I got the feeling it was exactly the kind of story I thought up when I was that age. Not saying I could have made the movie that topped the Sight & Sound “Greatest Films of All Time,” just saying I remember these young-woman thoughts.
Blame Wisconsin Governor Evers for delay in literacy funds
Lauren Greuel and Cory Brewer:
It’s not every day that the liberal-leaning Wisconsin Supreme Court unanimously sides with the Republican-run Legislature. But that’s what happened recently in a dispute over how $50 million of early literacy funds are distributed to Wisconsin schools.
In its ruling, the court rejected false narratives pushed by the governor and his allies at the state Department of Public Instruction (DPI) that these funds were somehow wrongfully withheld by the Legislature. They weren’t, the court agreed, and now kids will get access to badly needed funds for literacy.
In 2023, the Legislature passed a bipartisan package of bills aimed at addressing the state’s literacy crisis. With only 1 in 3 students scoring at proficiency in reading in 2022, lawmakers agreed something had to chang
———
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Is there a literacy crisis, or am I just old and thinking differently? The endless discourse about “kids can’t read” seems to be a never-ending cycle.
Every month or so, for the past few years, a new dire story has warned of how American children, from elementary school to college age, can nolonger read. And every time I read one of these stories, I find myself conflicted.
On the one hand, I am aware that every generation complains that the kids who come next are doing everything wrong and have gotten stupider and less respectful. I fear falling into this trap myself, becoming an old man yelling at cloud.
On the other hand, with every new story, I find myself asking: … Can the kids read, though?
I don’t think I’m alone in this confusion. Similar responses emerge almost every time a new piece arrives with tales of elite college students who can’t get through Pride and Prejudice or another report reveals just how far reading scores have plunged among America’s schoolchildren. “Ten years into my college teaching career, students stopped being able to read effectively,” Slate reported bleakly in 2024. Within days, a teacher’s blog offered a rebuttal, arguing that there has never been an era where adults were impressed by kids’ reading habits: “Find a news article published since the 1940s that shows that students not only read proficiently but eagerly and a lot. I’ll wait.”
————
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Reflections on Douglas Carnine’s classic article, “Why Education Experts Resist Effective Practices”
We think he is. Education, as it currently stands, is clearly not a science-based profession. When teachers face a tough classroom problem, they rarely turn to research for answers. More often, they rely on instincts, experience, or strategies picked up from colleagues. That’s not to say these things don’t have value—they absolutely do. But it’s striking how seldom research is consulted.
Research also plays a surprisingly small role in inservice training. More often than not, professional development promotes ideas that are familiar, popular, or easy to present, but not necessarily ones that are science-based. Teachers who participate in these training sessions might assume that the instructional materials have been rigorously vetted. In reality, that’s unlikely. Countless hours of professional development have been spent — and are still spent — on edu-fads like learning styles and multiple intelligences, in spite of decades of research that have failed to show any benefits for student learning.
Experienced teachers have told us stories of their schools committing to a new educational initiative one year, only to see it quietly abandoned the following year. This can cause teachers to become skeptical or even cynical about new initiatives. When the latest “big idea” is rolled out with great fanfare but disappears without clear results, teachers begin to see these efforts as trends rather than meaningful improvements. Over time, this pattern erodes trust in leadership and reduces teacher engagement with future professional development. Instead of asking, “How can I apply this to improve student learning?”, teachers may start to wonder, “How long until this one fades away too?”
Decrypted Generative Model safety files for Apple Intelligence containing filters
Here, the reject field contains exact phrases which will result in a guardrail violation. The removefield contains phrases that will be removed from the output, while the replace field contains phrases that will be replaced with other phrases. The regexReject, regexRemove, and regexReplace fields contain regular expressions that will be used to match and filter content in a similar manner.
One City Schools marks a decade educating kids with LeVar Burton event
One City Schools, the independent charter school on Madison’s south side, plans to hold a community rally Thursday at The Sylvee to celebrate its 10th anniversary.
Over the last decade, One City has raised $50 million to help serve underprivileged students in the area through innovative and unique ways, according to founder and CEO Kaleem Caire.
Caire said One City’s student demographics are distinct from other public schools in Madison. About 92% of its students are people of color, 70% come from poverty and 20% have special needs.
One City is also the only expeditionary learning (EL) school in Dane County and one of five in Wisconsin. An EL school is known for having strong foundations in literary and character development, Caire said.
“The academic results that our kids have generated recently have been phenomenal,” Caire said. “No school in Dane County has seen the marked increase in achievement among Black and Latino students that we’ve seen at One City.”
———
Notes and links on One City Schools.
A majority of taxpayer funded Madison School Board aborted the proposed Madison Preparatory Academy IB charter school.
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
Civics: Notes on taxpayer funded organization Governance Reform
A prime minister may now need not just a bulging folder of pre-cooked policies, but something tantamount to an invasion plan to transform the state
Indeed, when you talk to people on the Labour side, what is surprising is not just how scathing they are about their own party’s performance — even accounting for the less-than-ideal situation inherited from the Tories — but how gloomy they are about turning things round. Even before the welfare shambles, I’d been told more than once that Labour’s early mistakes had already been fatal, whether that be slashing the winter fuel allowance, the lack of a convincing pre-election narrative (or pre-election honesty about tax rises) or Sue Gray’s complete failure, as Starmer’s chief of staff, to plan for power.
As a result, a new consensus has taken hold in Westminster: that, to paraphrase the military, proper planning prevents pathetic performance. The secret to successful government, everyone now agrees, is to do mountains of work in opposition, in precisely the way that Starmer’s team didn’t. Just look at Trump 2 v Trump 1. Or Keith Joseph and the other revolutionaries that surrounded Margaret Thatcher, whose “hard work and good thinking” before 1979 was cited admiringly last week by Nigel Farage. Or Gordon Brown as chancellor, delivering Bank of England independence on day one. Or David Cameron and his education and welfare reforms.
For those of us who run think tanks — in my case, the one where Thatcher and Joseph did that very thinking — this is obviously welcome news. Coming up with ideas outside government is the literal definition of what we do.
——
Madison Schools: More $, No Accountability
The taxpayer funded Madison School District long used Reading Recovery…
The data clearly indicate that being able to read is not a requirement for graduation at (Madison) East, especially if you are black or Hispanic”
My Question to Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers on Teacher Mulligans and our Disastrous Reading Results
2017: West High Reading Interventionist Teacher’s Remarks to the School Board on Madison’s Disastrous Reading Results
Madison’s taxpayer supported K-12 school district, despite spending far more than most, has long tolerated disastrous reading results.
“An emphasis on adult employment”
Wisconsin Public Policy Forum Madison School District Report[PDF]
WEAC: $1.57 million for Four Wisconsin Senators
Friday Afternoon Veto: Governor Evers Rejects AB446/SB454; an effort to address our long term, disastrous reading results
Booked, but can’t read (Madison): functional literacy, National citizenship and the new face of Dred Scott in the age of mass incarceration.
When A Stands for Average: Students at the UW-Madison School of Education Receive Sky-High Grades. How Smart is That?
National Education Association’s 2025 resolutions
Corey DeAngelis summary:
The nation’s largest teachers union adopted a business item “to defend against Trump’s embrace of fascism by using the term facism [sic] in NEA materials correctly characterize Donald Trump’s program and actions.”
Notes on Baby Trump accounts
The employer contribution strikes me as important. Suppose that in addition to the initial $1000 government payment that on average $1000 is added per year for 18 years (by a combination of parent and parent employer contributions). Note that this is below the maximum allowed annual contribution of $5000. At a historically reasonable 7% rate of return these accounts will be worth ~36k at age 18, $58k at age 25 and $875k at age 65 subject to uncertainty of course as indicated below.
Why English doesn’t use accents
Our fictional monk Godwin lived in the wake of the single most significant event in the history of the English language: the Norman Conquest of 1066.
Before the Conquest, English — albeit an old form of English — was the language of power and government in England. After the Conquest, French took its place for centuries.
It was but a temporary replacement: English eventually re-established itself in the halls of power, thanks to the gradual loss of English territory in France and the birth of a new English identity during the Renaissance. But the period of French dominance left its mark on all aspects of the language, from vocabulary to pronunciation. And, as Godwin found to his chagrin, it had a revolutionary impact on English spelling.
In fact, this early French influence over English, which arose from the Norman Conquest, is the beginning of the reason why English is written without accent marks (é, à, ç, etc.), or, as linguists call them, diacritics, today.
Let’s keep calling them diacritics, since accent can mean so many things, from different regional ways of speaking to where in a word you place the emphasis.
Young people usually become less radical with time. Are we seeing an exception?
Young people typically start out on the political left but become more conservative as they get older. Baby boomers who once marched against the Vietnam war got jobs, got married and had children. Now their grandchildren see them as tethered to Fox News.
Today’s young Americans are following the first part of that pattern. Ask a group of them to choose between capitalism and socialism and they will split right down the middle. Their support was crucial in nominating Zohran Mamdani, who says he wants to capture “the means of production,” as the Democratic candidate for mayor of New York.
But will the young people outgrow their radicalism? There is reason to doubt. Record numbers of Generation Z are pursuing higher education, with 53% of those 18 to 24 having completed at least some college. That’s a troubling sign given how left-wing ideology has come to dominate higher ed.
College is where many young people learn that socialism means free stuff. They are indoctrinated to blame capitalism for racism, inequality and climate change. Unlike the older generations, they grew up after the end of the Cold War and have no memory of the atrocities committed by the Soviet Union, Maoist China and other socialist regimes. Maybe they’ll see socialism in action in New York.
Princeton Professor: “Capitalism sucks. Individualism is killing us.”
Peña is a self-professed radical who boasts of how she wants to dismantle the university from within & lays out an overtly ideological research agenda.
Colleges have always had radical faculty. What’s notable is Peña’s history of lavish funding and awards, including:
—the Johns Hopkins University African Diaspora Studies Postdoctoral Fellowship
—Future of Minority Studies Fellowship
—research support from the Ford Foundation
—research support from the Mellon Foundation
—the 2022 Angela Davis Prize for Public Scholarship
—a 2017 MIT Disobedience Award
List goes on. It’s no accident that we have so many faculty so out of line with the country. Huge and very intentionally craft career incentives brought us here.
How the State Pays to Undermine the Nation
David Friedberg’s recent All-In podcast argument sounds convincing: student debt creates desperate graduates, financial stress drives political radicalism, and young Americans embrace socialism because capitalism failed them economically. The analysis captures real and understandable pain but overlooks the underlying mechanisms.
Zohran Mamdani reportedly owes at least $200,000 from his college years. He studied African Studies and graduated without a job, but now he’s winning elections as a socialist candidate in New York City. Friedberg connects the financial dots, but the ideological picture remains invisible.
“Let the parents decide”
The consequences have been serious. Parents said principals are retracting previous assurances that they could enroll their children late, and there has been little flexibility with children with special circumstances. At least two families have been reported to the city’s child welfare agency for truancy because they did not send their 5-year-olds to kindergarten on time.
And the children whose families sought to give them more time to develop may be further behind. Students who spent an extra year in preschool or day care missed kindergarten, a year that focuses on playtime and socialization but has increased in academic rigor.
The number of students who started kindergarten late during the 2024-2025 school year was not immediately available Thursday, but district officials said they are aware of about 10 families who are trying to do so this fall.
—-
I think the answer to her question why is: It’s part of the struggle against (what is perceived as) white privilege: “It is difficult to determine exactly how common it is to delay a child’s enrollment in school. Some national data suggest it’s rare — somewhere between 3.5 percent and 5.5 percent of eligible children do it. Most of those students are boys born in the summer months. Academic redshirting is also more common among White children at schools that serve large numbers of wealthy families, who can afford an extra year of preschool or day care, according to an article published by the American Educational Research Association.” –Ann Althouse.
The relationship between word reading ability and spelling ability
Rebecca Treiman, Jacqueline Hulslander, Erik G. Willcutt, Bruce F. Pennington & Richard K. Olson:
The goal of the present study was to test theories about the extent to which individual differences in word reading align with those in spelling and the extent to which other cognitive and linguistic skills play different roles in word reading and spelling. Using data from 1,116 children ranging from 8 to 17 years, we modeled word reading and spelling as latent traits with two measures of each skill to reduce measurement error. The models also included five skills that have been theorized to relate differentially to reading and spelling: phonemic awareness, working memory, rapid automatized naming, arithmetic, and vocabulary. The latent-trait correlation for reading and spelling was very high, 0.96, although significantly less than perfect. Vocabulary correlated more strongly with reading (0.64) than spelling (0.56), but the correlations of the other skills with reading and spelling did not differ significantly. Breaking down the sample by age, we found a significantly higher latent-trait correlation between reading and spelling in the younger half (r= .98) than in the older half (r= .94). This difference may reflect the fact that the words on reading and spelling tests are more different from one another at older ages. Our results suggest that word reading and spelling are one and the same, almost, but that spoken vocabulary knowledge is more closely related to reading than to spelling.
——-
more.
AI’s great brain robbery — and how universities can fight back
ChatGPT and its like have swept through academia, changing how students work, write and think. The bots are here to stay, so we need to reimagine learning
——-
more.
——-
To make it pedagogical, LLM is an autocomplete function that randomizes based on the statistical frequency:
- Probability matching: if in the frequency space, the autocomplete is at 85% “take an umbrella” and 1/10^6 “have squid ink”, it will do 85% of the time “take an umbrella”.
- “Temperature” setting: you can pick up to 100% the highest probability: “take an umbrella”.
Advocates for eliminating tests and grades, favoring anecdotal comments for student needs.
I have been reading with interest the articles on our education system in Manitoba, starting with Grant Park removes advanced-placement-test due to student stress (April 29); Getting beyond just grading and tests (Think Tank, May 6); Grading by percentage is failing our students (Think Tank, May 7); and The importance of quality of assessment for students (Think Tank, May 12).
They all made me think, which is the sign of a good article. I learned that from my educators: to think for myself.
One of the articles stressed that percentages should be removed from schools due to student stress.
They advocate that no tests, no grades, and just anecdotal comments will better serve students’ needs. If this is what is happening in public schools today, I despair.
This rhetoric does not teach young people anything about striving for goals, or about having faith in their own ability to learn.
This type of thinking explains so much about the students I see in my first-year university classes. Students who can’t take constructive criticism, who bristle at instruction, and who don’t bother reading the grading rubrics before completing assignments.
They hand in anything that they have written at the last minute and expect an A because they submitted the assignment.
They come to see me at the end of the term telling me that they now have all of their late assignments ready and are wondering how to submit them.
When I explain that they can’t, they become defensive and wonder why, if it was acceptable in high school, I won’t accept them now.
They consistently miss classes and instruction and then want special treatment because they are stressed.
As a former colleague of mine at the University of Winnipeg told his students, if they aren’t stressed at university, then they aren’t trying. Life is stressful and it starts at school. Students have to know how to deal with stress when they are on their own.
It’s part of life to deal with situations that do not always go as planned.
School Discipline Climate
States are starting to remove more unruly students from schools, and the Trump Administration is getting out of the way.
The Texas Legislature in May passed a bill that makes it easier for teachers to remove misbehaving students from classrooms and extends the allowable time for in-school suspensions. Some 3,300 Texas district employees were targets of student assault in 2023-24, according to the Texas Tribune. Removing students for any “unruly, disruptive, or abusive” behavior, as the legislation allows, could help prevent such escalation.
Arkansas lawmakers in April passed a law that ensures students removed for violent behavior aren’t returned to the same classroom. The Legislature also stripped from state law a requirement that districts use “positive behavioral support”—which focuses on “conflict resolution” and “coping skills”—to address student misbehavior.
Washington state’s superintendent finalized rules, effective this month, that loosen restrictions on removing, suspending, or expelling students. Other stateshave taken similar action in recent years, including Louisiana and Nevada, where the state teachers union supported legislation making it easier to remove students.
“one fifth-grade project involved learning how to buy and run an Airbnb”
But because families have very different views on what a “good” afternoon program looks like, Alpha is now launching a series of microschools. The academic portion stays the same, but the afternoon programming varies depending on the focus. There’s one centered on sports, another on esports and gaming. But the one that stood out to me — and to the parent writing the review — is the GT School, their gifted and talented microschool. His three kids are all enrolled in GT. In that track, the afternoons lean heavily into more academic and competitive pursuits like chess and debate. But what’s different is that everything is tied to real-world validation. For example, if students do a storytelling assignment, the goal isn’t just to write the story, it’s to submit it to The Moth and get it accepted. Chess isn’t just about learning strategy; it’s about earning a national rating. Debate is expected to lead to actual competition results. The point isn’t just to complete a task. The point is to complete it and get external recognition. What really stood out, though, and what the parent-reviewer said is the true engine behind Alpha, is the school’s internal virtual currency: Alpha Bucks. Students earn Alpha Bucks for completing tasks, reaching goals, and going above and beyond. They can then spend them on real things: physical products, school events, even internal auctions. It’s an economic system that shapes motivation and behavior.
What I would say is genetic counseling is underhyped
Dwarkesh Patel interviews George Church:
Mirror life, if it can be weaponized, that would take it to a whole other level of concern. The concern was that if we got it to a certain point, then it would be easy to weaponize it. Again, there’s practical considerations that maybe that most people who consider weaponizing mirror life would probably be satisfied with weaponizing viruses that already exist, that are already pathogens. And they wouldn’t want to destroy themselves and their family and their legacy and everything like that. But all it takes is one, one group probably, or one person.
But your question is, is it inevitable? I don’t know. It might be. It’s quite possible it’s already here. In other words, we already have mirror life in our solar system or maybe even on our planet. It just hasn’t been weaponized.
What we were saying in the Science paper is that this seems like the sort of thing that could wipe out all competing life if were properly weaponized. But there are probably a few things like that. What we really need to do is reduce the motivation to do that, maybe increase our preparedness for a variety of existential threats. Some of which will be natural, some of which will be one disgruntled person who has essentially too much power.
Over the history of humanity, the amount of things that a single person can do has grown very significantly. It used to be, when you had your bare hands, there was kind of a limit to what one person could do. A large number of people could team up and get a mammoth or something like that. Today, one person with the right connections or right access to technology could blow up a city. That’s a huge increase in capability. I think we want to start dialing that back a little bit somehow.
civics: Obama’s Trump-Russia collusion report was corrupt from start: CIA review
A bombshell new CIA review of the Obama administration’s spy agencies’ assessment that Russia interfered in the 2016 presidential election to help Donald Trump was deliberately corrupted by then-CIA Director John Brennan, FBI Director James Comey and Director of National Intelligence James Clapper, who were “excessively involved” in its drafting, and rushed its completion in a “chaotic,” “atypical” and “markedly unconventional” process that raised questions of a “potential political motive.”
Further, Brennan’s decision to include the discredited Steele dossier, over the objections of the CIA’s most senior Russia experts, “undermined the credibility” of the assessment.
The “Tradecraft Review of the 2016 Intelligence Community Assessment [ICA] on Russian Election Interference” was conducted by career professionals at the CIA’s Directorate of Analysis and was commissioned by CIA Director John Ratcliffe in May.
AI “bias” detection
A new policy at Law360, the legal news service owned by LexisNexis, requires that every story pass through an AI-powered “bias” detection tool before publication.
The Law360 Union, which represents over 200 editorial staffers across the 350-person newsroom, has denounced the mandate since it went into effect in mid-May. On June 17, unit chair Hailey Konnath sent a petition to management calling for the tool to be made “completely voluntary.”
“As journalists, we should be trusted to select our own tools of the trade to do our information-gathering, reporting and editing — not pressured to use unproven technology against our will,” reads the petition, which was signed by over 90% of the union.
Reading for pleasure, a cherished pastime for many, is declining among young people
But of all the obstacles to improving reading, many attribute the greatest blame to technology.
“It’s a generational shift — text is less important [to young people] than video and audio,” says Douglas McCabe, chief executive and director of publishing at Enders Analysis.
“Tech is the biggest barrier,” agrees Sandown’s Tugwell. “They’re all on all the apps that they’re not old enough to be on, they all have WhatsApp, they’re all in massive group chats. They tell us they go on [their] X-Box [instead of reading].”
Zohran Mamdani’s 2009 application to Columbia University
I suspect Mamdani’s “thinking” was “I think it’ll be easier to get into Columbia if I lie and say I’m black.”
——-
If I’m understanding the left’s new Race Rules correctly, my children will be able to check “Native American” on their college applications.
The Scaling Fallacy: Larger LLMs won’t necessarily lead to Artificial General Intelligence.
The scaling hypothesis has been a very … wealthy one. With people like Sam Altman (OpenAI) and Dario Amodei (Anthropic) being believers, billions of dollars have gone into making large language models (“LLMs”) like ChatGPT and Claude bigger and … BIGGER.
The belief is that just by feeding an LLM with more training data, parameters, compute, and other resources (“scaling”), Artificial General Intelligence (“AGI”) will eventually emerge.
Elaborated error feedback, a crucial component of Mastery-Based Learning (MBL), often fails to be effective, particularly for those who require it most
Digital learning promises precision: personalized pathways, mastery checks, and detailed feedback to help students close gaps and build lasting understanding. But what happens when students simply ignore that feedback?
A new study dives into this hidden flaw inside a real-world mastery-based learning system , MasteryX, an adaptive German grammar app for secondary students. Its design will feel familiar to anyone who’s used systems like Khan Academy, ALEKS, or Duolingo:
- Students move through grammar courses structured by levels.
- To advance, they must pass formative mastery assessments (usually 80% or higher).
- After each test, the app shows them exactly what they got wrong and provides elaborated error feedback: what the right answer was, why they were wrong, and how to avoid the mistake.
Students can choose to read this feedback or skip it.
Why Thomas Jefferson is rolling in his grave
The drama unfolded largely under the radar and had an intramural angle. The investigation was led by two Justice Department officials: Harmeet Dhillon, the boss of the DoJ’s civil-enforcement division, who overlapped with Mr Ryan as a student at UVA’s law school; and Gregory Brown, another alumnus who sued UVA in 2023 and 2024 on behalf of students alleging mistreatment. Mr Trump stayed away; UVA was spared the Truth Social treatment.
The DoJ’s investigators worked with a UVA board that had been inching right in recent years. Mr Youngkin, elected in 2021, appointed 13 of its 17 members. UVA is hardly known as a bastion of radicalism but it was affected by the same charged years as everyone else. In 2020, after George Floyd’s murder, Mr Ryan promised to double down on diversity. Student tour guides emphasised Jefferson the slaveholder rather than Jefferson the founding father. Conservative faculty and students felt outnumbered and unwelcome. A group of alumni, calling themselves the Jefferson Council, criticised these developments.
On ignoring the noise and celebrating what matters
I read this in shock. Are we supposed to be embarrassed to be Americans instead of Colombians or Venezuelans? Was “Go west, young man” canceled while I was on a flight this week? Is a United States that codified religious freedom really not “spiritual”? And is a professor from Yale really arguing on Independence Day that America’s problem is that it’s insufficiently tuned in to the “interdependence of human existence”? The Fourth of July has its silly side and obviously is no sacred cow, but how pathological does a person have to be to chide America for its lack of collectivist spirit on a holiday celebrating individual liberty?
Not long ago, the basics of American citizenship were uncontroversial and the challenge for all of us was living up to the ideal. As Martin Luther King put it, “All we say to America is be true to what you said on paper.” Now it’s as if our historians look back and see massacres and misery, but no Edison, Elvis, Chuck Berry, or Muhammad Ali. I don’t love the parody version of patriotism touted by Trump, but it shines through in the writings of people like Professor Gandin that they’re not proud to be Americans at all. Who can sign up for that? Why are we continually asked to choose between too much pride, and none?
We should be encouraged on this of all days to remember the good things about this country that have nothing to do with politics, from baseball to airplanes to most of the Rocky movies to just-departed George Foreman, Roberta Flack, Val Kilmer, and Brian Wilson. That’s who we are, not this dumb argument. To hell with the sourpusses. Happy Birthday, America.
A quiet education revolution in England’s secondary cities
England’s teenagers are in limbo. They have sat their gcse exams, which most take at 16, and will receive the results on August 21st. If they are nervous, they should be. Good gcse grades open doors to colleges and universities, whereas bad grades shut them. But teenagers in big cities should worry less. They are likely to do better than their peers elsewhere, and better than their predecessors.
“We were known for having pretty terrible schools,” says Bev Craig, the leader of Manchester City Council. In 2005 just 27% of gcse takers in the city’s state schools got five grades C or above in English, maths and three other subjects. In England as a whole, 43% did. Pupils who were entitled to free meals because of their parents’ poverty fared worse. Only 15% of Mancunians from that deprived group cleared the bar, compared with 18% across England.
civics: Taxpayer Funded Dane County’s public health agency plans to utilize dating apps to enhance STD testing
The joint Madison and Dane County public health department is entering the world of online dating.
Not because it’s looking to meet other cute, single government agencies, but to better protect people from the scourge of sexually transmitted infections.
Public Health Madison and Dane County will send messages through the apps to the partners of people who test positive for STIs at agency clinics — with the goal of getting them on the phone to convince them to get tested themselves.
“As the dating landscape has changed, more people are meeting partners online,” Public Health spokesperson Morgan Finke said. “It’s just increasing our likelihood of reaching those partners by meeting them where they are.”
The messages will not contain information about the people who may have exposed them to an STI, and people will only be contacted through apps if the agency is able to confirm a profile matches a person who might have been exposed.
Wisconsin Supreme Court 4-3 on Abortion
Wisconsin Supreme Court strikes down 1849 abortion ban. Honoring campaign promises, 4-3 liberal majority proclaims the law was “impliedly repealed.” Decision leaves in place major restrictions. 🧵 1/
More. Choose life.
Ivy League Antitrust Pricing Investigation
The judiciary committee in the House of Representatives issued subpoenas on Tuesday to the heads of Brown University and the University of Pennsylvania, demanding they surrender documents by July 22.
The committee opened a probe into collusion earlier this year and requested documents in April, but described the universities’ responses to be “inadequate”.
The lawmakers also issued a subpoena to Harvard last month and have sought information from Columbia, Dartmouth, Cornell, Princeton and Yale, all Ivy League institution
Zohran Mamdani to receive NYC teachers union endorsement
By Matthew Fischetti and Carl Campanile
The Big Apple’s powerful teachers union is expected to announce its endorsement of Democratic mayoral nominee Zohran Mamdani — after its members passed on making a pick in the primary, The Post has learned.
Two sources close to the United Federation of Teachers said that the endorsement is coming soon from the nearly 200,000-member union after the results of the Democratic Party primary were made official this week.
The union had previously declined to endorse because members were split between Democratic socialist Mamdani, a 33-year-old state Assembly member, and former Gov. Andrew Cuomo, 67.
Notes on Wisconsin K-12 Taxpayer $pending and School Choice
Like any budget that is a result of compromise in divided government, there are positive and negative aspects. But one definite positive to come from this year’s budget agreement is the continued closing of the spending gap between private, charter, and traditional public schools.
Without getting too deep into the weeds, a number of factors came together to increase funding. First, there is a categorical aid in Wisconsin known as “Per Pupil Aid.” Governor Evers’ 400-year veto—which WILL fought against—was deemed to be legal by the state Supreme Court. This funding is also provided to private choice and independent charter schools in the state, leading to an annual $325 increase in funding. While this does represent new funding each year, it merely maintains parity with the increases public schools also receive. But also included in the budget were increases that were included in several motions approved by the Joint Committee on Finance. The committee approved Motion 48 and Motion 130, which added $135 and $174 respectively per pupil choice and charter funding in 2025, and both contributed$103 in net new funding in 2026. All of these factors are listed in the table below.
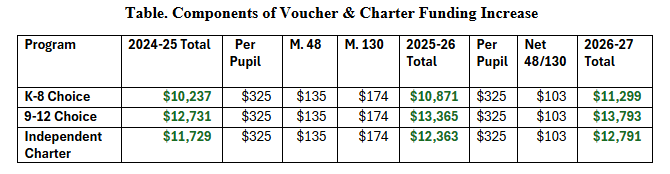
For the upcoming 2025-26 school year, K-8 voucher schools will have about $10,871 per student while high schools will have $13,365. Independent charter schools will have $12,363. Note that there are other forms of charter schools in Wisconsin that contract with school districts directly and are not directly impacted by these budget provisions. Their funding amounts are set in their contract, though they have often been tied to the independent charter school level historically.
——-
Madison taxpayers have long spent far more than most k-12 systems (currently +25k per student), this despite long term, disastrous reading results.
Middle-school test scores predict college and career outcomes
Darrin DeChane, Takako Nomi and Michael Podgursky
Standardized tests form the bedrock of school accountability systems and are a primary source of information for the public and policymakers alike. Over the past two decades, these tests also have come to define whether students are on track to being “college and career ready” at the end of high school, in line with state standards for what students should know and be able to do by the spring of each school year.
But many parents and educators have grown skeptical of standardized testing and the relevance of a student’s scores to their long-term success—especially tests given when children are still in elementary or middle school. Some question the typical practice of classifying students into different proficiency levels based on the scores they earned—such as below basic, basic, proficient, and advanced—to help parents and the public understand the results. What can a 14-year-old’s test scores and proficiency levels tell us about college readiness? We decided to find out and designed a study to assess the degree to which middle-school test performance and proficiency level predicts postsecondary success.
Middle-school test scores tell us quite a lot. Students with high scores on reading, math, and science tests in 8th grade are dramatically more likely to earn a bachelor’s degree within five years of finishing high school. We analyzed nine years of data for 260,000 students in Missouri, starting with their 8th-grade scores and following them through high school and the next five years to see which students graduated high school, attended college, and earned a degree. We looked at each subject test separately and in combination, and we looked at students as a whole and grouped by race and gender. Every analysis found the same trend: The higher a student’s middle-school test scores, the more likely they are to graduate high school, attend college, and earn a college degree.
Waukesha school district contemplates closing schools as enrollment declines
Wisconsin’s public schools have fewer students in the classrooms, leaving districts across the state considering closing and combining schools.
That includes the School District of Waukesha, where officials say enrollment has declined steadily since reaching about 13,000 students a decade ago.
Last school year, enrollment dropped to about 10,500 students. District officials predict enrollment will continue to decline based on birth trends.
Civics: Political Sausage Making and “ai” legislation
Democrats were unified against it, as much for partisan reasons as ideological ones. But there was also significant backlash from Republican state officials against this legislation, because many states have laws that regulate automated or AI systems. Last month, 40 GOP and Democratic attorneys general sent a letter opposing the provision, so you would think it would die. However Congress is a world apart from local concerns, and the amount of money put forward to Republican members of Congress for supporting something like this makes it hard to resist.
Still, opponents rallied. Tennessee Senator Marsha Blackburn, who is an iconoclast, “raised concerns the measure would block her home state’s Elvis Act, a law that prohibits the non-consensual use of AI to mimic musicians’ voices.” She was also concerned that the bill would disallow laws meant to protect kids. A number of other GOP Senators, like big tech foe Josh Hawley, were also worried. So Ted Cruz cut a deal with Blackburn, coming together with a “compromise” that would cut the moratorium to five years and include some ability to regulate. It’s likely this compromise was authored by Meta or one of the other big tech firms, because in some ways, it loosened protections for children. That overreach burned the compromise.
After Blackburn cut her compromise deal, there was an outcry by a host of child safety and online advocacy groups, which led to Bannon speaking with Blackburn. And she ended up opposing the full provision, either because of Senate procedure, or because the compromise was actually worse than promised. And when she flipped, Cruz realized he would lose, so he sided with her, and the provision went down 99-1.
Jim Crow Strikes Again in Chicago
Stacy Davis Gates warns of the Confederacy’s return to rally her base — but her actions have created a school system the Old South might well admire
Chicago Teachers Union (CTU) President Stacy Davis Gates is once again echoing Mayor Brandon Johnson’s Civil War rhetoric. “Trump has picked his side,” she claimed in last week’s address at the City Club of Chicago. “He is here to win the relitigation of the Civil War and finish the work of the Confederacy.” If Gates is searching for a school system that would be embraced by the old Confederacy, she need look no further than the CTU-dominated Chicago Public Schools (CPS).
CPS is a system that denies poor families educational alternatives to their often failing and nearly empty CTU-controlled neighborhood schools. This outcome is the direct result of the CTU’s relentless drive to secure its monopoly over public education — prioritizing the expansion of its membership and benefits, reducing workloads, and protecting jobs — while eliminating any real accountability for performance or even the behavior of its members.
The CTU and its former-employee-turned-mayor would have us believe that funding is the issue. Yet Chicago is the second-best-funded large urban school system, spending $30,000 per pupil, consuming 56 percent of all property taxes collected in the city, and receiving nearly $1 billion in additional city subsidies. Why, then, are only 11 percent of Black students proficient in reading and eight percent in math, while Latino students are only 18 percent proficient in reading and 15 percent in math?
What is College Good For?
Which raises a question: If this is what college graduates do, why exactly are we in a hurry to send so many people to college?
Over the years, we’ve seen a lot of justifications for sending people to college — by which I actually mean, for subsidizing people’s attendance at college, and for maintaining a taxpayer-funded higher education apparatus. Probably the most important are:
- Creating wealth. College graduates earn more, so creating more college graduates will create more high-earners. A related argument suggests that rich societies have more higher education, so more higher education will make a society richer.
- Promoting public values. Higher education is supposed to be a place where our society’s highest values are nurtured and taught, ensuring that they are propagated to future generations.
- Encouraging critical thinking: Teaching people to think for themselves, not to accept what they’re told or to go along with the crowd.
- Maintain intellectual capital — like knowledge of history, ancient languages, philosophy, etc. — that is valuable for society as a whole, but not readily supported outside of an academic environment.
Okay, so how are we doing in serving those purposes? Not so great. I’ve written about this before, but here’s a sum-up.